Recent Talks
List of all the talks in the archive, sorted by date.

Abstract
In this talk, I'll describe the full upgrade of OSIRIS at GTC telescope, once installed in the Cassegrain focal station including a new monolithic blue-sensitive detector. Changes in the standard operation of the instrument will be detailed, as well as a brief summary of the short-term instrumentation plan for GTC in 2023.
Unirse a la reunión Zoom
https://rediris.zoom.us/j/86985740449
ID de reunión: 869 8574 0449
Enlace de Youtube:
https://youtube.com/live/WxBPiiUkwJ4?feature=share

Abstract
La finalidad del proyecto TTNN es realizar la mejora del sistema de control de los telescopios IAC-80 y Carlos Sánchez con el objetivo que el nuevo entorno de software y hardware que se diseñe sea robusto
versátil, permitan controlar los telescopios de forma remota y facilitar, a posteriori, su operación automática. Para el cumplimiento de estos requerimientos en la parte software se está diseñando e implementando un sistema de control de alto nivel basado en ROS y una aplicación de escritorio escrita en pyQt5.
YouTube
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mbxU7VZzR8k&t=4s
Abstract
Youtube933518

Abstract
MAAT is a mirror-slicer integral field unit that will be installed in OSIRIS in 2024, breathing new life into the GTC's work horse instrument. As well as the opportunity to perform spatially-resolved spectroscopy over a field of 10"x7", MAAT will also offer increased signal-to-noise and resolution for point sources with respect to the standard long slit mode. As part of the preparations for the arrival of MAAT, we have implemented support for the reduction of OSIRIS data into the open-source, python-based spectroscopic reduction package PypeIt. Indeed, with the arrival of the new blue-sensitive CCD, PypeIt is now the only publicly available pipeline that continues to work for OSIRIS. With very little human intervention, PypeIt produces fully calibrated and coadded spectra that are near the Poisson limit for point sources. In this talk, I will present a brief overview of the philosophy behind PypeIt and demonstrate the ease with which OSIRIS data (and soon MAAT data) can be reduced.
Abstract
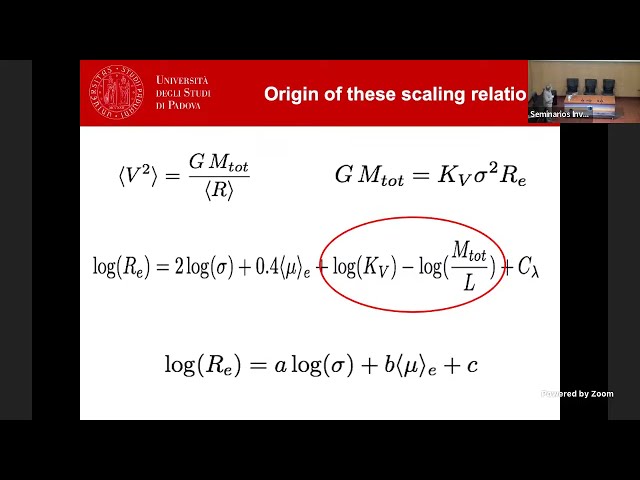
I present a detailed analysis of the scaling relations of ETGs and suggest a way to predict the evolution of the distributions of galaxies in these planes. This new approach is able to account of several features observed in the FP projections and of the tilt of the Fundamental Plane.
Abstract
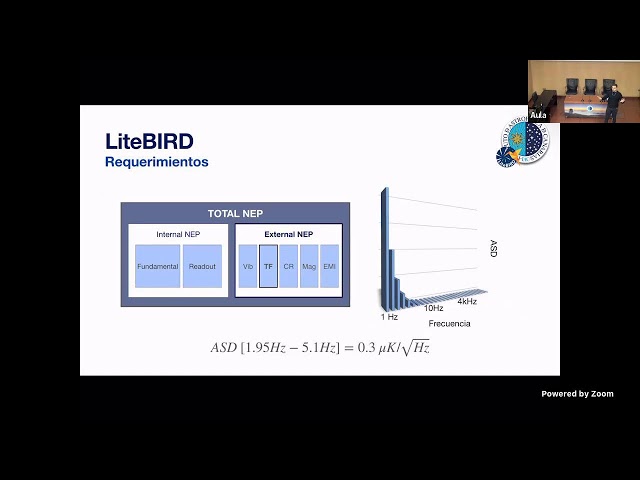
El próximo proyecto en estudiar es fondo cósmico de microondas (CMB) es LiteBIRD, un satélite de la JAXA que pretende estudiar la polarización de los modos-B. En él se encuentran integrados tres telescopios que recorren un rango frecuencial desde los 34 hasta los 448 GHz, donde se encuentran los Transition-Edge Sensor Detectors (TES), que operan a una temperatura de 100mK y que requieren de una estabilidad térmica estricta. En el Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias se están estudiando mecanismos de control de la temperatura para convertir los requisitos térmicos en una realidad.
Youtube:
https://youtube.com/live/9Cq9Oy-aicY?feature=share

Abstract
Meeting ID: 817 0462 3667
Passcode: 643393
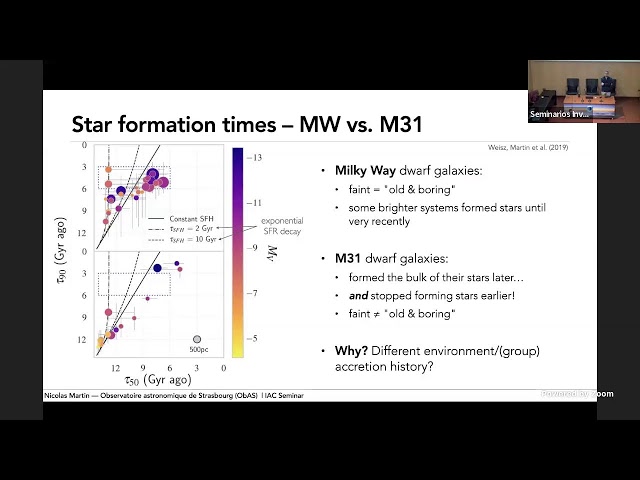
Abstract
Dwarf galaxies are powerful tools of near-field cosmology and galactic archaeology: their numbers, distribution, and star formation can be linked to both the tenets of LCDM (the missing satellite "problem," their (an)isotropic distribution, their dark matter content) and to the build up of their hosts and their environment (accretion, quenching). The exquisite detail offered by observation of the nearby Milky Way dwarf galaxies has built a picture of what dwarf galaxies are and how they evolved through time. In this talk, I will review the increasingly sharp view we are building of the dwarf-galaxy system of the Milky Way's "sister" galaxy, Andromeda, and emphasize key similarities and differences between these two systems of satellites in the hope to learn what features are common or, on the contrary, driven by the different pasts of the Milky Way and Andromeda.
Meeting ID: 841 1580 773
Passcode: 603521

Abstract
TNO is big non-profit Dutch company with more than 3000 professionals. In this talk an introduction about TNO and its capabilities applied to astronomy will be presented. TNO has done the preliminary design of the Adaptive Secondary Mirror for the European Solar Telescope. TNO also develops other optical devices for ground based and space astronomy and also for optical communications.
Youtube: https://youtube.com/live/_b6Tdzr_Cq0?feature=share
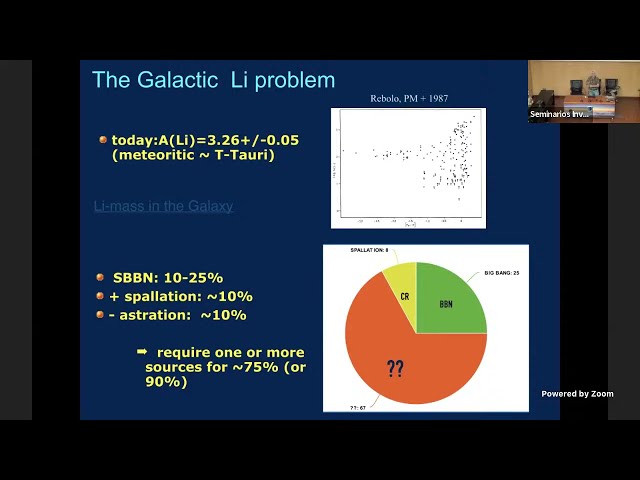
Abstract
Lithium is a key element which plays an important role in astronomy as well as everyday human life. Nevertheless it is probably the only element whose astronomical origin is still a mystery. A fraction of about 30% of what is measured today was made in the first 3 minutes of the Universe and about 10% is made by spallation reactions of cosmic rays with the atoms in the interstellar medium. However, as stars burn Li in their hot interiors and what makes the remaining ~60% is still unknown. The recent detections of 7Li and 7Be in the outburst of classical novae is a landmark in the solution of this long standing mystery. The discovery confirms a theoretical speculation made about 50 years ago but which was never supported by observations. Since then the presence of Be-7 has been confirmed to be ubiquitous in about a dozen classical novae and very recently also in the recurrent nova RS Oph that blew out in August 2021. However, the observed values show tension with theory being one order of magnitude greater than predictions. Detailed Li Galactic chemical evolution models assuming the "observed" yields show that indeed Novae could be the long sought source for the Galactic 7Li.
Upcoming talks
No talks scheduled for the next days.