Recent Talks
List of all the talks in the archive, sorted by date.
Abstract
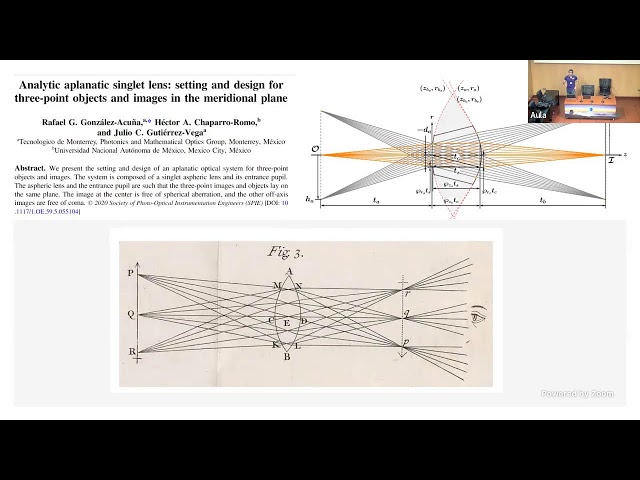
Una imagen estigmática es aquella libre de aberraciones ópticas. Es posible obtener sistemas formadores de imagen estigmáticos de manera analítica. Esas expresiones analíticas pueden utilizarse para diseñar numerosos sistemas ópticos desde cero.

Abstract
The Magellanic Clouds (MCs) are the closest example of a three-body
interacting system composed of the Milky Way (MW), the Large Magellanic Cloud
(LMC), and the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC). Therefore, the unique opportunity
provided by their relative proximity allowed us to analyse with matchless detail
the dynamical and morphological evolution that a galaxy experience as a
consequence of the mutual gravitational interaction with its neighbors. In this
context, we performed a multi-faceted analysis, taking advantage of astrometric,
kinematics, and photometric data, with the main goal of unveiling the past
evolutionary path of the MCs and their intense interaction history. We tackled
this task by using two complementary approaches: (i) we adopted the properties
of the MCs star cluster (SC) system to get insights into their past evolution
and (ii) we probed the low-luminous regime of the outer regions of the MCs as
they are the most sensitive to recent or past tidal stripping events. I will
discuss the main outcomes up-to-date of this project and its future perspectives
in light of the new ongoing facilities.
Zoom link: https://rediris.zoom.us/j/81617686828?pwd=YUpBMXpobUpnYzlpUzluTGo1N2hRQT09
Meeing ID: 816 1768 6828
Passcode: 990310
https://youtu.be/q1b98yBliFQ

Abstract
Until relatively recently, high-resolution infrared spectrographs could examine only tiny portions of individual spectral windows in a single exposure. Silicon immersion gratings, combined with sensitive, large-format IR detectors have made it possible to observe broad swaths of the IR at once at very high resolution and to do so on much fainter systems. We discuss the development of Si diffractive optics and of the H and K spectrograph IGRINS (now in use on the Gemini South Telescope) and the Giant Magellan Telescope Infrared Spectrograph, which will observe from 1.08 μm to 5.4 μm at R=λ/Δλ=65,000-85,000 in a single exposure. We present results from IGRINS that demonstrate its sensitivity and versatility as it sheds new light on the atmospheres of exoplanets and cool brown dwarfs, on the evolution of YSO’s and on the physics of the ISM.

Abstract
In September 2015 Roger Hoyland gave two talks on the nature of everyday equipment using microwaves and giving special attention in the latter to mobile phones. Now, 7 years on, he presents the latest findings about the effects mobile phones have on the brain. In addition to this update he introduces the effect now known as the Havana Syndrome. This is a different mechanism to those previously discussed in which microwaves can affect the brain and to some people the belief is that it has be weaponised by certain entities so that it can be used in covert war operations as is suspected in the Havana Syndrome. In this presentation the Havana Syndrome is explained and the accusation that it is caused by a microwave source is investigated using scientific basis.

Abstract
Exciting things may have happened sometimes to the stars we see in the sky today. For example, Betelgeuse, also known as Alpha-Ori, an M-type red supergiant, the 10th brightest sky in the sky (usually), may well have been a binary star in the past. Its rapid rotation, peculiarly large Galactic velocity, and unusual chemical abundances all point to it being kicked out from the birth environment and merging as a binary star. By comparing a Monte-Carlo stellar cluster population model with the observed populations of Galactic O- and B- type stars (progenitors of red supergiants), I will show that the story of Betelgeuse is not at all uncommon. In distant galaxies, closely related scenarios may give rise to peculiar core-collapse supernovae. I will conclude by briefly discussing how the diversity of such binary and triple stellar evolution histories reflects in the variety of the currently discovered core-collapse supernovae.

Abstract
Dentro del diseño preliminar de EST se está realizando el estudio del diseño preliminar del control del mismo. En la presente charla hablaremos sobre los retos que plantea su diseño, los problemas y las posibles soluciones que estamos estudiando.
Enlace de Youtube
https://youtu.be/U7kpPBHConU
Abstract
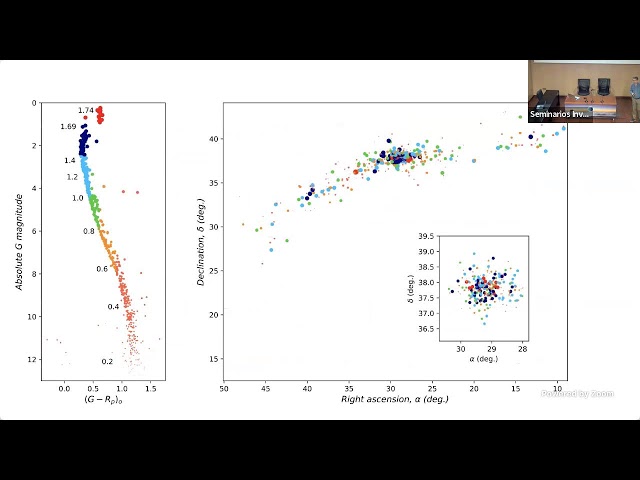
The tidal tails of stellar clusters are an important tool for studying the clusters’ birth conditions, their evolution, coupling, and interaction with the Galactic potential, and to understand how field stars populate the Milky Way. Thanks to Gaia, much progress has been accomplished in finding tails of open clusters. We will show here that the physical size of such tidal tails is larger than previously thought. Their identification requires combining the sophisticated analysis of the Gaia catalogue using machine learning techniques to the use of N-body simulations and the new compact convergent point method. We will highlight recent results about the tails of the Hyades and of NGC 752, which extend over several hundreds of parsecs and present puzzling asymmetries that likely provide constraints on the potential of Milky Way. Finally, we will also present the extension of our studies to a large ensemble of open clusters and show how our analysis opens a completely new window on the study of open clusters, whose potential will be fully unleashed with future Gaia data releases.
Abstract
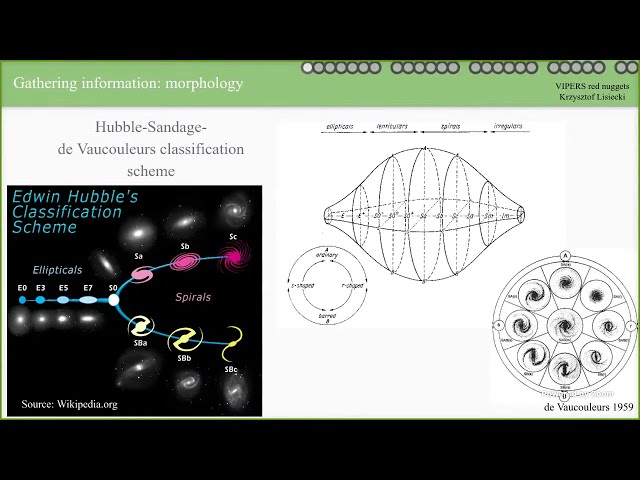
Vimos Public Extragalactic Redshift Survey (VIPERS) is a spectroscopic survey designed to investigate the spatial distribution of ~90k galaxies on redshift 0.4<z<1.2. The catalogue of spectroscopic observations, combined with auxiliary photometric data, is perfect for evolutionary studies of different types of galaxies. But also for tracing rare objects. One of them are the so-called “red nuggets”, progenitors of the most massive galaxies in the local Universe. The discovery of red nuggets - highly massive, passive and extremely compact galaxies - at high redshift challenged the leading cosmological models, as they do not fit into the evolutionary paths of passive galaxies. Taking into account that the galaxies' mergers are stochastic events, it is possible that some red nuggets remain relatively unaltered for billions of years. Those survivors constitute a group of unique galaxies in the local Universe, commonly named “relics”. Despite numerous studies dedicated to red nuggets and relics, the link between the population of compact, massive, passive galaxies in the early Universe and their remnants in the local Universe, is still poorly understood.
In my talk I will present the first spectroscopically selected catalogue of red nuggets at the intermediate redshift. It is the most extensive catalogue of this kind of galaxies above redshift z > 0.5. Selected under the most strict criteria, the group of 77 objects consists of a statistically important sample, which allows for analysis of physical properties of those rare passive giants. I will discuss the influence of compactness criteria on the sample size. Moreover I will present VIPERS red nuggets number densities and discuss the environmental preferences of those exceptional galaxies.

Abstract
Algunas palabras pueden ser seductoras y llegar a impulsar grandes hazañas, o pueden herir y, por despecho, motivar enormes esfuerzos, mover personas y sus creencias y con ellas arrastrar a las naciones. Un grupo de hombres, motivados por estas palabras, se enfrentaron a sus circunstancias y cruzaron las fronteras del mundo conocido, transformando la realidad.
Hubo dos viajes de exploración que consolidaron un imperio y un modelo socio–político y económico. En 1969 el hombre pisó la Luna y en 1519 navegó alrededor de la Tierra. Lejanos en el tiempo, estos viajes de exploración guardan mucho en común.
Hablar de la carrera espacial —en especial el viaje del hombre a la Luna— es también hablar de la Guerra Fría; de un enfrentamiento entre dos modelos políticos y económicos, antagónicos entre sí, liderados por la Unión Soviética y los Estados Unidos de América, en busca de la hegemonía geopolítica del planeta. Pero esa historia no era nueva. Quinientos años antes, España y Portugal, dos imperios nacientes, compitieron, en circunstancias muy parecidas, por el control de las rutas comerciales a Oriente. Su rivalidad los llevó a circunnavegar la Tierra, a ocupar un puñado de islas y a dominar el mundo conocido.

Abstract
El Telescopio Solar Europeo espera alcanzar el diseño preliminar de todo el telescopio en 2023. Algunos subsistemas han pasado la Revisión de Diseño Preliminar (PDR) como es el caso de la Estructura del Telescopio, la Cubierta y Pilar, subsistemas en los que se centrará este seminario repasando su estado actual y sus prestaciones principales, así como los análisis y test con los que se han comprobado dichas prestaciones.
Enlace de youtube:
https://youtu.be/o9UwtmJL1IY
Upcoming talks
- High-accuracy spectral modeling and chemical abundances for the oldest starsDr. Junbo ZhangThursday December 11, 2025 - 10:30 GMT (Aula)