Recent Talks
List of all the talks in the archive, sorted by date.
Abstract
En este seminario se hablará de las características del sistema de control de GTC y cuáles son los componentes que hay que desarrollar para que un instrumento esté integrado dentro de la arquitectura del GCS.
Abstract
The ExoMol project (www.exomol.com) provides comprehensive spectroscopic data (line lists) for the study of atmospheres of exoplanets and other hot bodies. These line lists serve as input for models of radiative transport through hot atmospheres and are useful for a variety of terrestrial applications. The basic form of the database is extensive line lists; these are supplemented with partition functions, state lifetimes, cooling functions, Landé g-factors, temperature-dependent cross sections, opacities, k-coefficients and pressure broadening parameters. Currently containing 80 molecules and 190 isotopologues totaling over 700 billion transitions, the database covers infrared, visible and UV wavelengths. The field of the HR spectroscopy of exoplanets is growing extremely fast and urgently demands molecular data of high precision. Failure to detect molecules in atmospheres of exoplanets is often attributed to the lack of the underlying quality of
the line positions. These developments have led us to begin a systematic attempt to improve the accuracy of the line positions for the line lists contained in the database. Our new ExoMolHD project aims to provide comprehensive line lists to facilitate their use in characterization of exoplanets using high resolution Doppler shift spectroscopy. Progress on this objective will be presented.

Abstract
The Thirty Meter Telescope is a new class of extremely large telescopes that will allow us to see deeper into space and observe cosmic objects with unprecedented sensitivity. With its 30 m prime mirror diameter, TMT will be three times as wide, with nine times more area, than the largest currently existing visible-light telescope in the world. This will provide unparalleled resolution with TMT images more than 12 times sharper than those from the Hubble Space Telescope. When operational, TMT will provide new observational opportunities in essentially every field of astronomy and astrophysics. Observing in wavelengths ranging from the ultraviolet to the mid-infrared, this unique instrument will allow astronomers to address fundamental questions in astronomy ranging from understanding star and planet formation to unraveling the history of galaxies and the development of large-scale structure in the universe. This talk will present the current stage of TMT development.

Abstract
The MAGIC telescopes are a stereoscopic system
of two 17m mirror diameter Cherenkov telescopes for gamma-ray observations, in operation since many years on the island of
La Palma at the Observatorio del Roque de los Muchachos.
A new installation allows us to use those telescopes as optical
intensity interferometer which enables us to measure the size of bright
objects in the range of 0.6-1.5 milli-arcsec and other physical
parameters. In this presentation the setup is explained, our physics
targets, first results and also a future outlook of this project
with respect to the Cherenkov telescope array (CTA) currently
in construction.
IAC
Abstract
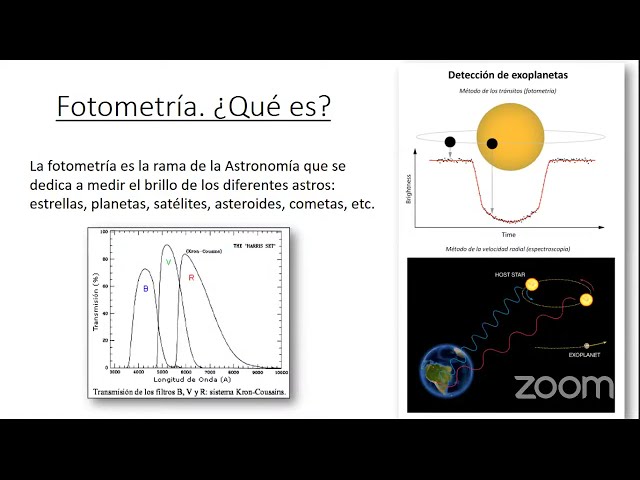
Dentro de la Astrofísica las curvas de luz conforman una herramienta fundamental en el estudio de cuerpos celestes de brillo variable, resultando útiles para detectar tránsitos de exoplanetas, evaluar el carácter variable de determinadas estrellas, etc. Con el fin de analizar en tiempo real las curvas de luz que se pretendan obtener con el telescopio IAC80, se ha desarrollado una pipeline en Python basada en fotometría diferencial, haciendo uso del módulo Photutils. Así, en esta charla se pretende explicar en primer lugar el funcionamiento del programa, mostrar algunos resultados obtenidos, y por último ilustrar cómo hacer uso de la pipeline.
Tema: Seminario de Instrumentación: lc80, la nueva pipeline en tiempo real para análisis de curvas de luz del telescopio IAC80
Hora: 9 jul. 2021 12:00 p. m. Atlantic/Canary
Unirse a la reunión Zoom
https://rediris.zoom.us/j/88394669340
https://youtu.be/VrppDSMYq2g

Abstract
We summarize here some of the results reviewed recently by Sanchez (2020) and Sanchez et al. (2021), comprising the advances in the comprehension of galaxies in the nearby universe based on integral field spectroscopic galaxy surveys. We review our current knowledge of the spatially resolved spectroscopic properties of low-redshift star-forming galaxies (and their retired counterparts) using results from the most recent optical integral field spectroscopy galaxy surveys. We briefly summarize the global spectroscopic properties of these galaxies, discussing the main ionization processes, and the global relations described by the star-formation rates, gas-phase oxygen abundances, and average properties of their stellar populations (age and metallicity) in comparison with the stellar mass. Then, we present the local distribution of the ionizing pro-cesses down to kiloparsec scales, and how the global scaling relations found using integrated parameters (like the star-formation main sequence, mass–metallicity relation, and Schmidt–Kennicutt law) have local/resolved counterparts, with the global ones being, for the most part, just integrated/average versions of the local ones. The main conclusions of the most recent explorations are that the evolution of galaxies is mostly governed by local processes but clearly affected by global ones.
Abstract
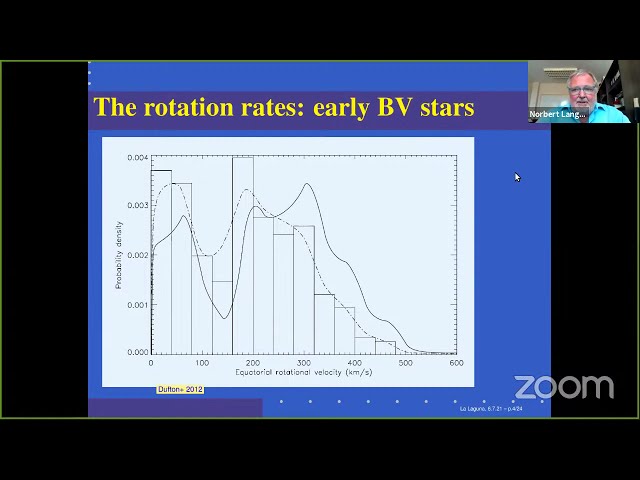
Massive stars are generally fast rotators, however, with significant dispersion. We discuss the hypothesis that all OB stars are all born with very similar spins, with slower and faster rotators being produced by close binary evolution. We review supporting evidence from recent observations of young and rich star clusters, from OB star surveys, and from dense grids of detailed binary evolution models. We connect the OB star spins with the likelihood of evolved/compact binary companions, and with the variety of the explosive end states of massive stars.
Youtube: https://youtu.be/yJHMQFmLsGE
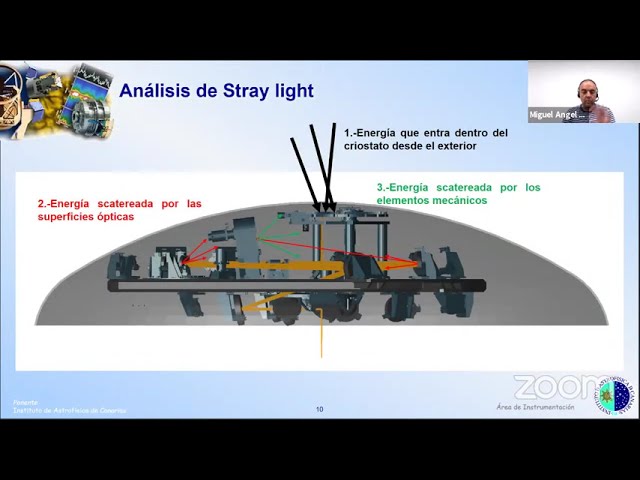
Abstract
En esta charla se pretende realizar un resumen del análisis de stray light que se está realizando en el instrumento Harmoni, tanto a nivel de sistema como de subsistema, analizando las ventajas e inconvenientes de la estrategia utilizada.
Tema: Seminario de Instrumentación: Análisis de stray light en instrumentación astrofísica
Hora: 2 jul. 2021 12:00 p. m. Atlantic/Canary
https://youtu.be/GRrUM_A1sGs
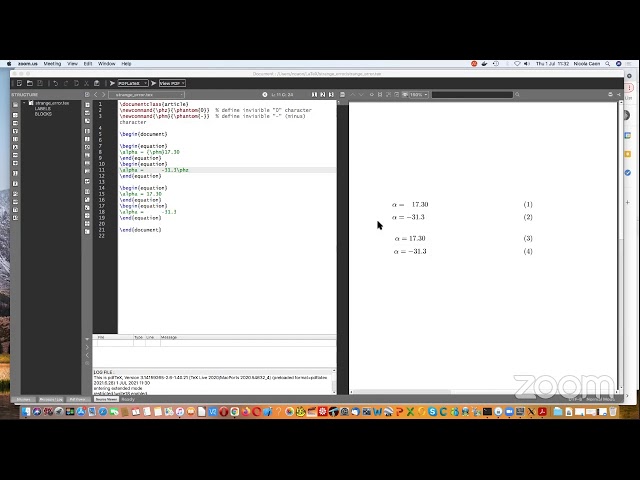
Abstract
This talk will present an overview of what Latex is, discuss when to use it and when not, show installing and editing options, introduce classes and packages, and give some usage recommendations and troubleshooting tips.
Abstract
Artificial intelligence techniques are increasingly used in our daily lives. They also play an important role in science, including astrophysics. I am particularly interested in the use of machine learning regressors. I will present an overview of the current situation and some recent uses of these methods in the study of planetary nebulae or HII regions.
Upcoming talks
- ML x Cosmology with 50 Million GalaxiesDr. Changhoon HahnTuesday May 7, 2024 - 12:30 GMT+1 (Aula)
- Unveil the Composition and the Origin of Primitive Asteroids through Sample-Return MissionsDr. Tania LepivertTuesday May 14, 2024 - 12:30 GMT+1 (Aula)









