Recent Talks
List of all the talks in the archive, sorted by date.

Abstract
Abstract
From the structure of PHL 293B and the physical properties of its ionizing cluster and based on results of hydrodynamic models, we point at the various events required to explain in detail the emission and absorption components seen in its optical spectrum. We ascribe the narrow and well centered emission lines, showing the low metallicity of the galaxy, to an HII region that spans through the main body of the galaxy. The broad emission line components are due to two off-centered supernova remnants evolving within the ionizing cluster volume and the absorption line profiles are due to a stationary cluster wind able to recombine at a close distance from the cluster surface as originally suggested by Silich et al. 2004. Our numerical models and analytical estimates confirm the ionized and neutral column density values and the inferred X-ray emission derived from the observations.
Abstract
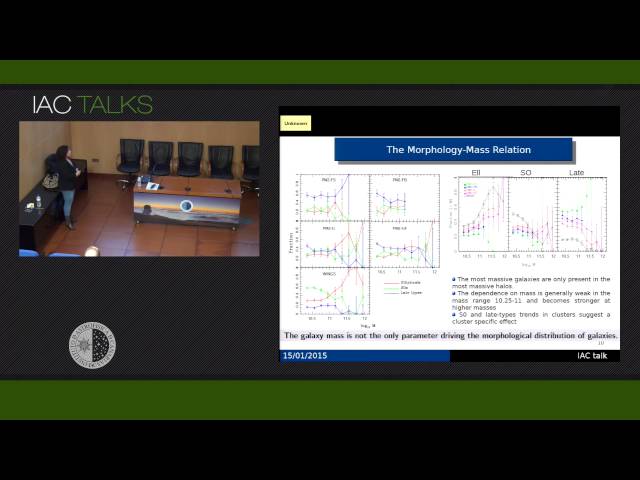
One of the important questions in extragalactic astronomy concerns the debate between nature and nurture scenarios. Are the observed galaxy local properties the end product of the different conditions at birth or the product of the interactions, or other local processes, since a galaxy is not an isolated object? In this talk I will present the results of the analysis of some galaxy properties, morphologies and mass functions, obtained comparing, for the first time in a consistent manner, galaxies in the widest range of environments at low redshift (groups, clusters, binary systems, isolated galaxies). The aim was to understand the most important factors that drive galaxy evolution, trying to disentangle the importance of galaxy mass and global environment.
In addition I will present the first results concerning the two projects in which I am involved at IAC: the ALBA project, aimed to explore the signs of a proto-cluster at z~6.5, and the analysis of dust emission of a sample of local tadpole galaxies.

Abstract
Stellar population synthesis has reached a high degree of sophistication that has been exploited to understand to a certain extent the mechanisms of formation, assembling, and evolution of galaxies in our universe. Progress is based on solid results in the field of stellar evolution and spectrophotometric observations of large numbers of stars and galaxies. However, there are certain phases of stellar evolution, like the thermally pulsing asymptotic giant branch (TP-AGB) phase, the Wolf-Rayet stage, and the presence of interacting binaries, whose treatment is either ignored or extremely simplified in galaxy evolution models due to the uncertainties in their description. In this talk I will present results from models that add the state of the art in the treatment of these evolutionary phases to traditional population synthesis models.

Abstract
Magnetic fields break through the solar surface in a hierarchy of magnetic elements ranging from Earth-sized sunspots down to tiny concentrations that are barely resolved in the highest-resolution photospheric images. In the chromosphere they combine in intricate, highly dynamic, and continuously evolving fibrilar patterns. Movements of the photospheric field-line footpoints drive, guide, and control the flows of energy and mass into the corona, and trigger energy-releasing magnetic reconnection through relentless topological rearrangement. The conversion from convectively driven footpoint motion to outer-atmosphere outflows and loading takes place in the dynamic, fine-structured chromosphere.
A number of important facilities for observing the solar chromosphere have recently come on line (e.g. the SDO and IRIS satellites and ground-based Fabry-Perot interferometers) or will become operational in the near future (e.g. DKIST). The overwhelming complexity of the chromosphere makes it necessary to have numerical simulations for the interpretation of the observations. Such realistic simulations, spanning the solar atmosphere from the convection zone to the corona, are now becoming feasible.
This presentation will introduce the fascinating aspects of chromospheric physics and review recent results from both observations and numerical simulations.
Abstract
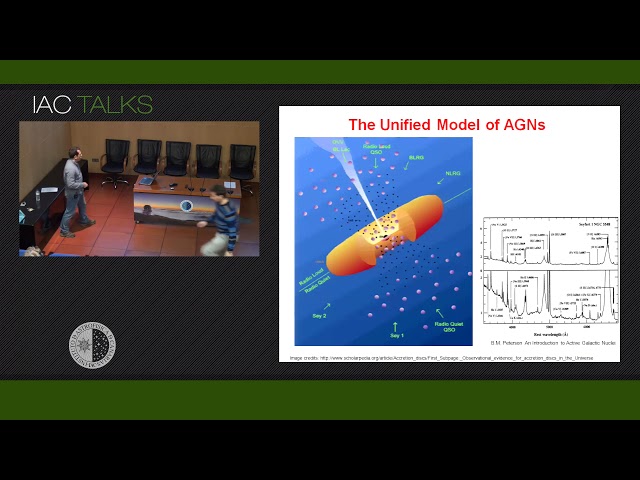
FeII comprises up to one third of the line emission in AGNs. For that reason it is an important coolant that needs to be taken into accountto fully understand the energetics of the broad line region (BLR). In thistalk I will discuss new approaches to study the excitation mechanisms ofthe FeII based on a semi-empirical template we derived in thenear-infrared region (NIR). We correlate the strength of the NIR andoptical iron lines to assess the relative contribution of the differentmechanisms that produces that emission. We found that in all casesLy_alpha fluorescence plays an important role, being a process that needsto be considered in any approach aimed at understanding this complexemission. We also compare the width of the individual FeII lines with thatof other lines emitted in BLR. Our results confirm previous assumptionsand results from variabilty studies that the gas responsible for the FeIIemission is the outer portion of the BLR.

Abstract
Recent observations of the solar atmosphere have provided new insights concerning medium-sized jet phenomena taking place in the solar corona. These jets are magnetically controlled and typically take place in regions where the mean magnetic field has an open structure. Observations indicate that at least two different types of jets exist. A simple jet that generally has a near steady state evolution phase with a well behaved and collimated outflow stream. The second type typically combines the characteristics of the first type with an explosive behaviour that significantly changes the topological structure of the jet outflow. Models have attempted to provide physical explanations to the observations, and are in general able to capture a number of the observational characteristics. This talk will discuss both the observations and the models, emphasizing where we succeed and where new progress is need

Abstract
Cold gas streaming along the dark-matter filaments of the cosmic web is predicted to be the major provider of resources for disc buildup and star formation in massive galaxies in the early universe. We use hydrodynamical simulations to study to what extent these cold streams are traceable in the extended circum-galactic environment of galaxies via Ly alpha emission, Ly alpha absorption and selected low ionisation metal absorption lines. We predict the strength of the absorption signal produced by the streams and find that it is consistent with observations in high redshift galaxies. The characteristics of the Ly alpha emission of our simulated galaxies are similar in luminosity, morphology and extent to the observed Ly alpha blobs, with distinct kinematic features. We analyse the characteristics of the cold streams in simulations and present scaling relations for the amount of infall, its velocity, distribution and its clumpiness and compare our findings with observations.

Abstract
The angle between the stellar spin axis and the orbital planetary angular momentum of a planet, also referred to as the obliquity of the system, is a matter of intense study in recent years, for the transiting planets of the Kepler mission in particular. Some evidence was found for two populations of hot Jupiters - one around cool stars with orbits well-aligned with the stellar rotational axes, and the other one around hot stars with isotropic distribution of obliquities, including planets with retrograde motion. It was suggested that the primordial planetary obliquity is isotropic, and cool stars have reached their zero-obliquity state by tidal re-alignment.
The talk will summarize the observational techniques for measuring planetary obliquities, and the different theoretical approaches to interpret this new, unexpected feature of exo-planet population. Finally, I will present a surprising statistical new result that emerges from the study of Kepler light curves of stellar rotation, suggesting the alignment of cool stars is probably not the result of tidal interaction.

Abstract
Massive stars shape and drive our Universe. Many issues such as their formation, their stability and the mass loss effects for example, are nowadays far for being completely understood. To improve our understanding, asteroseismology provides a powerful tool and excellent results have been obtained over the last years. Recent ground-based and space observations have shown the presence of pulsations in massive main sequence and post-main sequence stars, such as acoustic and gravity modes excited by the kappa-mechanism and even solar-like oscillations. Theoretical studies emphasized the presence of strange modes in massive models, excited by the strange mode instability mechanism. Moreover, recent theoretical analyses have shown that hot supergiants can also pulsate in oscillatory convective modes propagating in the superficial layers of these stars. I will expose here the instability domains of massive stars as well as their excitation mechanisms and present the latest results in the domain.
Upcoming talks
- HAYDN: A Next-Generation ESA Mission Concept for Stellar Structure and Evolution and its impact on exoplanet and galaxy formationAndrés MoyaThursday January 15, 2026 - 10:30 GMT (Aula)
- Plato's view on supermassive black hole binariesNicholas JannsenThursday January 22, 2026 - 10:30 GMT (Aula)