Recent Talks
List of all the talks in the archive, sorted by date.
Abstract
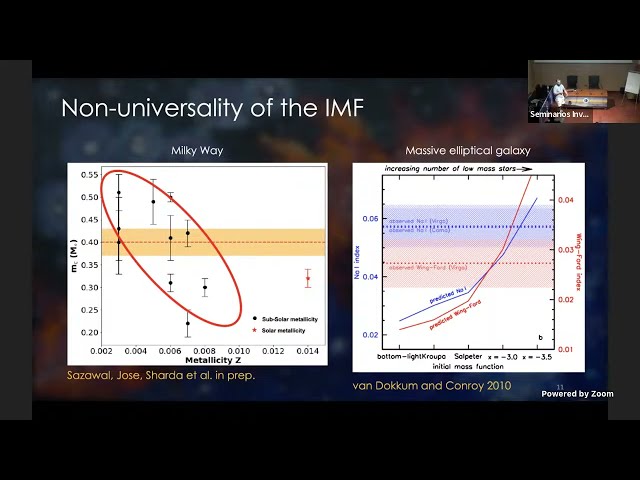
From the time the first stars formed to the present-day, metals have witnessed the assembly of structure in the Universe in great detail. Although metals only form in stars and stellar remnants, they are ubiquitously present everywhere. However, we still do not understand how metals are effectively dispersed throughout the Universe, and the various roles they play in shaping galaxies. In this talk, I will present a multi scale approach to study the role of metals in galaxy evolution, from molecular clouds to galactic discs. On smaller scales, I will focus on physical processes that shape up the initial mass function (IMF, with a particular emphasis on metal-free and metal-poor environments) that directly set the integrated yield of metals in the first and early galaxies. I will discuss results from high resolution radiation chemo-magnetohydrodynamic simulations that study the impact of turbulence, radiation feedback and magnetic fields on the primordial IMF, and describe analytical models of dusty molecular clouds that explain the transition in the IMF as the metal abundance grows over cosmic time. On larger scales, the talk will cover the physics of gas-phase metal distribution in galaxies. Using a combination of spatially-resolved gas-phase metallicity measurements and novel semi-analytical models, I will present recent results that advance our understanding of metallicity gradients in (late type) galaxies. In particular, I will show how self-consistently incorporating metal dynamics into galaxy evolution models is key to explaining the observed trends in metallicity gradients with galaxy mass, metallicity, and kinematics. I will end by highlighting how ongoing/upcoming astronomical facilities will transform our understanding of metal evolution in galaxies.

Abstract
Galaxies are embedded within a network of interconnected filaments, essential for their formation and growth. Simultaneously, they emit radiation and enriched matter back into their environment, influencing the evolution of the cosmic gas. Recent advancements in wide-field spectrographs offer a unique perspective, allowing us to probe the spatial distribution and properties of the circumgalactic medium at high redshift, particularly the Lyman-alpha line emitted by cold hydrogen gas. These insights are especially valuable in overdense regions, like protoclusters and groups, where we can explore most of the physical mechanisms at play. By combining data from instruments such as KCWI, MOSFIRE, IRAC, LRIS, and HST, we aim to decipher the various mechanisms that steer the evolution of galaxies and protocluster environments around the Cosmic Noon epoch, unveiling how mergers, AGN feedback, and galactic outflows influence both the large-scale gas distribution and the general properties of the galaxies themselves. Nonetheless, several degeneracies persist among the observed properties of the gas and the potential physical mechanisms responsible, underscoring the necessity for improved models of these cosmic phenomena and a larger statistical sample of protocluster environments.

Abstract
We will review both theoretical and obsevational aspects of gravitational wave backgrounds of cosmological origin. We will present a classifcation of backgrounds and a quantification of our ability to use them as a probe of early Universe phenomena, opening a new observational window to energy scales well above the reach of any terrestrial means. Our discussion will include the latest results from Pulsar Timing Array collaborations (e.g., Nanograv), which have recently anounced the first evidence on the existence of a background of gravitational waves. This talk wll be given in a Colloquium style, making it accessible to a wide audience of physicists.
Abstract
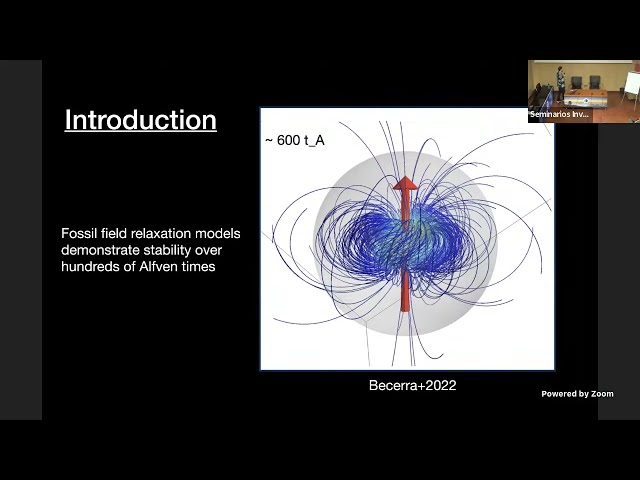
Magnetism is ubiquitous in the Universe, yet understanding the magnetic properties of stars continues to present intriguing challenges. Recent advancements owe their success to large-scale optical spectropolarimetric surveys, asteroseismic inferences, and new modelling methodologies. This presentation focuses on the evolution of massive stars with OB spectral types, with a particular emphasis on the incorporation of magnetic field effects into one-dimensional (1D) evolutionary model calculations. We explore the distinctiveness of these magnetic models in contrast to their non-magnetic counterparts, shedding light on the substantial influence of large-scale, organized magnetic fields on the physical characterization of stars. In particular, we investigate surface phenomena, such as mass loss and angular momentum loss, and their profound impact on the evolutionary trajectories of hot, massive stars. We will conclude by outlining future avenues to improve 1D models and addressing some of the remaining challenges in describing the magnetic characteristics of stars.

Abstract
At the beginning of the XX century, pilots and scientists realized that the detection of certain cosmic events like eclipses were better obtained by installing observatories on top of aircraft. This story starts with a 30-year old John Beckman, now professor at the IAC and then airborne astronomer pioneer, chasing the Sun over west africa on the wings of a French supersonic airplane. Controlling a Michelson interferometer with one hand and filling with liquid helium at 17.000 m from the ground while flying at 2000 km/h, John broke both the barried of sound and the Guiness record of the longest eclipse ever observed. The legacy of that one in a lifetime mission made ESA and NASA start the astronaut selection program for the Space Shuttle and set the bases of the SOFIA airborne observatory, a mission that made our team able to detect the shape of the magnetic fields in external galaxies.
Abstract
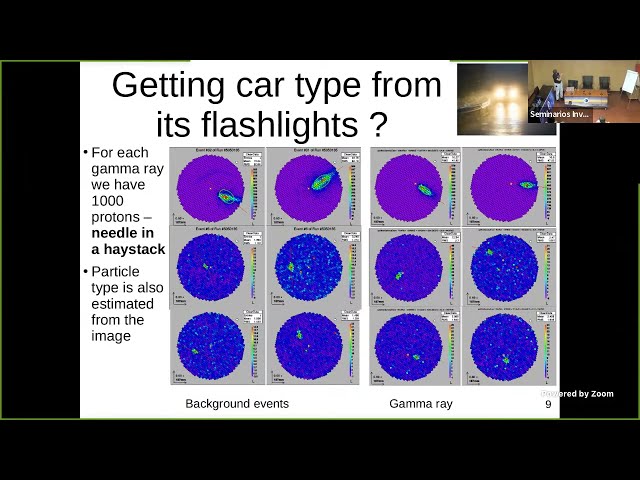
Very-high-energy (VHE >~100 GeV) gamma rays are absorbed in Earth's
atmosphere and thus cannot be detected directly on Earth. Their fluxes
are also typically too low to efficiently study them with satellite
instruments. A VHE gamma ray entering the atmosphere initiates an
electromagnetic cascade that induces faint flashes of blueish
Cherenkov light. Such flashes can be then detected by Imaging
Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescopes registering images of passage of
individual gamma rays through the atmosphere.
The usage of atmosphere as a part of the detector allows us to achieve
a collection area of gamma rays over two orders of magnitude higher
than the physical size of the detector. But it also introduces
systematic errors connected with the atmosphere's transparency. In
particular, cloud presence during the observations can significantly
affect the data. In this seminar I will cover different methods used
to correct the influence of the clouds. I will show how lack of such a
correction introduces bias in the energy estimation of gamma rays. I
will present how the affected images of showers are degraded and thus
can be confused with background events, lowering the collection area
of the telescope. Finally, I will show a novel method of correcting
the influence of the clouds already at the image level, and discuss
the possibility of measuring the parameters of a cloud directly with
the observations by the Cherenkov telescopes.

Abstract
Abstract: Solar jets are ubiquitous, sharp-edged collimated plasma ejections that are detected in all layers of the Sun from the photosphere to the corona. Observed as impulsive events, jets can originate in all kinds of solar environments, from active regions to the quiet Sun. Occasionally, these jets interact with large scale solar filaments and can set them into oscillation, sometimes followed by instability and eruption. I will present high spatial, temporal, and spectral resolution observational studies of jets to probe the fundamental physical process behind them and integrate these observations with theoretical models. We use the coordinated observations from space-borne (SDO, IRIS) and ground-based (SST) telescopes. Space-borne telescopes provide the EUV/UV data for the outer atmosphere of the sun (chromosphere, transition region and corona), while ground-based telescopes give access to high resolution data for the inner solar atmosphere (lower chromosphere, photosphere) through H-alpha, Ca II, and Fe I lines. In this way, coordinated observations cover the solar atmosphere in multi-wavelength range from the photosphere to the corona through the chromosphere and transition region.
Meeting ID: 823 7488 1929
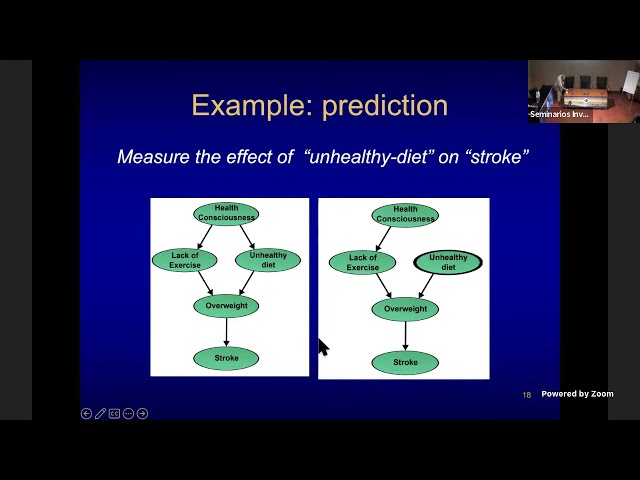
Abstract
Current intelligent systems mainly make "predictions". That is, given an input, they estimate the most probable value of the output. These systems have many limitations, they can be easily confused when presented with a different case from their training set and they cannot explain how they arrive to a certain result. Causal models are an alternative to extend the capabilities of current systems; explain the reasons for certain decisions, predict the effect of interventions and imagine alternative situations. In this talk, I will present an introduction to causal models, in particular to causal graphical models. We will see how we can make inferences based on these models: predictions and counterfactuals; as well as learning causal models from data. I will illustrate the application of causal models in various domains: estimation of effective connectivity in the brain, causal modeling of COVID-19, and incorporating causal models in reinforcement learning and its application in robotics. Finally, I will discuss some potential applications of causal modeling in astrophysics.

Abstract
Abstract
Gone are the days when we used workstations as our main day to day computer. Backing-up your data has always been important, but the risks were much fewer then. Today, when most of us use a laptop as our main computer, the risks are much higher: added to human error, disk failures, etc. we have to consider that losing, dropping or getting your laptop stolen is a real possibility, which brings the added risk of getting your sensitive data accessed by prying eyes. In this talk I will share my overall backup plan. While my setting is likely more complicated than that of most of you, hopefully you can mix & match the strategies and tools that I use (mainly Borg, but also Timeshift, Clonezilla, Syncthing, gocryptfs, ...) to suit your needs. While a complete and thorough backup plan might take some time to prepare and execute, you shouldn't postpone it. Something is better than nothing!, and you can start with something very simple, which can be very easy to implement, and can be improved over time.
Upcoming talks
No talks scheduled for the next days.