Found 42 talks width keyword dark matter
Abstract
Abstract
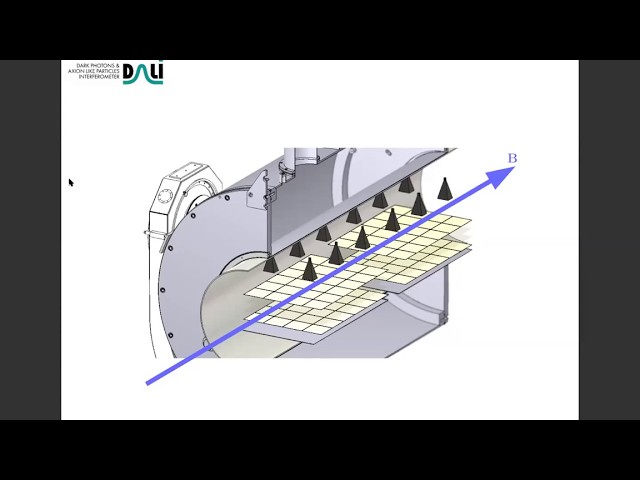
Axion detection would be one of the most exciting moments in the entire history of science. This hypothetical particle can simultaneously explain two fundamental problems in Modern Physics: the mystery of dark matter and the CP problem of the strong interaction. In this talk, I will provide an overview of the status for the search for axions and I will explain how the DALI experiment can go beyond these frontiers.
https://rediris.zoom.us/j/98051612614

Abstract
Cold gas streaming along the dark-matter filaments of the cosmic web is predicted to be the major provider of resources for disc buildup and star formation in massive galaxies in the early universe. We use hydrodynamical simulations to study to what extent these cold streams are traceable in the extended circum-galactic environment of galaxies via Ly alpha emission, Ly alpha absorption and selected low ionisation metal absorption lines. We predict the strength of the absorption signal produced by the streams and find that it is consistent with observations in high redshift galaxies. The characteristics of the Ly alpha emission of our simulated galaxies are similar in luminosity, morphology and extent to the observed Ly alpha blobs, with distinct kinematic features. We analyse the characteristics of the cold streams in simulations and present scaling relations for the amount of infall, its velocity, distribution and its clumpiness and compare our findings with observations.

Abstract
Two main families of models explain that, at least in appearance, something like 90% of the mass of the Universe is still undetected. One (supported by an overwhelmingly large fraction of the community) is the dark matter model, in which the missing mass is postulated to be made of exotic non-baryonic particles. The other one, is modifying gravity (MOND, MOG, ...) in such a way that it compensates the apparent lack of mass. Both approaches are purely ad-hoc and so far not based in first principles of fundamental physics. Since I am not a specialist, in dark matter or modified gravities, the talk I am proposing is intended to be made purely from a philosophical/sociological/historical point of view. I expect the talk to be an open debate. The philosophical thesis I will defend is that the order in the discovery of some astronomical landmarks has led the community to favour dark matter model. In my opinion, this has caused darkmatter to receive a larger funding and become more successful at describing reality than alternative models. I will try to expose to the audience that, from a purely philosophical point of view, the dark matter model and the modified gravity models are equally speculative and equally (in)valid. I will make the point that dark matter has to be taken only as an extremely complex model which is useful for the description of reality and not as reality itself.
Abstract
Dark matter makes up most of the mass of the Universe but remains mysterious. I discuss recent progress in constraining its properties by measuring its distribution in the Universe from tiny dwarf galaxies to giant galaxy clusters, and comparing this with numerical simulations. The latest results favour a cold, collisionless particle that must lie beyond the standard model of particle physics. I discuss the known small scale problems with this model: the cusp-core and missing satellites problems, and I argue that these are likely due to baryonic "feedback" during galaxy formation. I conclude with a discussion of experiments underway to detect dark matter particles, and the role that astrophysics has to play in these too. There is an exciting a very real prospect of detecting a dark matter particle in the next five years.

Abstract
Observational studies show that voids are prominent features of the large scale structure of the present day Universe. Even though their emerging from the primordial density perturbations and evolutionary patterns differ from dark matter halos, N-body simulations and theoretical models have shown that voids also merge together to form large void structures. In this study, progressing from previous works, we formulate a toy model to construct a merger tree algorithm of isolated spherical voids by adopting the halo merging algorithm given by Lacey and Cole (1993) in the Einstein de Sitter (EdS) universe. To do this, we take into account the general mass distribution of voids which consists of two main void sociologies: merging and collapsing. We show that the mass distribution function can be reduced to a simple form by neglecting the collapse void contribution. As a result of this, the void mass fraction has a contribution only from isolated gradually merging voids. This algorithm becomes the analogue of the halo merging algorithm. Based on this isolated spherical void distribution, we obtain the void merging algorithm, void merging rate and void survival times in terms of the self similar and standard cold dark matter models in the EdS universe.

Abstract
The concordance model of cosmology with its constituents dark matter and dark Energy is an established description of some anomalous observations. However, a series of additional contradictions indicate that the current view is far from satisfactory. Rather than describing observations with new numbers, it is argued that science should reflect its method, considering the fact that real progress was usually achieved by simplification. History, not only with the example of the epicycles, has shown many times that creating new ad-hoc concepts dominated over putting in doubt what had been established earlier. Also critical astrophysicists often believe that lab-tested particle physics has reliable evidence for its model. It is argued instead that the very same sociological and psychological mechanisms have been at work and brought particle physics in a still more deperate situation long ago. As an example, a couple of absurdities of the recent Higgs boson announcements are outlined. It seems inevitable that physics needs a new culture of data evaluation, raw data and source code must become equally transparent and openly accessible.
Abstract
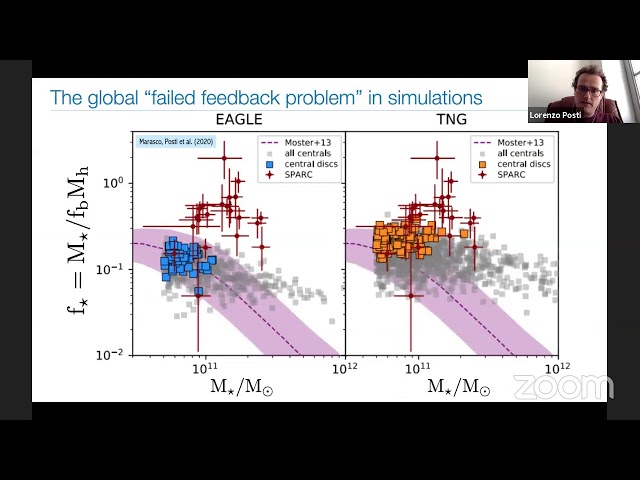
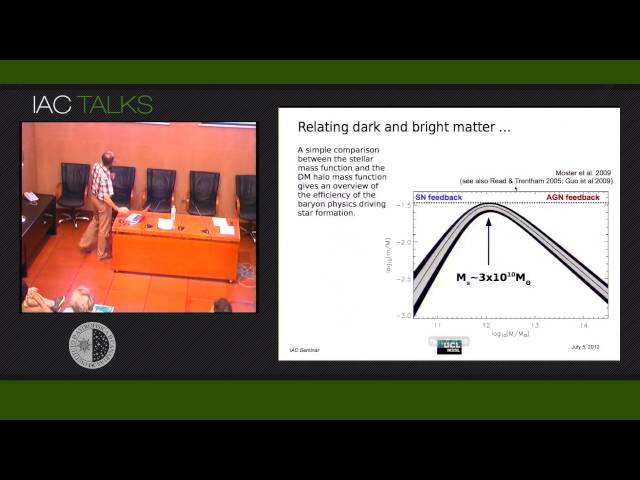
Massive early-type galaxies constitute an ideal test bed to probe our understanding of galaxy formation and evolution. Their high mass, spheroidal morphology and overly old stellar populations, along with their presence over a wide range of redshifts put to the test our current paradigm of formation via hierarchical growth. In this talk I will review recent work focused on the dark and bright sides of this problem. The former is tackled via gravitational lensing, comparing the dark matter and luminous components out to several effective radii, probing the efficiency of baryon collapse and ejection, and its feedback on the dark matter distribution (adiabatic compression). The bright side of early-type galaxies is approached via photo-spectroscopic analyses of the stellar populations, revealing a complex formation and assembly history with two well-defined phases of growth, and an intriguing connection with the "microphysics" of star formation.

Abstract
I will discuss how the acoustic oscillations that propagate in the photon-baryon fluid during the first million years of the Universe provide a robust method for measuring the cosmological distance scale. The distance that the sound can travel can be computed to high precision and creates a signature in the late-time clustering of matter that serves as a standard ruler. Galaxy clustering results from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey reveal this feature, giving a geometric distance to a redshift of 0.3 and an accurate measurement of Omega_matter. I will review our recent work on the theory and practice of the acoustic oscillation method and our latest cosmology results from SDSS-II. I will then present SDSS-III, which will use the acoustic method to produce 1% distance measurements in order to map the curvature and expansion history of the Universe and measure the evolution of dark energy.
Abstract
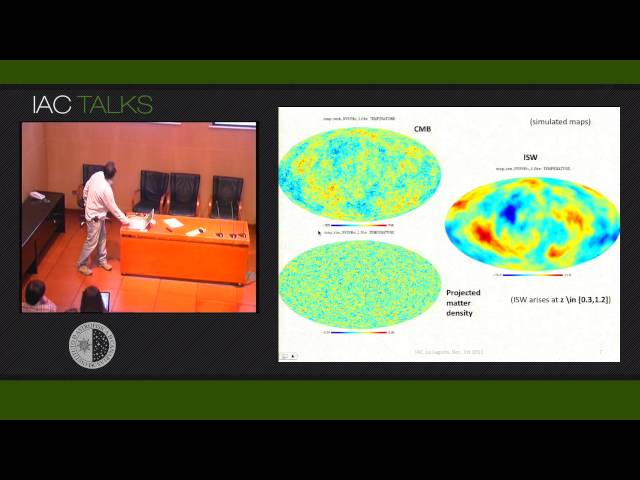
I revisit the claim of Dark Energy detection after stacking CMB data on the angular position of voids and superclusters in Sloan Data. I examine the theoretically expected amplitude for the ISW-induced signal and explore its scale dependence. I next confront these predictions with results obtained from real WMAP data, and evaluate the degree of agreement and the possible presence of contaminants. In a more general context, I address the possibility of unveiling the signature of Dark Energy on the CMB by looking at isolated regions on the sky hosting high-threshold projected under/over-densities: this constitutes a novel approach since it is less sensitive to large angle systematics commonly present in large scale structure surveys.
<< First « Newer 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 Older » Last >>