Found 42 talks width keyword dark matter

Wednesday October 1, 2008
Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, Spain
Abstract
Since its discovery in 1964, the cosmic microwave background (CMB) has been one of the basic pillars of the cosmological model. However, it is only very recently that CMB observations have become one of the most powerful tools in modern cosmology, due to the increasing accuracy of the experiments measuring the CMB anisotropies. In this talk, I will present a brief historical perspective of the history of the CMB observations, since the discovery until nowadays, with special emphasis on the implications and the impact of those observations in cosmology. Experiments like COBE, Tenerife, WMAP or PLANCK will be described. The last part of my talk will be devoted to describe the future of this field, and in particular, will be focused on the possibility of the detection of primordial gravitational-waves.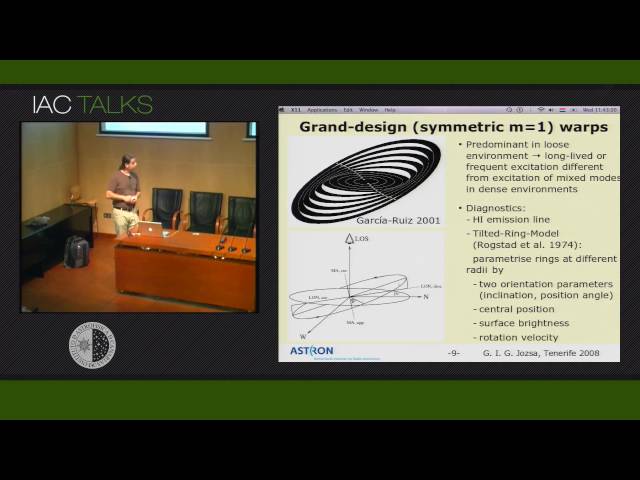
Wednesday July 16, 2008
Netherlands Institute for Radio Astronomy, the Netherlands
Abstract
Warps of disk galaxies are ubiquitous. In almost every disk galaxy a bending of the disk occurs where the stars fade away and hence where the dark matter halo becomes dominant. A clear understanding of this phenomenon has not been reached yet. Analysing H I observations of a small sample of symmetric, warped disk galaxies we found that they exhibit a two-disk structure, the warp being the transition from the inner flat disk to an outer, inclined one. At the transition radius, the rotation curve changes. This points towards symmetric warps being a long-lived phenomenon reflecting an internal change in the structure of the Dark Matter halo.While warps usually occur where the stellar disks fade, examples of extreme warps are known that commence already at the centre of galaxies. One is present in the neutral gas disk of the "Spindle Galaxy "NGC 2685, formerly thought of as being a two-ringed polar ring galaxy. Utilising deep HI observations, we found that the two-ringed appearance is due to projection effects and that it rather possesses one coherent,extremely warped HI disk. Our success in fitting a tilted-ring model to the HI component, and, with that, assuming circular orbits of the tracer material, and the shape of the fitted rotation curve hint towards a rather spherical shape of the overall potential.
<< First « Newer 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 Older »
Upcoming talks
- Quantum Simulators for the Cosmos: From Confining Strings to the Early UniverseDr. Enrique Rico OrtegaThursday December 4, 2025 - 10:30 GMT (GTC)
- Colloquium by Junbo ZhangDr. Junbo ZhangThursday December 11, 2025 - 10:30 GMT (Aula)