Found 219 talks archived in Galaxies

Abstract
CALIFA is the largest IFS survey ever performed up to date. Recently started, it will observe ~600 galaxies in the Local Universe with PPAK at the 3.5m of the Calar Alto Observatory, sampling most of the size of these galaxies and covering the optical wavelength range between 3700-7100 Å, using to spectroscopic setups. The main goal of this survey is to characterize the spatially resolved spectroscopic properties (both the stellar and ionized gas components) of all the population of galaxies at the current cosmological time, in order to understand in detail the how is the final product of the evolution of galaxies. To do so, the sample will cover all the possible galaxies within the color-magnitude diagram, down to MB ~ -18 mag, from big dry early-types to active fainter late-type galaxies. The main science drivers of the survey is to understand how galaxies evolve within the CM-diagram, understanding the details the process of star formation, metal enrichment, migrations and morphological evolution of galaxies.

Abstract
Using the k-means cluster analysis algorithm, we carry out an unsupervised classification of all galaxy spectra in the seventh and final Sloan Digital Sky Survey data release (SDSS/DR7). Except for the shift to rest-frame wavelengths and the normalization to the g-band flux, no manipulation is applied to the original spectra. The algorithm guarantees that galaxies with similar spectra belong to the same class. We find that 99% of the galaxies can be assigned to only 17 major classes, with 11 additional minor classes including the remaining 1%. The classification is not unique since many galaxies appear in between classes; however, our rendering of the algorithm overcomes this weakness with a tool to identify borderline galaxies. Each class is characterized by a template spectrum, which is the average of all the spectra of the galaxies in the class. These low-noise template spectra vary smoothly and continuously along a sequence labeled from 0 to 27, from the reddest class to the bluest class. Our Automatic Spectroscopic K-means-based (ASK) classification separates galaxies in colors, with classes characteristic of the red sequence, the blue cloud, as well as the green valley. When red sequence galaxies and green valley galaxies present emission lines, they are characteristic of active galactic nucleus activity. Blue galaxy classes have emission lines corresponding to star formation regions. We find the expected correlation between spectroscopic class and Hubble type, but this relationship exhibits a high intrinsic scatter. Several potential uses of the ASK classification are identified and sketched, including fast determination of physical properties by interpolation, classes as templates in redshift determinations, and target selection in follow-up works (we find classes of Seyfert galaxies, green valley galaxies, as well as a significant number of outliers). The ASK classification is publicly accessible through various Web sites.

Abstract
We present recent theoretical and empirical results concerning the accuracy of Cepheid distance estimates based on optical and near-infrared (NIR) Period-Luminosity (PL) relations. In particular, we plan to discuss the dependence of both slope and zero-point on the metal content using a large sample of extragalactic Cepheids. Moreover, we discuss pros and cons of optical and NIR reddening free Period-Wesenheit relations. We also mention the impact that GAIA will have on the precision of the Cepheid distance scale and the role that E-ELT will play in the identification of Cepheids beyond the Local Volume.
Abstract
(1) In this talk I will present a recent study of the bar fraction in the Coma Cluster galaxies based on a sample of 190 galaxies selected from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey Data Release 6 and observed with the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Advanced Camera for Survey (ACS). The unprecedented resolution of the HST-ACS images allows us to explore the presence of bars, detected by visual classification, throughout a luminosity range of 9 mag (-23 < Mr < -14), permitting us to study the poor known region of dwarf galaxies. We find that bars are hosted by galaxies in a tight range of both luminosities (-22 < Mr < -17) and masses (109 < M/M? < 1011). This result holds when compared with a sample of bright/massive field galaxies. In addition, we find that the bar fraction does not vary significantly when going from the center to the cluster outskirts, implying that cluster environment plays a second-order role in bar formation/evolution. The shape of the bar fraction distribution with respect to both luminosity and mass is well matched by the luminosity distribution of disk galaxies in Coma, indicating that bars are good tracers of cold stellar disks. We discuss the implications of our results for the formation and evolution scenarios of bars and disks.
(2) The Herschel Space Observatory was launched on 14 May 2009. After a short commissioning and performance verification period, the science demonstration observations started in September 2009. Herschel is carrying out now routine science observations. The three instruments (SPIRE, PACS and HIFI) are working extremely well. The first results of the many Herschel Key Projects were presented at the ESLAB 2010 conference in ESTEC on May 4-7 2010 and will be published in a special issue of Astronomy and Astrophysics. In this talk I will introduce the observing capabilities of Herschel and will review some of the first results in extragalactic astronomy and in particular those of the Herschel Multi-tiered Extragalactic Survey (HerMES).
IAC
Abstract
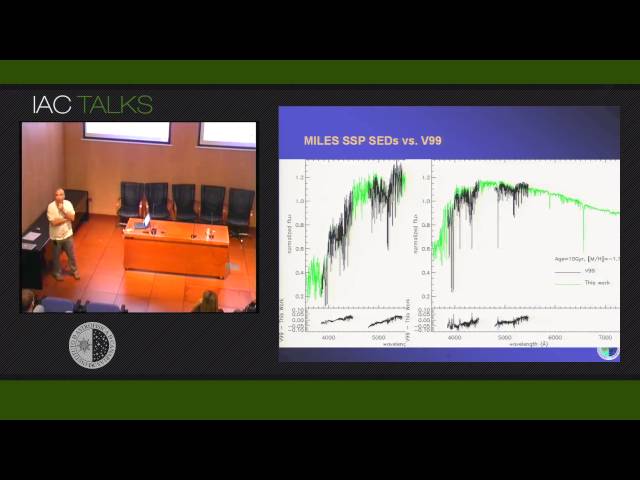
We present the new stellar population synthesis models based on the empirical stellar spectral library MILES, which can be regarded nowadays as standard in the field of stellar population studies. The synthetic SEDs cover the whole optical range at resolution 2.3 Å (FWHM). The unprecedented stellar parameter coverage of MILES allowed us to extend our model predictions from intermediate- to very-old age regimes, and the metallicity coverage from super-solar to [M/H] = -2.3. Observed spectra can be studied by means of full spectrum fitting or line-strengths. For the latter we propose a new Line Index System (LIS) to avoid the intrinsic uncertainties associated with the popular Lick/IDS system and provide more appropriate, uniform, spectral resolution. We present a web-page with a suite of on-line tools to facilitate the handling and transformation of the spectra. Online examples with practical applications to work with stellar spectra for a variety of instrumental setups will be shown. Furthermore we will also show examples of how to compute spectra and colors with varying instrumental setup, redshift and velocity dispersion for a suite of Star Formation Histories.
Abstract
Spectral energy distributions (SEDs) of the central few tens of parsec region of some of the nearest active galactic nuclei (AGN) are presented. Peering into the nucleus at these scales, it is found that the intrinsic shape of the spectral energy distribution of an AGN and inferred bolometric luminosity largely depart from those currently on use, mostly extracted from low resolution data. The shape of the SED is different and the AGN luminosities can be overestimated by up to two orders of magnitude if relying on IR satellite data.Although the shape of these SEDs are currently limited by the availability of high angular resolution data beyond ~20 μ, a prediction from this work is that a major contribution from cold dust below 100 K to these cores is not expected. Over the nine orders of magnitude in frequency covered by these SEDs, the power stored in the IR bump is by far the most energetic fraction of the total energy budget in these cores, accounting for more than 70% of the total.

Abstract
Despite speculation that both starburst and nuclear activity in galaxies may be intimately linked via the common triggering mechanism of mergers and interactions, very little is known about the true nature of the link. Thus, the role of AGN in the formation and evolution of galaxies is still not well established. I will present deep Gemini/GMOS imaging observations which are used to investigate the triggering mechanism(s) in a complete sample of radio-loud AGN for which, uniquely, we have quantified the level of both the AGN and star formation activity. I will show results on the proportion of powerful radio galaxies triggered in galaxy mergers and also on the link between the degree of star formation/AGN activity and the interaction status of the host galaxies.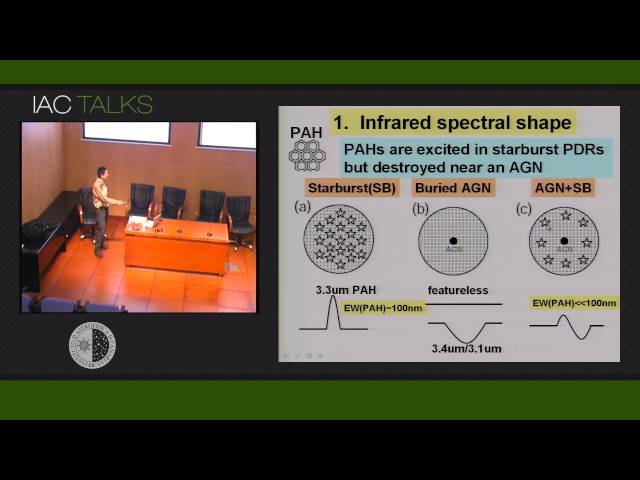
Abstract
We present the results of our systematic search for optically elusive, but intrinsically luminous buried AGNs in >100 nearby (z < 0.3) luminous infrared galaxies with L(IR) > 1011 L⊙, classified optically as non-Seyferts. To disentangle AGNs and stars, we have performed (1) infrared 2.5-35 μ low-resolution (R ~ 100) spectroscopy using Subaru, AKARI, and Spitzer, to estimate the strengths of PAH (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon) emission and dust absorption features, (2) high-spatial-resolution infrared 20 micron imaging observations using Subaru and Gemini, to constrain the emission surface brightnesses of energy sources, and (3) millimeter interferometric measurements of molecular gas flux ratios, which reflect the physical and chemical effects from AGNs and stars. Overall, all methods provided consistent pictures. We found that the energetic importance of buried AGNs is relatively higher in galaxies with higher infrared luminosities (where more stars will be formed), suggesting that AGN-starburst connections are luminosity dependent. Our results might be related to the AGN feedback scenario as the possible origin of the galaxy down-sizing phenomenon.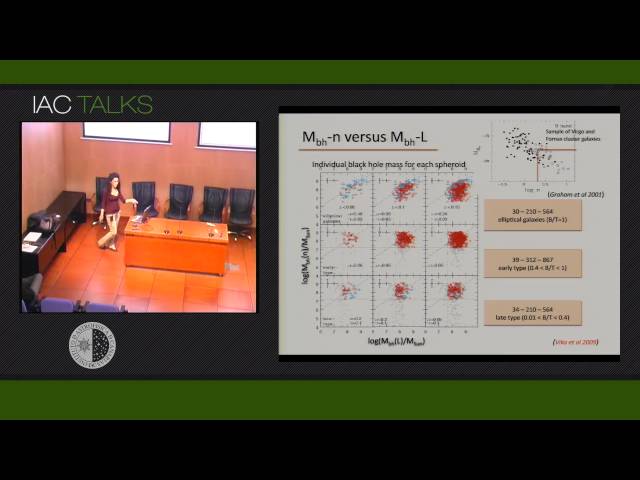
Abstract
We present our latest measurement of the SMBH mass function at redshift zero based on detailed structural studies of 1743 galaxies extracted from the B-band Millennium Galaxy Catalogue. Using the empirical correlations between the mass of the black hole and the photometric properties of the spheroid, MBH-L and MBH-n we estimated the SMBH mass of each galaxy and from this construct empirically derived SMBH mass functions. In addition, using a sample of 30 nearby elliptical and spiral galaxies, we will present new results showing the near-IR correlation between bulge properties and SMBH mass.
Abstract
This talk is divided into two related parts. First, we will call your attention to a basic, but often overlooked worrying fact, and presents ways of dealing with it. The fact is: an enormous number of galaxies in surveys like the SDSS have emission lines which are too weak (low S/N) to be classified by usual schemes (ie, diagnostic diagrams). It turns out that most of these are AGN-like, so ignoring them on the basis of low S/N (which most people do) leaves as much as 2/3 of these emission line galaxies unaccounted for. The solution: We present a number of alternative methods to rescue this numerous population from the classification limbo. We find that about 1/3 of these weak-line galaxies are massive, metal rich star-forming systems, while the remaining 2/3 are more like LINERs. In the second part, we revisit the old idea by Binette et al (1994) that post-AGB stars can account for the emission line properties of some galaxies. A "retired galaxy" model is presented and compared to data in the SDSS. We find that about 1/4 of the galaxies classified as LINERs in the SDSS are consistent with this model, where all ionizing radiation is of stellar origin. More dramatically, nearly 100% of weak-line LINERs are perfectly consistent with being just retired galaxies, with no active nucleus. If these ideas are correct, contrary to current practice, relatively few LINERs should be counted as bona fide AGN.Upcoming talks
No talks scheduled for the next days.