Recent Talks
List of all the talks in the archive, sorted by date.

Abstract
Introducción del subdirector del Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, Carlos Martinez, en la segunda jornada del curso "Introducción a la instrumentación para satélites de observación de la Tierra".
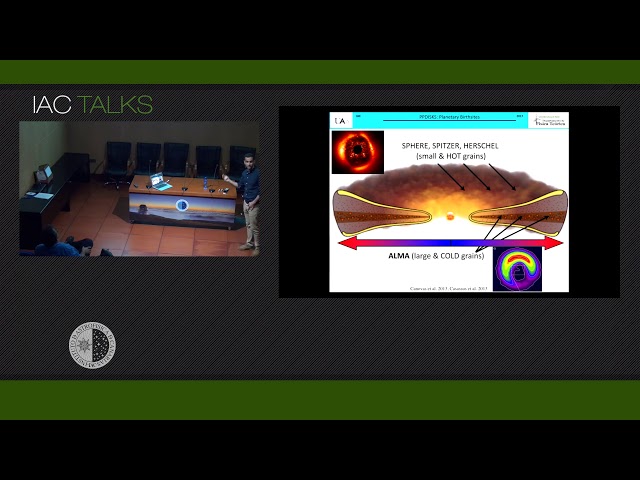
Abstract
With more than 3000 detected exoplanets it is now clear that planet formation is a natural outcome of stellar
formation. However, the mechanisms by which planets do form remain uncertain. The most promising way to understand
this process is to study protoplanetary disks that show signposts of planet formation: the so-called transitional
disks. In this talk I will first introduce the observational techniques and instruments that are revolutionizing this field
I will finish presenting ALMA and SPHERE/VLT observations of transitional disks around low-mass stars
that, according to our current understanding, show evidences of planet-disk interactions.

Abstract
El Consejo Europeo de Investigación (ERC, European Research Council) busca financiar a largo plazo proyectos de investigadores excelentes y de sus equipos de investigación, a fin de que lleven a cabo una investigación novedosa y potencialmente muy rentable, pero de alto riesgo. Su objetivo específico es “reforzar la excelencia, el dinamismo y la creatividad de la investigación europea”.
La excelencia científica es el único criterio para la concesión de subvenciones y funcionará sobre una base «ascendente», sin prioridades predeterminadas. Las subvenciones del ERC están abiertas a equipos de investigadores de cualquier edad y de cualquier país del mundo que trabajen en Europa.

Abstract
Introducción a los aspectos a tener en cuenta en el diseño de la mecánica de instrumentación aeroespacial, con una breve descripción de las especificaciones propiciadas por el ambiente, cargas, materiales, aspectos térmicos finalizando con diseños de optomecánica y mecanismos.

Abstract
Fundamentos de detectores de imagen en el rango visible y su uso en aplicaciones de observación de la Tierra.

Abstract
Diferentes usos de la observación desde el espacio. Descripción de los sistemas ópticos, ejemplos de misiones y algunos problemas del pasado.

Abstract
Visión global de todas las fases que sigue el ciclo de vida de un proyecto aeroespacial.

Abstract
A la hora de diseñar un satélite debemos considerarlo como parte de un sistema más grande compuesto por el segmento Tierra, el lanzador y por último el segmento espacio. El diseño de un satélite estará determinado por el tipo de misión que realizará, su presupuesto y duración; por el lanzador, su modo y trayectoria de lanzamiento; por los materiales y piezas a usar y su vida útil; por la estación en Tierra; etc. En esta charla se hace un breve resumen de los elementos que forman parte del segmento Tierra y del lanzador y se habla más extensamente del satélite, i.e. la plataforma y la carga útil.

Abstract
La primera parte de la charla está dedicada a una introducción a las misiones espaciales, presentando una breve perspectiva histórica de los casi 60 años de vida de la exploración espacial, junto con un análisis de los retos y tendencias actuales asociados al auge de los satélites de pequeño tamaño. La segunda parte de la charla está dedicada al análisis de las condiciones extremas de operación en el espacio y sus efectos sobre la intrumentación, incidiendo especialmente en los efectos de la radiación sobre los sistemas electrónicos.

Abstract
Presentación del curso "Introducción a la instrumentación para satélites de observación de la Tierra" por parte de Pablo Redondo y Alex Ozcoz.
Upcoming talks
No talks scheduled for the next days.