Recent Talks
List of all the talks in the archive, sorted by date.
Abstract
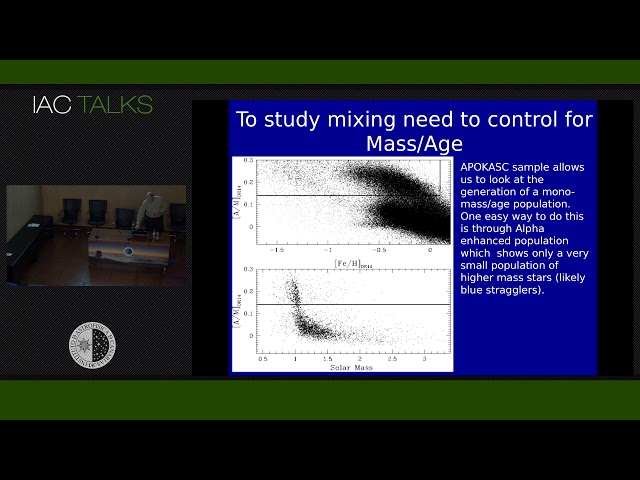
Despite being some of the most abundant elements in the Universe the determination and understanding of the chemical evolution of C and N is still very uncertain. One of the main limitations in understanding chemical evolution of C and N is the fact that C and N are altered as during the first dredge-up on the red giant branch. We present old red giants at various metallicities and luminosities in a sample that is more than 100 times larger than the seminal work of Gratton et al. 2000. Using this we can see the impact of the first dredge-up as well as the on set of "extra" mixing at the bump in the luminosity function for giants more metal-poor than [Fe/H] < -0.4. These observations can be used to constrain future models of mixing. At a fixed metallicity younger stars have a stronger mixing response during dredge-up. This fact allows up to infer ages from the first dredge-up [C/N] ratio. We demonstrate that we are able to interpret the DR14 [C/N]-[Fe/H] abundance distributions as trends in age-[Fe/H] space. Our results show that an anti-correlation between age and metallicity, which is predicted by simple chemical evolution models, is not present at any Galactic zone. Stars far from the plane (|Z| > 1 kpc) exhibit a radial gradient in [C/N]. The [C/N] dispersion increases toward the plane. We measure a disk metallicity gradient for the youngest stars from 6 kpc to 12 kpc, which is in agreement with the gradient found from other surveys. Older stars exhibit a flatter gradient, which is predicted by simulations in which stars migrate from their birth radii. We also find that radial migration is a plausible explanation for the observed upturn of the [C/N]-[Fe/H] abundance trends in the outer Galaxy, where the metal-rich stars are relatively enhanced in [C/N].

Abstract
Thanks to its unique capabilities, the MUSE integral field spectrograph at ESO VLT has given us new insight of the Universe at high redshift. In this talk I will review some breakthrough in the observation of the Hubble Ultra Deep field with MUSE including the discovery of a new population of faint galaxies without HST counterpart in the UDF and the ubiquitous presence of extended Lyman-alpha haloes around galaxies.
Abstract
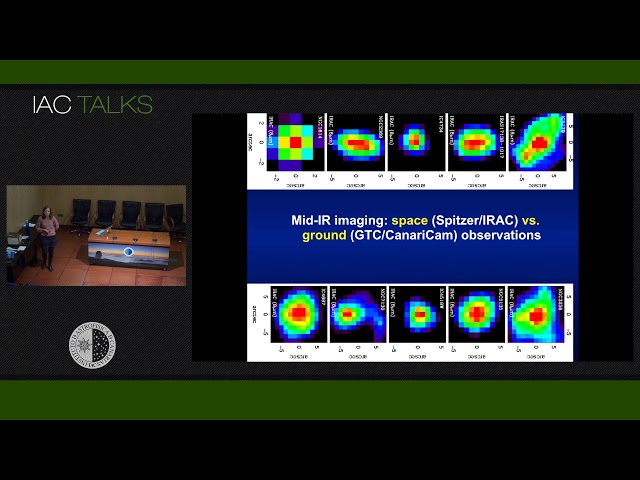
In the past 10-15 years our view of AGN has significantly evolved thanks to the combination of new observations and models. X-ray, infrared and sub-mm data have been crucial to peer into the inner region of AGN and study the properties of the tori, circum-nuclear disks and nuclear outflows. In this talk I will summarize our current view of nuclear obscuration in AGN, focusing on the variations of the torus properties with gas phase. I will also present preliminary results from a new project aimed to characterize nuclear outflows in a sample of nearby quasars and study their impact in the stellar populations, on-going star formation and molecular gas reservoirs of the galaxies.

Abstract
A young just married couple of Astrophysicist decided going to Kenya for they honeymoon. There, they meet Dr. Dismas Simiyu at Meru University, in Meru town, 240 km north from Nairobi. All of them together organised an Astrophysics Workshop in order to introduce both students and staff, into the Astrophysics and Computer Programming word. Follow the adventures in Kenya of this two young Astrophysicists next Thursday in the IAC seminar!
Abstract
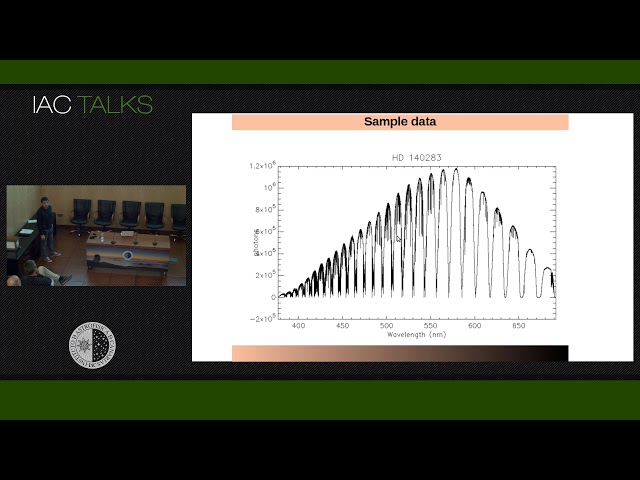
The High Optical Resolution Spectrograph (HORuS), is now ready for operation on Gran Telescopio Canarias (GTC). HORuS is mainly a recyled instrument, largely based on components from UES, which was available at the WHT in the 90's. HORuS offers single-object R=25,000 spectroscopy with broad spectral coverage (380-700 nm, with gaps in the red). A 3x3 integral field unit (IFU) covering 4.4 arcsec2 gathers the light on the focal plane into optical fibers that later align to form a pseudo-slit at the entrance of the spectrograph.
The science fibers can be illuminated with light from calibration lamps. On the detector, with the IFU acting as an image slicer, monochromatic light spreads over hundreds of pixels, enabling the possibility of achieving, for very bright targets, signal-to-noise ratios per resolution element of several thousand in a single exposure. For fainter targets (12<V<16), readout noise is minimized by on-chip binning 8 (spatial) x 2 (spectral). From direct comparison of spectra of the same targets, the combined efficiency of HORuS+GTC is about 40% lower than UVES+VLT. For a V=7 star, the signal-to-noise per resolution element in a 900-seconds integration is about 1500 at 525 nm.

Abstract
APOGEE contains more than hundred thousands new giant stars. This enabled
us to collected an unprecedented and homogeneous sample of giant stars with
light-element abundance variations similar to observed in “
*second-generation*” globular cluster stars. If they are really former
members of dissolved globular clusters, stars in these groups should show
some of the basic SG-like chemical patterns known for stars currently
belonging to the Milky Way globular clusters, such as depletion in C and O
together with N and Al enrichments. Here, I will present the results of an
updated census of *SG-like* stars from a near-infrared manual analysis
using the Brussels Automatic Stellar Parameter (BACCHUS) code to provide
the abundances of C, N, O, Mg, Si, Al, Fe, Ce and Nd for every line of
possible cluster member stars, which they migrate to the disk, halo and
bulge as unbound stars, and become part of the general stellar population
of the Milky Way. By combining wide-field time-series photometry with
APOGEE-2S spectroscopy data, we are in a good position to put the big
picture together. The VVV survey have produced a large variability dataset
towards the Milky Way bulge and disk, including data in the near-IR (J and
Ks). These data will allow us to place constraints on the “polluters" that
are responsible for the chemical peculiarities, with candidates including
TP-AGB stars, binary mass transfer, accretion of material from the winds of
AGB stars, etc. A cross match between VVV sources and APOGEE targets is
ongoing.

Abstract
We present the discovery of a small 0.2'' (60 pc) radius kinematically decoupled core, as well as an outflow jet, in the archetypical AGN-starburst "composite" galaxy NGC 7130 from integral field data obtained with the adaptive optics-assisted MUSE-NFM instrument on the VLT. Correcting the already good natural seeing at the time of our science verification observations with the four-laser GALACSI AO system we reach an unprecedented spatial resolution of around 0.15''. We confirm the existence of star-forming knots arranged in an 0.58'' (185 pc) radius ring around the nucleus, previously observed from UV and optical Hubble Space Telescope and CO(6-5) ALMA imaging. We determine the position of the nucleus as the location of a peak in gas velocity dispersion. A plume of material extends towards the NE from the nucleus until at least the edge of our FOV at 2'' (640 pc) radius which we interpret as an outflow jet originating in the AGN. The plume is not visible morphologically, but is clearly characterised in our data by emission lines ratios characteristic of AGN emission, enhanced gas velocity dispersion, and distinct non-circular gas velocities. Its orientation is roughly perpendicular to line of nodes of the rotating host galaxy disk. An 0.2''-radius circumnuclear area of positive and negative velocities indicates a tiny inner disk, which can only be seen after combining the integral field spectroscopic capabilities of MUSE with adaptive optics.
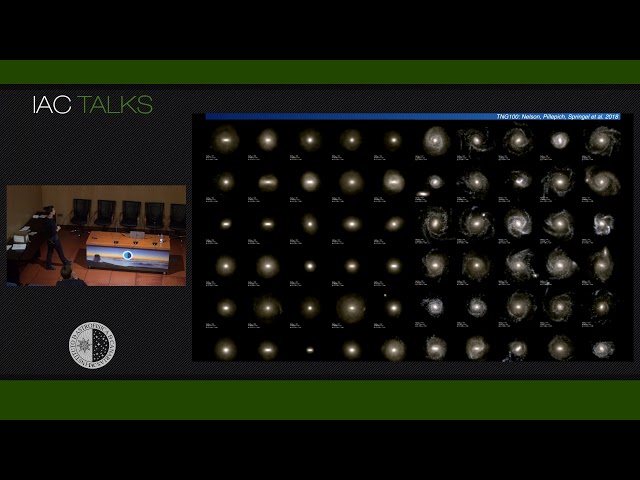
Abstract
I will describe the numerical efforts to simulate galaxies with the moving-mesh code AREPO across an unprecedented range of halo masses, environments, evolutionary stages and cosmic times. In particular, I will focus on the IllustrisTNG project (www.tng-project.org <http://www.tng-project.org>), a series of three gravity+magnetohydrodynamics cosmological volumes of 50, 100, and 300 Mpc a side, respectively, in a LCDM cosmology. With these, we are capable of both resolving the inner structures of galaxies as small as the classical dwarfs of the Milky Way, as well as of sampling the large scale structure of the Universe with thousands among massive groups and clusters of galaxies. I will discuss what is explicitly and empirically solved in gravity+magnetohydrodynamics simulations for galaxy formation in a cosmological context and what is required and what it means to “successfully” reproduce populations of galaxies which resemble the real ones. I will therefore show novel insights allowed by the new simulations, ranging from the assembly of the most massive structures in the Universe, to the effects of baryons of the phase-space properties of dark matter and to the changes in the star-formation activity and morphological mix of galaxies at early epochs.
Abstract
Abstract
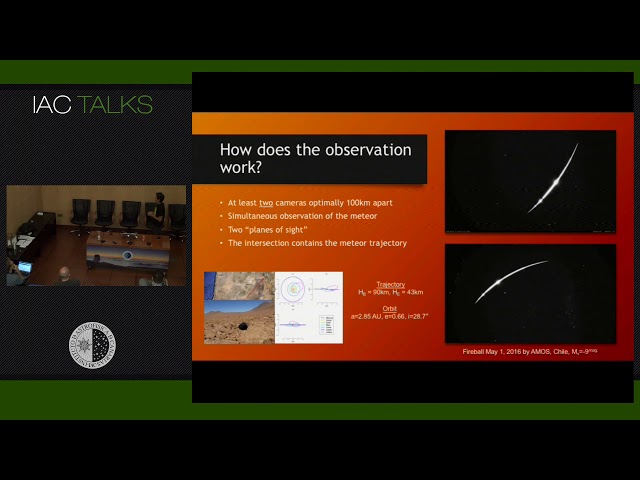
In this talk, I will briefly introduce Slovak instrument AMOS - all-sky meteor orbit system. We designed and developed a GUI tool for calculating and visualizing trajectories of meteors in Earth's atmosphere and Solar system from multiple-station observations. The current version of the program includes calculation of 1) atmospheric trajectory and velocity, 2) Solar system trajectory, 3) photometric mass, 4) dark flight and impact, 5) Monte Carlo simulation of errors. The program is written in Lazarus/Object Pascal and can be run under Windows as well as Linux systems. Numerical simulations and graphical outputs are produced in R.
In the second part of the talk, I will discuss the python-based photometry pipeline by Mommert (2017) for reducing 4-colour MuSCAT2 images. We implemented several modifications to significantly increase the number of successfully reduced images. I will discuss how the modifications combine data through colors as well as time to obtain more results.
Upcoming talks
No talks scheduled for the next days.