Recent Talks
List of all the talks in the archive, sorted by date.

Abstract
The Faculty of Mathematics, Physics and Informatics of Comenius University in Bratislava, Slovakia (FMPI CU) operates its own Astronomical and Geophysical Observatory in Modra, Slovakia (AGO). AGO consists of several optical systems, from which some were developed by FMPI. One of the mentioned systems is a 70-cm Newton telescope (AGO70) with primary focus on the space debris research, space surveillance and tracking (SST) to support the European attempts for autonomous SST operations.
AGO70 has several parallel scientific programs with primary focus on space debris characterization. In the last two years we created our own space debris light curve catalogue which is available for scientific community. The light curve catalogue is further used for the BVRI photometry where the shape of the phase-diagram and the synodic rotation period define the strategy for the data acquisition and processing once acquired with multi-band filters. Astrometric measurements are used for three goals. To validate and calibrate the AGO70 system’s data, to support the cataloguing efforts which requires orbit determination and improvement, and to improve the tracking efficiency of Satellite Laser Ranging stations.
Part of the improvement of AGO70 system is also hardware and software modifications. There have been efforts given to the improvement of the image processing software responsible for the real-time processing of acquired FITS frames. This so-called Image Processing Elements (IPE) pipeline is based on the modular design to make it more flexible for modifications and implementation to other systems. Currently, there are nine IPEs in total responsible for many different tasks like image segmentation, astrometric reduction, tracklet building or object correlation.
In our work we will present the AGO70 system’s technical characteristics and observation programs. We will introduce the overall design of the system and its functionalities. The planning, acquisition and processing of light curves, BVRI photometric data, and astrometric measurements will be discussed in detail. We will present the image processing pipeline which improves the obtained data’s quality and latency.
Abstract
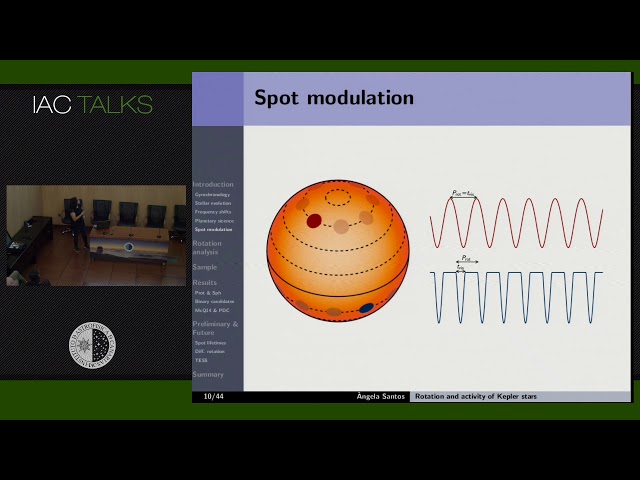
Brightness variations due to dark spots on the stellar surface encode information about stellar surface rotation and magnetic activity. As stars slow down and become less active, the rotation rate is observed to decrease, thus rotation is often used as a diagnostic for age. Rotation and magnetic fields affect stellar evolution and the mode frequencies used to infer fundamental properties of stars. Furthermore, rotation itself is an important ingredient for dynamo mechanisms. Therefore, it is of extreme importance to constrain surface rotation and magnetic properties of stars. In this work, we analyze the spot modulation in light-curves for main-sequence and subgiant stars observed by Kepler main-mission. We analyze four data sets: KADACS time-series obtained for 20-, 55-, and 80-day filters; and PDC-MAP time-series. The rotation estimates are retrieved through a combination of wavelet analysis and the autocorrelation function of light-curves. Reliable rotation periods are determined by comparing the rotation estimates obtained from the different diagnostics and for the different time-series. We recover rotation periods for more than 60% of the targets. For those, we also study the photometric activity level and lifetime of active regions. We find the rotation rate to increase with effective temperature and mass, while the photometric activity proxy increases towards fast rotators. Active region lifetimes are found to be longer with increasing rotation rate and photometric activity. In this analysis we also identify potential polluters, such as mis-classified Red Giants, classical pulsator candidates, and photometric pollution of light-curves.

Abstract
The mass and structural assembly of galaxies is still a matter of intense debate. Current theoretical models predict the existence of a linear relationship between galaxy effective radius (R_e ) and the host dark matter halo virial radius (R_h ).
By making use of accurate and transparent semi-empirical models compared to the size distributions of central galaxies from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, I will provide robust constraints on the normalization and scatter of the Re − Rh relation in the framework of Halo Abundance Matching. Specifically, I will explore the parameter space
of models in which the relation between galaxy size and halo radius is mediated by the dynamical or structural properties of the dark matter halo. Within the same framework, I will also discuss the size evolution of Ultra Massive Galaxies, which is still poorly understood.
I will show that the data require extremely tight relations for both early-type and late type galaxies, especially for more massive galaxies. These constraints challenge models based on angular momentum conservation, which predict significantly wider distributions of galaxy sizes and no trend with stellar mass. I will also show that a constant Re-Rh relation is able to reproduce the size evolution of Ultra Massive Galaxies and provide a framework to the size evolution of galaxies with any mass.
I will conclude showing that the normalization and scatter of the size-halo radius relation of both early- and late-type galaxies might be consistent with pure merger models, though a complete picture for the structural evolution of galaxies remains elusive.
Abstract
For the beginning of my presentation, I would like to briefly present the astronomy program at the Faculty of Mathematics, Physics and Informatics of Comenius University in Bratislava, Slovakia.
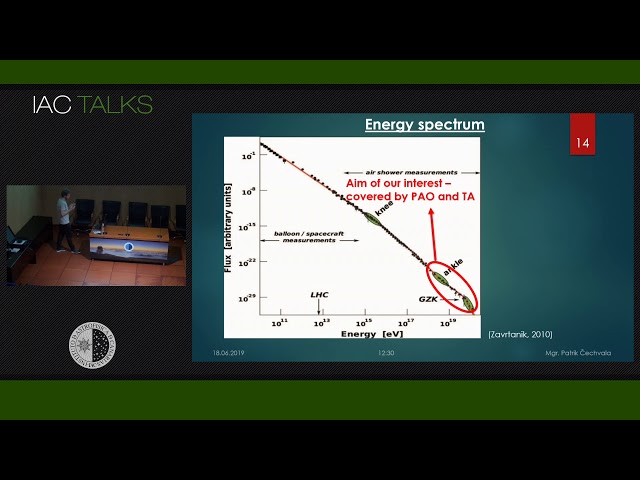
Continuing, the main results of my diploma thesis will be presented during which I simulated the propagation of ultra-high energy cosmic rays throught the Universe using the simulation code SimProp v2r4 modelling the characteristics of possible sources. The results were compared with the observations from the Pierre Auger Observatory which is situed in Argentina. Thesis has been made with the cooperation of the Institute of Physics of Czech Academy of Sciences in Prague. Ultra-high energy cosmic rays (UHECRs) represent the subatomic particles, mainly protons and nuclei of different elements, which can attain energies up to 1020 eV. Colliding with the Earth´s atmosphere they create the shower of secondary particles which can be detected by specific detectors on the ground. Origin of these particles with the highest energies is still a problem which haven´t been solved to these days.
Besides the corpuscular particles, the Earth is permanetly bombarded also by high energy photons or gamma rays. These are formed in the vicinity of exotic objects like active galactic nuclei (AGN) or supernova remnants (SNRs) or as a product of UHECRs. Colliding with the atmosphere, they also create a shower of secondary particles which is narrower than in the case of UHECRs. To observe this shower the Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescopes (IACTs) have been developed observing the Cherenkov light formed as a product of the cascade. Such telescopes are for example the MAGIC telescopes situed at Observatorio del Roque de los Muchacos (ORM) on La Palma or the future Cherenkov Telescope Array (CTA) which northern part will be also situed at ORM.
Study of gamma rays represents currently the main topic of my PhD project. For this reason I am glad to had an opportunity to participate on ERASMUS+ mobility at IAC for 3 months and to cooperate with the astroparticle physics group. During this period I have been analyzing archival data taken by MAGIC telescopes of the active region around SNR G24.7+0.6. Specifically we are interested in a source labeled as 2FHL J1839.5-0705. Preliminary results of my study will be presented.

Abstract
Although the name 'fundamental metallicity relation' (FMR) may sound a bit bombastic, it really represents a fundamental relation in the sense of revealing a fundamental process in galaxy formation. Numerical simulations predict that accretion of cosmic web gas feeds star formation in star-forming galaxies. However, this solid theoretical prediction has been extremely elusive to confirm. The FMR, i.e., the fact that galaxies of the same stellar mass but larger star formation rate (SFR) tend to have smaller gas-phase metallicity (Zg), is one of the best observational supports available yet. The talk will introduce the FMR and then present recent results of our group showing how the FMR emerges from a local anti-correlation between SFR and Zg existing in the disks of galaxies. Thus, understanding the FMR is equivalent to understanding why active star-forming regions tend to have low relative metallicity. The existence of the local anti-correlation SFR-vs-Zg is found by Sanchez-Menguiano+19 ApJ and Sanchez Almeida+18 MNRAS, whereas the equivalence between local and global laws is in Sanchez Almeida & Sanchez-Menguiano 19 ApJL.

Abstract
Supernova SN1987A in the Large Magellanic Cloud offers an unprecedented opportunity to tackle fundamental issues of supernova explosions: dust and molecule formation, interaction with the circumstellar medium, particle acceleration, pulsar formation, etc. Since 2011, instruments like ALMA have been fundamental for such endeavor. Tomographic techniques have recently permitted to obtain 3D-images of the molecular emission. High-resolution images of dust emission have recently been obtained. All those results, compared with predictions from hydro-dynamical simulations, are paving the way to a better understanding of supernovae explosions. In the talk, the main results will be highlighted with emphasis on the advances produced since 2017 in the understanding of the structure of the inner ejecta or debris.
Abstract
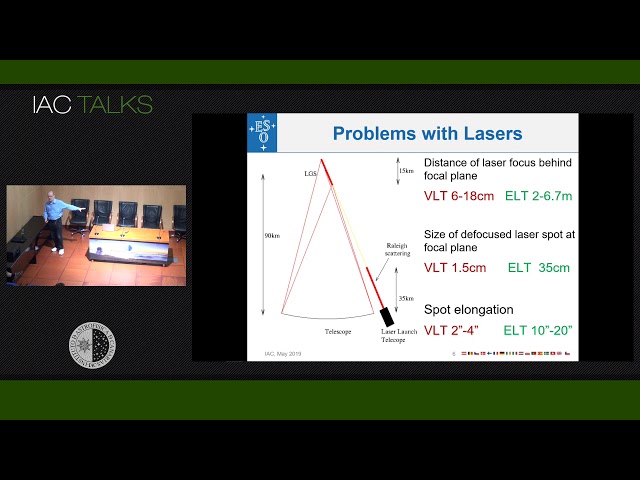
This talk looks at the challenges in developing instruments for extremely large telescopes. It then discusses the impact of these on the ELT first light instruments and their current status. The instruments are HARMONI, a visible - Near IR integral filed unit; MOARY/MICADO a multi-conjugate AO system and camera and METIS a thermal IR spectrometer and camera.
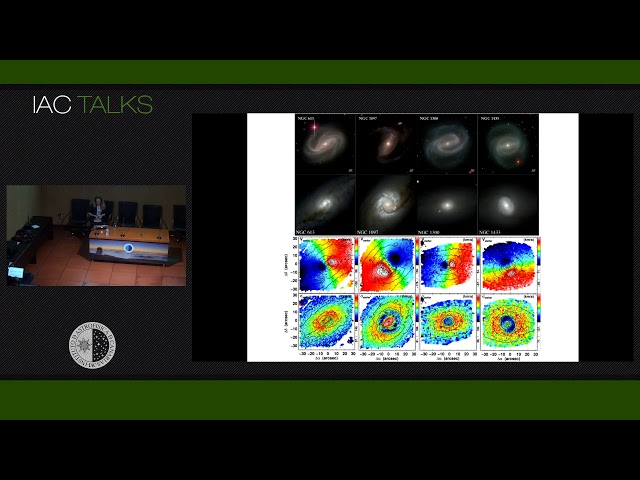
Abstract
The Time Inference with MUSE in Extragalactic Rings, TIMER, is a project dedicated to study the central regions
of 24 nearby galaxies with the integral field spectrograph MUSE. The spatial resolution of this instruments
allows the detailed study of the different structural components in these galaxies and, therefore, disentangle
their star formation histories, kinematics and dynamics of both, the gaseous and the stellar constituents.
In this talk, I will give an overview of the project as well as some details on how the dataset can be used for a plethora of scientific applications, like
understanding the stellar and AGN feedback, the role of primary and secondary bars, the dynamics of nuclear
spiral arms, barlenses, box/peanuts and bulges.

Abstract
The rotation rate of a cool star provides an additional method beyond the usual ones to characterize and understand its behavior. Increasingly large samples of rotation periods are now emerging from both ground- and space-based work. This talk will present some systematic behaviors of these rotation periods, including dependencies on age and mass, especially as probed by open cluster studies. The results suggest that it is often possible to derive an age for a cool star (and its planets) from such rotation period measurements, via a procedure called gyrochronology. This talk addresses the possibilities of this emerging area of work, and also certain complexities and cautions that should be considered in this Kepler, TESS, and soon, PLATO era.

Abstract
In this talk, I will present the highlights from our recent study of 22
local (z < 0.025) type-1 LINERs from the Palomar Survey, on the basis of
optical long-slit spectroscopic observations taken with TWIN/CAHA,
ALFOSC/NOT and HST/STIS (Cazzoli et al. 2018, MNRAS 480, 1106–1162).
In this study, we explored the AGN-nature of these type-1 LINERs by
studying the broad (BLR-originated) Hα component. Then, we derived
reliable interpretation for the different component of emission lines by
studying their kinematics and ionization mechanism. Finally, we studied
the neutral gas in the nuclei of these LINERs by modeling of the NaD
absorption.
Upcoming talks
No talks scheduled for the next days.