Found 5 talks width keyword Galactic center

Abstract

Abstract
The lowest metallicity stars that still exist today represent a window into the early Universe. Studying these stars gives us a local avenue to guide our understanding of star formation and supernova feedback in the early Universe, the early build-up of galaxies like our Milky Way, and the epoch of reionization. In this talk I will present recent results of the Pristine survey, a narrow-band photometric survey of the Milky Way designed to get metallicity information for millions of stars very efficiently. I will discuss what we have learned from our analysis of the most metal-poor stars about the early formation of the Milky Way. Moreover, I will highlight the bright future for this type of study in synergy with the upcoming highly-multiplexed spectroscopic surveys.

Abstract
Bosonic ultra-light dark matter (ULDM) in the mass range m ~ $10^{-22} - 10^{-21} \rm eV$ has been invoked as a motivated candidate with new input for the small-scale `puzzles' of cold dark matter. Numerical simulations show that these models form cored density distributions at the center of galaxies ('solitons'). These works also found an empirical scaling relation between the mass of the large-scale host halo and the mass of the central soliton. We show that this relation predicts that the peak circular velocity of the outskirts of the galaxy should approximately repeat itself in the central region. Contrasting this prediction to the measured rotation curves of well-resolved near-by galaxies, we show that ULDM in the mass range m ~ $10^{-22} - 10^{-21} \rm eV$ is in tension with the data.
Abstract
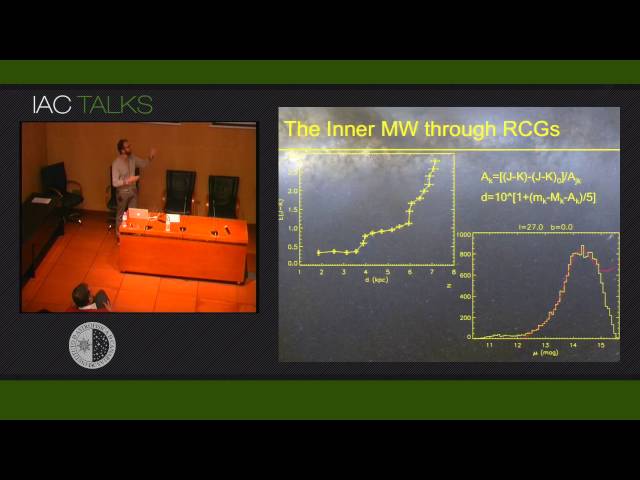
Abstract: The study of the structure of our Galaxy, particularly its inner disc, has always been hindered by two factors: interstellar extinction dims even the brightest stars at optical wavelengths and the high source density prevents us, as the proverbial trees, to see the big galactic picture.
Abstract
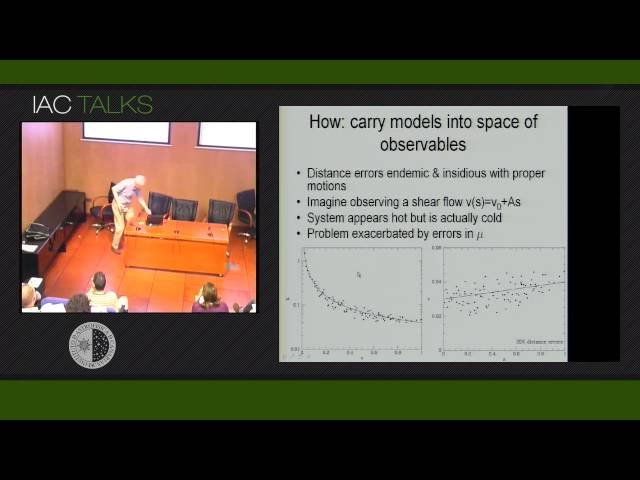
The study of the Milky is expected to have a major impact on our understanding of how galaxies form and evolve. "Near-field cosmology" is being vigorously pursued through a series of major surveys of the Galaxy's stellar content (2-MASS, SDSS, RAVE, Hermes, Apogee, Gaia) that are either in hand or pending. It will be argued that what we want to know is deeply buried in these data and can only be extracted by comparing the surveys with a hierarchy of dynamical models of ever increasing complexity. Work currently being done to build such hierarchical models will be described, and some early results from this work will be summarised.« Newer Older »
Upcoming talks
- Quantum Simulators for the Cosmos: From Confining Strings to the Early UniverseDr. Enrique Rico OrtegaThursday December 4, 2025 - 10:30 GMT (GTC)
- Colloquium by Junbo ZhangDr. Junbo ZhangThursday December 11, 2025 - 10:30 GMT (Aula)