Found 6 talks archived in Astrometry and celestial mechanics
Abstract
After placing the Gaia mission in the context of current astrophysical research, the astrometric, photometric, and spectroscopic data provided by the satellite, as presented in its third data archive, DR3, will be reviewed. Gaia third archive contains, in addition to the measurements from the satellite's instruments, an extensive set of astrophysical parameters derived by the DPAC data processing consortium, for stars, unresolved galaxies, and solar system objects. These parameters correspond to about 1.8 billion sources repeatedly observed by the satellite during the first 34 months of operation. In the case of the Milky Way stars, DR3 contains information for about 1% of its stars, which has made it possible, for the first time, to study the dynamics of the disk and the halo, and to reconstruct the tumultuous evolutionary history of our galaxy, which is etched in its halo. Studying the integrals of the motion and the orbital actions, some 15 episodes of accretion of other galaxies by our galaxy have been identified, which shows that our Galaxy is the result of billions of years of "galactic canibalism". Accretion phenomena and tidal current trails are frequently observed in other galaxies and show that our Universe evolves through a hierarchical formation of galaxies.
-------------------------------------------------
Meeting will be held online
Youtube: https://youtu.be/ns78Go3FM7I
Zoom: https://rediris.zoom.us/j/87455295473?pwd=dnd2SkppQ1F2UlN2K0FLbmlLZEFmZz09
Meeting ID: 874 5529 5473
Passcode: 941406

Abstract
En marzo de 106 AD el Reino Nabateo fue anexado por el emperador Trajano creando la nueva provincia de Arabia (Petraea). Nabatea y su antigua capital, la ciudad rosa de Petra, ha sido uno de nuestros objetivos de investigación desde nuestra primera campaña de campo en la región en 1996, hace ahora 20 años. En 2011 se llevó a cabo una campaña intensiva que deparó resultados muy sugerentes. En diciembre de 2015 se realizó una nueva visita a la zona en coincidencia con el solsticio de invierno. Se observaron y documentaron varios efectos de iluminación e importantes hierofanías en los principales monumentos de Petra. Estos hallazgos se han contrastado a la luz de las fuentes literarias y epigráficas y del simbolismo astronómico, En este sentido, como colofón, se ha analizado en detalle una de las piezas más fascinantes y enigmáticas del mundo nabateo, el llamado zodiaco de Khirbet et-Tannur, encontrado en un templo construido en la cima del Djebel Tannur en el Siglo II d.C. posiblemente bajo gobierno romano, y que ha supuesto un cambio de paradigma en nuestra forma de ver y comprender la civilización nabatea.


Abstract
En esta charla se presenta una puesta al día de los resultados más importantes de un estudio arqueoastronómico interdisciplinar realizado en varias decenas de yacimientos arqueológicos de las culturas ibérica y tartesia del primer milenio a.C. en el levante y sur peninsular. En el caso de los templos tartésicos, posiblemente muy influidos o construidos por colonos fenicios, muestran un patrón de orientación muy bien definido que podría estar relacionado con el ocaso más meridional de Venus y, posiblemente, con el culto a la diosa fenicia Astarté, asociada a dicho planeta según los historiadores de la antigüedad. Por otra parte, encontramos que una fracción importante de los santuarios ibéricos estudiados, todos ellos dedicados a una diosa femenina, muestran marcadores del orto u ocaso solar sobre elementos destacados del horizonte en los equinoccios o una fecha muy cercana a estos, posiblemente el punto medio temporal entre solsticios. Esta relación astronómica equinoccial, la más clara de todas las encontradas en el mundo ibérico, sugiere la existencia de ritos asociados a la estacionalidad, festividades agrarias de la fecundidad similares a otras bien conocidas del Mediterráneo antiguo. La cronología más temprana de los santuarios relacionados con los equinoccios indican que comenzaron a funcionar alrededor de mediados del siglo IV a.C., momento de cambios importantes en la ideología de la sociedad ibérica y de un incremento de la influencia cartaginesa en la zona.
Abstract
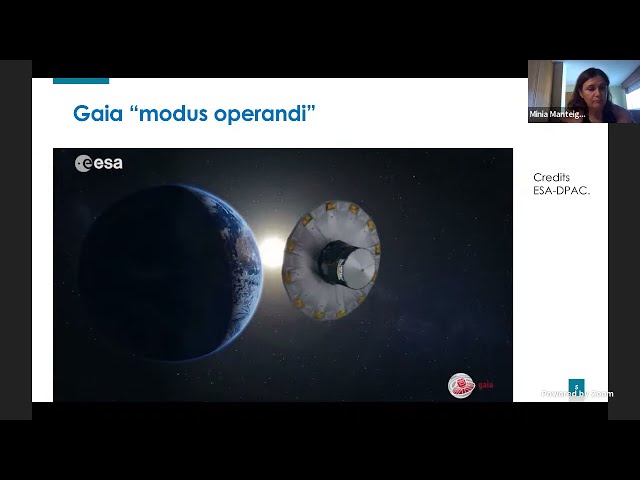
Gaia - the ESA cornerstone astrometric mission - was launched in December 2013, with the goal of censing the Milky Way population in a 6D space (positions and velocity) of 10^9 point-like obects, with errors
100-1000 times smaller than Hipparcos, with three color magnitudes and spectra as well. The scientific impact of its data will be large in many fields of astrophysics, from Galactic science, to Solar system objects, to stellar astrophysics, to galaxies and Quasars; from the distance ladder revision to fundamental physics. I will describe the mission concept, the scientific goals, and the present status of the mission, with special attention to the flux calibration of Gaia data.

Abstract
I present a general overview of the PLAnetary Transits and Oscillations of stars (PLATO) space mission. PLATO was approved by ESA’s Science Programme Committee, together with Euclid and Solar Orbiter missions, to enter the so-called definition phase, i.e. the step required before the final decision is taken (only two missions will be implemented). To be launched in 2018, PLATO is a third generation mission, which will take advantage of the scientific return from the currently flying space missions CoRoT (CNES, ESA, launched in 2006), and Kepler (NASA, launched in 2009). Moreover, the preparation and exploitation of the missions will benefit from the GAIA (ESA) mission data, together with new generation ground-based instrumentation like North-HARPS, GIANO, CARMENES, etc. Finally, I summarize the current organization status of the mission,focusing on the Spanish role within the consortium.
Upcoming talks
- Quantum Simulators for the Cosmos: From Confining Strings to the Early UniverseDr. Enrique Rico OrtegaThursday December 4, 2025 - 10:30 GMT (GTC)
- Colloquium by Junbo ZhangDr. Junbo ZhangThursday December 11, 2025 - 10:30 GMT (Aula)