Found 11 talks width keyword solar chromosphere

Abstract
We performed full Stokes spectropolarimetric observations of loop footpoints in the active region NOAA 13363 during a C-class flare with the GREGOR Infrared Spectrograph (GRIS) on 2023 July 16. The observed spectral region included the photospheric Si I 10 827 A and Ca I 10 839 A lines and the chromospheric He I 10 830 A triplet. Simultaneously, high-cadence and high-resolution imaging observations were carried out with the improved High-resolution Fast Imager (HiFI+) in the Ca II H line and TiO bands. The observations were conducted under excellent seeing conditions, as confirmed by the Fried-parameter measurements. Speckle-restored HiFI+ Ca II H images revealed thin flare-related filaments and diffuse haze-like emissions, further confirmed by background-subtracted solar activity maps (BaSAMs), which localized chromospheric variability near the sunspot. The He I triplet showed enhanced emission during the flare events and developed intense red- and blue-shifted components, with the decisive shift of 90 km/s, suggesting the significant energy release and plasma motion triggered by the flare. Simultaneously, a delayed increase in the Si I line wing intensity was observed approximately 6 minutes after the He I emission, suggesting that the upper photosphere experienced secondary heating, possibly due to thermal conduction rather than energetic particles. This time delay and spatial correlation support a scenario where dynamic flare processes influence chromospheric and upper photospheric layers. Our results demonstrate a temporal and spatial coupling between chromospheric and upper photospheric regions, and the time delay rules out direct heating by flare-accelerated electrons, so we propose thermal conduction or ionization effects as possible mechanisms.
Abstract
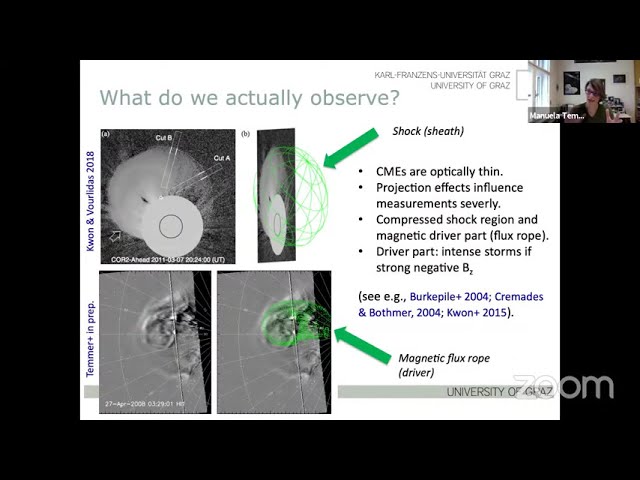
The Sun is an active star that influences the Earth as well as the entire solar system. Most dynamic phenomena on the Sun are observed as coronal mass ejections (CMEs) and flares. CMEs present massive clouds of magnetized plasma having speeds up to a few thousand km/s, that may propagate over Sun-Earth distance within less than a day and may cause strong geomagnetic disturbances at Earth (Space Weather). As CMEs are optically thin, using remote sensing data measurements of intrinsic properties such as speed, width, propagation direction, density etc. are severely affected by projection effects. By combining image data with in-situ measurements, valuable information is provided enabling CME 3D analyzes, and with that facilitate a better quantification of the uncertainties in the observational measurements that are used to feed CME propagation models. With that, a much better understanding of CMEs as they propagate in interplanetary space could be gained.
The talk will cover the physisc about CME-flare phenomena, the interplanetary propagation behavior of CMEs related to the background solar wind, and Space Weather forecasting.
Zoom link: https://rediris.zoom.us/j/92170419398

Abstract
Emerging flux regions (EFRs) are seen as magnetic concentrations in the photosphere of the Sun. From a theoretical point of view, the EFRs are formed in the convection zone and then emerge because of magnetic buoyancy (Parker instability) to the solar surface. During the formation process of EFRs, merging and cancellation of different polarities occur, leading to various configurations of the magnetic field. Often, EFRs are visible in the chromosphere in form of magnetic loops loaded with plasma, which are often called “cool loops” when seen in the chromosphere along with dark fibrils and they can reach up to the corona. Nowadays, we refer to them as an arch filament system (AFS) which connects two different polarities. The AFSs are commonly observed in several chromospheric spectral lines. A suitable spectral line to investigate chromospheric features and particularly AFSs is the He I 10830 Å triplet. The new generation of solar telescopes and instruments such EST and DKIST, will allow us to record very high spectral, spatial, and temporal resolution observations necessary to investigate the dynamics, magnetic field, and characteristics of AFSs. These observations will help us to answer many open questions related to flux emergence such: (1) What are the observational consequences of the emerging flux? (2) How do EFRs evolve with time in the different layers of the solar atmosphere and how are these layers linked? (3) Is it possible to measure the height difference between the photosphere and the chromosphere connected by the legs of the AFSs?

Abstract
Magnetic fields break through the solar surface in a hierarchy of magnetic elements ranging from Earth-sized sunspots down to tiny concentrations that are barely resolved in the highest-resolution photospheric images. In the chromosphere they combine in intricate, highly dynamic, and continuously evolving fibrilar patterns. Movements of the photospheric field-line footpoints drive, guide, and control the flows of energy and mass into the corona, and trigger energy-releasing magnetic reconnection through relentless topological rearrangement. The conversion from convectively driven footpoint motion to outer-atmosphere outflows and loading takes place in the dynamic, fine-structured chromosphere.
A number of important facilities for observing the solar chromosphere have recently come on line (e.g. the SDO and IRIS satellites and ground-based Fabry-Perot interferometers) or will become operational in the near future (e.g. DKIST). The overwhelming complexity of the chromosphere makes it necessary to have numerical simulations for the interpretation of the observations. Such realistic simulations, spanning the solar atmosphere from the convection zone to the corona, are now becoming feasible.
This presentation will introduce the fascinating aspects of chromospheric physics and review recent results from both observations and numerical simulations.

Abstract
The Chromosphere and Prominence Magnetometer (ChroMag) is a synoptic instrument with the goal of quantifying the intertwined dynamics and magnetism of the solar chromosphere and in prominences through imaging spectro-polarimetry of the full solar disk in a synoptic fashion. The picture of chromospheric magnetism and dynamics is rapidly developing, and a pressing need exists for breakthrough observations of chromospheric vector magnetic field measurements at the true lower boundary of the heliospheric system. ChroMag will provide measurements that will enable scientists to study and better understand the energetics of the solar atmosphere, how prominences are formed, how energy is stored in the magnetic field structure of the atmosphere and how it is released during space weather events like flares and coronal mass ejections. An essential part of the ChroMag program is a commitment to develop and provide community access to the `inversion' tools necessary to interpret the measurements and derive the magneto-hydrodynamic parameters of the plasma. Measurements of an instrument like ChroMag provide critical physical context for the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph (IRIS) as well as ground-based observatories such as the future Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope (DKIST). A prototype is currently deployed in Boulder, CO, USA. We will present an overview of instrument design and capabilities, show some recent observations, and discuss the future of the project.

Abstract
The chromosphere is the interface between the photospheric solar surface and the outer corona and wind. In this complex domain the
solar gas becomes transparent throughout the ultraviolet and in the strongest spectral lines while magnetic pressure becomes dominant over gas pressure even in weak-field regions. Fine-scale magnetically caused or guided dynamic processes in the chromosphere constitute the roots of mass and energy loading of the corona and solar wind. Notwithstanding this pivotal role the chromosphere remained ill-understood after its basic NLTE radiation physics was formulated in the 1960s and 70s. Presently, both chromospheric observation and
chromospheric simulation mature towards the required sophistication. The open-field features seem of greater interest than the easier-to-see closed-field features. For the latter, the grail of coronal topology and eruption prediction comes in sight.
I will start with an introductory overview, show movies to present the state of art in observation and simulation, and treat some
recent success stories in more detail.

Abstract
Flares are among the most energetic magnetic solar phenomena. They are often accompanied by ejections of charged particles, which have a direct influence on the Earth in terms of Aurora or radio and satellite outages. The sudden nature of flares - some of them only last minutes - makes them an elusive feature when observed from ground-based telescopes. These measurements are especially challenging when we focus on magnetic fields and velocities in the different solar layers where flares develop and occur. I will present flare observations taken with different instruments, each targeting different observables, and I will show what we can learn from ground-based polarization measurements.

Abstract
Solar magnetism may look deceptively boring (a rather common star with relatively low activity). As it turns out, even the most quiet areas of the Sun (away from the sunspots) harbour a rich and interesting magnetic activity which is extremely complex and dynamic at spatial scales as small as ~100 km. And more importantly, this magnetism permeates most of the Sun, all the time. Therefore, it is not surprising that it might play an important role for solving some longstanding questions of stellar magnetism as: how is the million degree corona maintained when all sunspots have disappeared during the minimum of magnetic activity? And this is of interest not only for solar physics but for stellar astrophysics too, since it is expected that every star with a convective envelope harbours small-scale magnetic activity that we cannot hope to observe with the great detail we observe it in the Sun. From the first evidence of the presence of magnetic fields in the quiet areas of the Sun to the discovery of the smallest organised magnetic structures ever observed in a stellar surface just 30 years have passed. In this seminar, I will give an overview of our present knowledge about the small-scale quiet Sun magnetism. In particular, I will show how small loops of sizes of several hundreds of kilometers appear in the surface and travel across the solar atmosphere, reaching upper layers and having direct implications on chromospheric (coronal) magnetism. I will also show some of the properties of these newly discovered magnetic structures such as their spatial distribution, a key ingredient for understanding their origin.
Abstract
Fibrils are thin elongated features visible in the solar chromosphere in and around magnetized regions. Because of their visual appearance they have been traditionally considered a tracer of the magnetic field lines. In this work we challenge that notion for the first time by comparing their orientation to that of the magnetic field, obtained via high-resolution spectro-polarimetric observations of Ca II lines. The short answer to the question posed in the title is that mostly yes, but not always.

Abstract
The Sun presents us with many unsolved mysteries. In this talk I discuss three of them that have intrigued me for the last 50 years. Solar flares are the most powerful explosions in space between here and the nearby stars. The only viable power source is stored magnetic energy. Yet definitive observations of changes in the magnetic field associated with flares have been lacking until recently. Measurements with the GONG network have helped to address this mystery and the results are surprising. Efforts to observe the weak magnetic fields in the solar photosphere date nearly to the discovery of magnetism on the Sun. Improvements in observational capabilities have made this area a 'hot' topic with many important contributions from people at the IAC. High resolution observations are clarifying many features. I will focus on the role played by lower resolution work in defining the uniformity of the still mysterious weak magnetic fields over large spatial and temporal scales. Physics changes from hydrodynamic to magnetic dominance as one moves upward from the photosphere to the chromosphere. This leads to significant and complicated changes in the magnetic field in both the active and quiet Sun. Observations of the chromospheric magnetic field show several unexpected and mysterious features. Solving these mysteries will be an exciting area as observational and spectral inversion capabilities develop.« Newer 1 | 2 Older » Last >>
Próximas charlas
- Quantum Simulators for the Cosmos: From Confining Strings to the Early UniverseDr. Enrique Rico OrtegaThursday December 4, 2025 - 10:30 GMT (GTC)
- Colloquium by Junbo ZhangDr. Junbo ZhangThursday December 11, 2025 - 10:30 GMT (Aula)