Found 11 talks width keyword turbulence

Abstract
We present the extended data release of the Calar Alto Legacy Integral Field Area (CALIFA) survey (eDR). It comprises science-grade quality data for 895 galaxies obtained with the PMAS/PPak instrument at the 3.5 m telescope at the Calar Alto Observatory along the last 12 years, using the V500 setup (3700-7500Å, 6Å/FWHM) and the CALIFA observing strategy. It includes galaxies of any morphological type, star-formation stage, a wide range of stellar masses ( ∼10^7-10^12 Msun), at an average redshift of ∼0.015 (90\% within 0.005 < z <0.05). Primarily selected based on the projected size and apparent magnitude, we demonstrate that it can be volume corrected resulting in a statistically limited but representative sample of the population of galaxies in the nearby Universe. All the data were homogeneously re-reduced, introducing a set of modifications to the previous reduction. The most relevant is the development and implementation of a new cube-reconstruction algorithm that provides an (almost) seeing-limited spatial resolution (FWHM PSF ∼1.0"). Furthermore we present the analysis performed using the pyPipe3D pipeline for these dataset. We include a description of (i) the analysis performed by the pipeline, (ii) the adopted datamodel for the derived spatially resolved properties and (iii) the catalog of integrated, characteristics and slope of the radial gradients for a set of observational and physical parameters derived for each galaxy. All these data has been distributed through the following webpage: http://ifs.astroscu.unam.mx/CALIFA_WEB/public_html/
Abstract
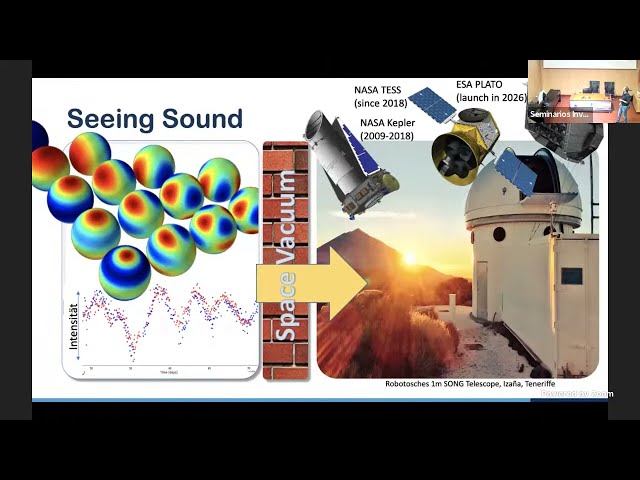
Understanding stellar structure and evolution significantly impacts our understanding of the tight-knit evolution of galaxies and exoplanet systems. However, hidden behind the luminous layers of the stellar atmosphere, the deep interior of a star is eluding from direct measurements. The seismic study of waves propagating the deep interior provides the only way to measure the internal structure, dynamics, and mixing in any given star and compare it to theoretical models.
With the photometric data from space missions, such as the NASA Kepler telescope, a golden age has begun for seismology. In particular, the seismic studies of thousands of solar-like have led to numerous breakthroughs in our understanding of the stellar structure of red-giant stars. Complimentary information on stellar binarity, tidal forces, rotation, and lithium abundance provide additional constraints to characterize the advanced evolution of stars further and provide high-resolution insights into complex internal adjustments. Approaching a sample of ~1000 identified solar-like oscillators in binary systems, provided by the ESA Gaia and NASA TESS missions draws an exciting picture on the interaction of stellar and orbital evolution.
https://rediris.zoom.us/j/89275150368?pwd=QnNxc09KbmJMTmdaRmVGdjZYSlBqdz09
ID de reunión: 892 7515 0368
Código de acceso: 101169
https://youtube.com/live/6Iproe6Zwb4?feature=share
Abstract
I will review the status of the QUIJOTE (Q-U-I JOint TEnerife) experiment, a project led from the IAC with the aim of characterising the polarisation of the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) and other galactic or extragalactic physical processes that emit in microwaves in the frequency range 10-42GHz, and at large angular scales (1 degree resolution). QUIJOTE consists of two telescopes and three instruments operating from the Teide Observatory, and started operations about 10 years ago, in November 2012.
I will discuss the status of the project, and I will present the latest scientific results associated with the wide survey carried out with the first QUIJOTE instrument (MFI) at 11, 13, 17 and 19GHz, covering approximately 29000 deg$^2$ with polarisation sensitivities in the range of 35-40 $\mu$K/deg. These MFI maps provide the most accurate description we have of the polarization of the emission of the Milky Way in the microwave range, in a frequency domain previously unexplored by other experiments. These maps provide a unique view of the Galactic
magnetic field as traced by the synchrotron emission. These results have been presented in an initial series of 6 scientific articles published on January 12th, 2023.
Finally, I will describe the prospects for future CMB observations from the Teide Observatory.

Abstract
Massive stars (at least eight times as massive as the Sun) possess strong stellar winds driven by radiation. With the advent of the so called MiMeS collaboration, an increasing number of these massive stars have been confirmed to have global magnetic fields. Such magnetic fields can have significant influence on the dynamics of these stellar winds which are strongly ionized. Such interaction of the wind and magnetic field can generate copious amount of X-rays, they can spin the star down, they can also help form large scale disk-like structures. In this presentation I will discuss the nature of such radiatively-driven winds and how they interact with magnetic fields.
https://youtu.be/jKmifm17bno

Abstract
Mathematics of atmospheric fronts: S.Q.G.(Surface Quasigeostrophic Equation) is a relevant model to understand the evolution of atmospheric fronts. It represents also a mathematical challenge, because of its non-linear and non-local character, which illustrates the rôle of mathematics in the development of science.
This colloquium will be held in person in the Aula

Abstract
Following Cowling's anti-dynamo theorem of 1933, there was a long period during which the very existence of dynamos was unclear. Even with the emergence of three dimensional simulations in the late 1980s, people were careful to distinguish true dynamos from just some sort of amplification. Meanwhile, we know of many examples of true dynamos - not only from simulations, but also from several laboratory experiments. Nevertheless, there are still problems, fundamental ones and also very practical ones. After all, we are really not sure how the solar dynamo works. Today, global three-dimensional simulations seem to have an easier time to reproduce the behaviors of superactive stars, but not really the group of inactive stars, to which also the Sun belongs. The Sun itself may actually be special; it has so well defined cycles and it is at the brink of becoming very different. Theoretically, slightly slower rotators should have antisolar rotation, but it is possible that some of those stars never become that slow if stellar breaking ceases for some reason. Sun and starspots are very evident indicators of solar and stellar activity. Their formation is also not well understood. Polarimetry reveals their magnetic helicity, which can be detected even with the solar wind.
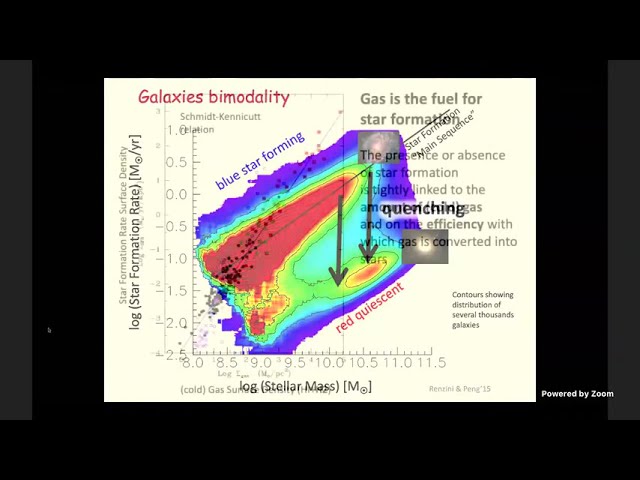
Abstract
In the local universe most of the stellar mass is in passive galaxies, where star formation is
absent or at very low levels. Understanding what are the mechanisms that have been
responsible for quenching star formation in galaxies, and transforming them into passive,
quiescent systems, is one of the main observational and theoretical challenges of extragalactic
astrophysics. I will give a brief overview of the several possible quenching causes and physical
processes that have been proposed so far, ranging from feedback from black hole accretion and
starburst activity, to effects associated with the large scale environment in which galaxies live.
Although most of these mechanisms and causes play a role in different classes of galaxies and
at different epochs, multi-band observations are providing growing evidences that just a few of
them play the key, dominant role.
I will conclude by providing prospects for further investigating these aspects and tackling open
questions with the next generation of observing facilities.

Abstract
Abstract
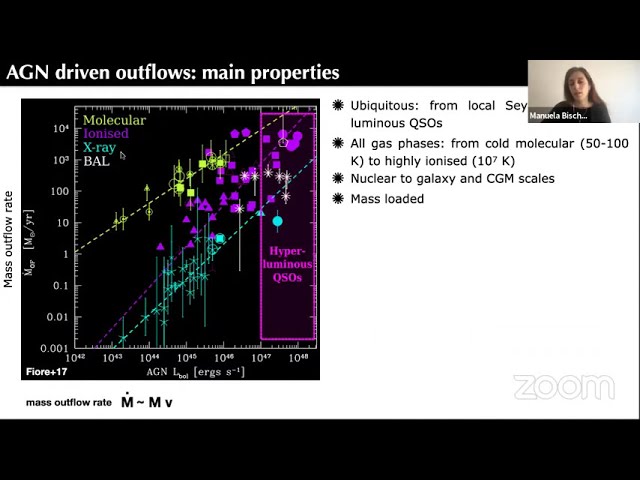
This talk will be dedicated to luminous (LBol~1E47 erg/s),
high-redshift quasars, which are ideal targets to investigate (i) feedback
from SMBHs, and (ii) the early growth phases of giant galaxies. I will
present evidence of SMBH-driven outflows at all Cosmic epochs, back to
the early Universe. These outflows involve all gas phases (molecular,
neutral, ionised) and extend on nuclear to galactic and circum-galactic
scales. I will report on the first systematic study of the molecular gas
properties in the host-galaxies of the most luminous quasars, fundamental
to probe the impact of SMBH feedback on the host-galaxy evolution. I will
show that luminous quasars pinpoint high-density sites where giant galaxies
assemble, and I will discuss the major contribution of mergers to the final
galaxy mass. To this aim, I will present a wealth of multi-wavelength (UV
to sub-millimeter) observations from the WISE/SDSS hyper-luminous quasars
survey at z~2-5 (WISSH), and recent results from the ESO large program
XQR-30, the Ultimate X-SHOOTER Legacy Survey of Quasars at the Reionization
epoch.
Abstract
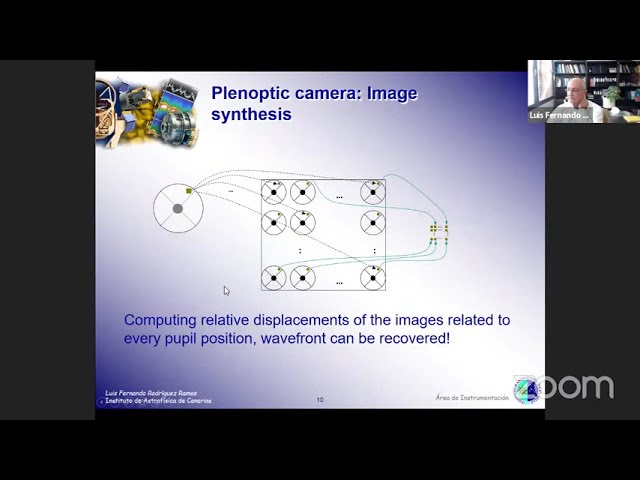
An original method for measuring the atmospheric turbulence is described, capable of even measuring the tip-tilt, which normally requires a dedicated natural star and nowadays defines the practical limit of the adaptive optics technique. The method is based in the illumination of a wide area of the Sodium Layer, and to use their inhomogeneities as a reference. Sevaral analysis and simulation results will be presented.
Zoom link:
https://rediris.zoom.us/j/87053930312
Enlace youtube: https://youtu.be/c1TCdt_-S_o
« Newer 1 | 2 Older » Last >>
Próximas charlas
- Quantum Simulators for the Cosmos: From Confining Strings to the Early UniverseDr. Enrique Rico OrtegaThursday December 4, 2025 - 10:30 GMT (GTC)
- Colloquium by Junbo ZhangDr. Junbo ZhangThursday December 11, 2025 - 10:30 GMT (Aula)