Found 17 talks width keyword galactic nuclei

Abstract
There is increasing speculation that quasars are intimately linked to the evolution of their host galaxies. Not only are they triggered as galaxies build up mass through gas accretion, but they also have the potential to drive massive outflows that can directly affect galaxy evolution by heating the gas and expelling it from galaxy bulges. However, there remain considerable uncertainties about how, when and where quasars are triggered as galaxies evolve, and the true energetic significance for the quasar-induced outflows and their acceleration mechanism have yet to be established. In this talk I will present new Gemini, VLT, Spitzer and Herschel results on samples of luminous AGN in the local Universe which provide key information on the triggering mechanisms for quasars and physics of their outflows.

Abstract
Luminous Infrared Galaxies (LIR=10^11-10^12Lsun) have star formation rates in the range of ~20-200Msun/yr. In the local Universe ~50% LIRGs show AGN or AGN/SB composite nuclear activity from optical spectroscopy. We decompose Spitzer/IRS 5-35micron spectra of a complete sample of 50 local (d<75Mpc) LIRGs using SB and AGN clumpy torus model templates. We derive a mid-IR AGN detection rate in our sample of local LIRGs of 50%. We also compare the continuum mid-IR AGN detection with other indicators in the mid-IR, optical and X-rays. We estimate for the first time the AGN bolometric contribution to the IR luminosity of the galaxies in local LIRGs. We find that one-third of local LIRGs have LAGN(bol)/LIR>0.05, with only ~10% having a significant contribution LAGN(bol)/LIR>0.25. This is in line with results of Nardini et al. (2010) that only at LIR>3x10^12Lsun the AGN starts dominating bolometrically the IR luminosity in the majority of the systems.

Abstract
I will present new mid-infrared imaging data for a sample of ~20 nearby Seyfert galaxies obtained with T-ReCS and MICHELLE on the Gemini Telescopes at subarcsecond resolution. Our aim is to compare the properties of Type-1 and Type-2 Seyfert tori using clumpy torus models and a Bayesian approach to fit the infrared nuclear spectral energy distributions (SEDs). These dusty tori have physical sizes smaller than 10 pc radius, as derived from our fits. Unification schemes of AGN account for a variety of observational differences in terms of viewing geometry. However, we find evidence that strong unification may not hold, and that the immediate dusty surroundings of Type-1 and Type-2 Seyfert nuclei are intrinsically different. The Type-2 tori studied here are broader, have more clumps, and these clumps have lower optical depths than those of Type-1 tori. The larger the covering factor of the torus, the smaller the probability of having direct view of the AGN, and vice-versa. In our sample, Seyfert 2 tori have larger covering factors and smaller escape probabilities than those of Seyfert 1. Thus, on the basis of the results presented here, the classification of a Seyfert galaxy as a Type-1 or Type-2 depends more on the intrinsic properties of the torus rather than on its mere inclination, in contradiction with the simplest unification model.
Abstract
Spectral energy distributions (SEDs) of the central few tens of parsec region of some of the nearest active galactic nuclei (AGN) are presented. Peering into the nucleus at these scales, it is found that the intrinsic shape of the spectral energy distribution of an AGN and inferred bolometric luminosity largely depart from those currently on use, mostly extracted from low resolution data. The shape of the SED is different and the AGN luminosities can be overestimated by up to two orders of magnitude if relying on IR satellite data.Although the shape of these SEDs are currently limited by the availability of high angular resolution data beyond ~20 μ, a prediction from this work is that a major contribution from cold dust below 100 K to these cores is not expected. Over the nine orders of magnitude in frequency covered by these SEDs, the power stored in the IR bump is by far the most energetic fraction of the total energy budget in these cores, accounting for more than 70% of the total.

Abstract
I will present grid-adaptive computational studies of both magnetized and unmagnetized jet flows, with significantly relativistic bulk speeds, as appropriate for AGN jets. Our relativistic jet studies shed light on the observationally established classification of Fanaroff-Riley galaxies, where the appearance in radio maps distinguishes two types of jet morphologies. We investigate how density changes in the external medium can induce one-sided jet decelerations, explaining the existence of hybrid morphology radio sources. Our simulations explore under which conditions highly energetic FR II jets may suddenly decelerate and continue with FR I characteristics. In a related investigation, we explore the role of dynamically important, organized magnetic fields in the collimation of the relativistic jet flows. In that study, we concentrate on morphological features of the bow shock and the jet beam, for various jet Lorentz factors and magnetic field helicities. We show that the helicity of the magnetic field is effectively transported down the beam, with compression zones in between diagonal internal cross-shocks showing stronger toroidal field regions. For the high speed jets considered, significant jet deceleration only occurs beyond distances exceeding hundred jet radii, as the axial flow can reaccelerate downstream to internal cross-shocks. This reacceleration is magnetically aided, due to field compression across the internal shocks which pinch the flow.
Abstract
The centers of massive galaxies are special in many ways, not least because all of them are believed to host supermassive black holes. Since the discovery of a number of relations linking the mass of this central black hole to the large scale properties of the dynamically hot component of its host galaxy (bulge) it has become clear that the growth of the central black hole is intimately connected to the evolution of its host galaxy. However, for bulge-less galaxies, the situation is much less clear. Interestingly, these galaxy often host star clusters in their nuclei, and unlike black holes, these nuclear star clusters provide a visible record of the accretion of stars and gas into the nucleus. I will present my ongoing projects on nuclear star clusters that aim to understand their formation process and might give a hint on how black holes get to the centers of galaxies.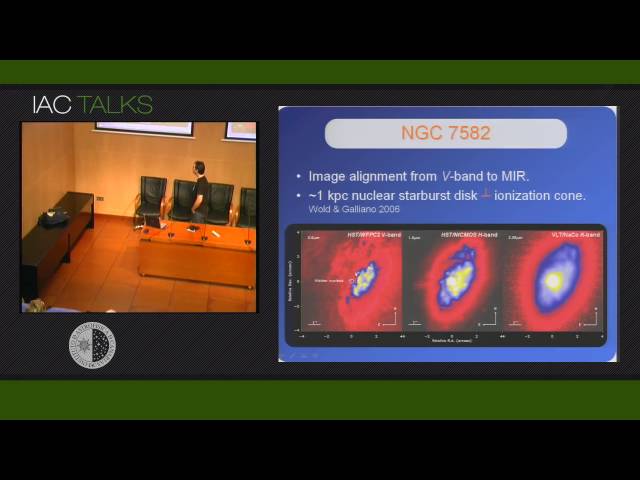
Abstract
Starbursts and AGNs are frequently coupled in the central kiloparsecs of Seyfert galaxies, where molecular gas plays a critical role in fueling nuclear starburst activity and feeding the central black hole. Unveiling the dusty nuclear regions with high-spatial resolution techniques in the near-infrared (NIR) permits us to disentangle the AGN and the stellar clusters, characterizing both sources separately. In this context, a small sample of nearby galaxies have been observed with VLT/NaCo adaptive optics in the NIR. These observations were completed with similar high-spatial resolution data in the mid-infrared (VLT/VISIR), optical (HST) and radio wavelengths (VLA). A new alignment for the starburst galaxy NGC 253 was found based on NIR and radio data, due to the high-spatial resolution in both spectral regions, finding NIR counterparts for 8 known radio sources. It is remarkable the lack of any optical or IR counterpart for the radio core, proposed as a low luminosity AGN, which presents an IR-to-radio emission ratio similar (or even lower) than Sgr. A*. Using the high-spatial resolution aligned dataset from optical-IR to radio wavelengths we derived a representative spectral energy distribution (SED) based on 37 young dust embedded clusters resolved in the inner 0.4 kpc. The template is characterized by a maximum at 20 μ and a gentle bump in the 1-2 μ range. These features, absent in lower spatial resolution templates, can be well reproduced by considering an important contribution of very young stellar objects to the IR, and are thus associated with hot dust surrounding the protostars. The average SED was then compared with the nuclear star forming regions found in the Seyfert 2/starburst galaxy NGC 7582.<< First « Newer 1 | 2 Older »
Upcoming talks
- Quantum Simulators for the Cosmos: From Confining Strings to the Early UniverseDr. Enrique Rico OrtegaThursday December 4, 2025 - 10:30 GMT (GTC)
- Colloquium by Junbo ZhangDr. Junbo ZhangThursday December 11, 2025 - 10:30 GMT (Aula)