Found 6 talks width keyword Magellanic Clouds

Abstract
The Magellanic Clouds (MCs) are the closest example of a three-body
interacting system composed of the Milky Way (MW), the Large Magellanic Cloud
(LMC), and the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC). Therefore, the unique opportunity
provided by their relative proximity allowed us to analyse with matchless detail
the dynamical and morphological evolution that a galaxy experience as a
consequence of the mutual gravitational interaction with its neighbors. In this
context, we performed a multi-faceted analysis, taking advantage of astrometric,
kinematics, and photometric data, with the main goal of unveiling the past
evolutionary path of the MCs and their intense interaction history. We tackled
this task by using two complementary approaches: (i) we adopted the properties
of the MCs star cluster (SC) system to get insights into their past evolution
and (ii) we probed the low-luminous regime of the outer regions of the MCs as
they are the most sensitive to recent or past tidal stripping events. I will
discuss the main outcomes up-to-date of this project and its future perspectives
in light of the new ongoing facilities.
Zoom link: https://rediris.zoom.us/j/81617686828?pwd=YUpBMXpobUpnYzlpUzluTGo1N2hRQT09
Meeing ID: 816 1768 6828
Passcode: 990310
https://youtu.be/q1b98yBliFQ
Abstract
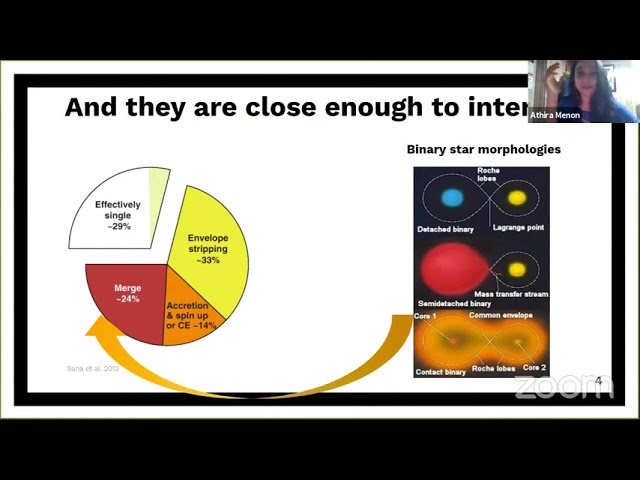
The majority of massive stars are born in close binary systems with orbital periods of a few days. At some point during their core-hydrogen burning phase, both members of these close binaries inevitably overflow their Roche lobes simultaneously and get bound by a common equipotential surface. The characteristics of this `contact phase’ will determine the fate of the binary system: whether the stars will merge on the main sequence or evolve further towards becoming potential gravitational-wave progenitors. Although data is available for several of these massive contact binaries in the Magellanic Clouds and the Milky Way, there has not been a dedicated study of these systems so far. In this talk, I will present the first set of detailed binary models covering a wide range of initial masses (20-80 Msun) and initial periods (0.6-2 days), focusing especially on the properties of the contact phase. We find that our models can approximately reproduce the period-mass ratio trend of the observed binaries although for the higher masses of our grid, our model predictions do not match with what is observed. We also find that those binary models which are in contact over nuclear timescales evolve towards equal masses before ultimately merging on the main sequence. This first study of massive contact binaries has allowed us to gain insights into the physics of massive contact systems and also provide reasonable predictions for the final fate of close massive binary stars.
Abstract
The Magellanic Clouds are the closest star forming galaxies, and their star formation histories can be derived in great details from color-magnitude diagrams reaching the oldest main sequence turnoffs. In the last several years, we have been conducting a wide research program on the Magellanic Clouds, including both photometry and spectroscopy, and have analysed the star formation history across both the Large and the Small Magellanic Clouds. This has revealed the nature of the stellar population gradients of these galaxies, as well as signatures that can possibly be related to their interaction history, among them and with the Milky Way.

Abstract
The fate of ionizing radiation from massive stars has fundamental consequences on scales ranging from the physics of circumstellar disks to the ionization state of the entire universe. On galactic scales, the radiative feedback from massive stars is a major driver for the energetics and phase balance of the interstellar medium in star-forming galaxies. While even starburst galaxies appear to be largely optically thick in the Lyman continuum, ionization-parameter mapping shows that significant populations of HII regions within galaxies are optically thin, powering the diffuse, warm ionized medium. I will discuss our multi-faceted work to clarify our understanding of radiative feedback in star-forming galaxies from the Magellanic Clouds to starbursts.

Abstract
Asymptotic Giant Branch (AGB) stars are a principal source of gas and dust input into the interstellar medium, being an important driver of chemical evolution in galaxies. Rubidium is a key element to distinguish between high mass (~4-8 M⊙) AGB stars and low mass (~1-4 M⊙) AGBs - high mass AGBs are predicted to produce a lot of rubidium as a consequence of the genuine nucleosynthetic processes (the s-process) that characterise these stars. The Magellanic Clouds (MCs) offer a unique opportunity to study the stellar evolution and nucleosynthesis of AGB stars in low metallicity environments where distances (and so the star's luminosity) are known. We present the discovery of extragalactic rubidium-rich AGB stars in the MCs confirming that the more massive AGB stars are generally brighter than the standard adopted luminosity limit (Mbol~-7.1) for AGB's. In addition, massive MC-AGBs are more enriched in Rb than their galactic counterparts, as it is qualitatively predicted by the present theoretical models; the Rb over-abundance increase with increasing stellar mass and with decreasing metallicity. However, present theoretical models are far from matching the extremely high Rb overabundances observed.
Abstract
I will present results from a survey of the star formation properties of nearby galaxies, using H alpha narrow-band imaging. The first half of the talk will cover the `expected' results of such a survey: how total star formation rates depend on galaxy morphology, the contribution of different types to the global star formation activity per unit volume of the nearby Universe, constraints on star formation histories, and indications of how stellar mass has been assembled in disks from the spatial distributions of young and old stars. The second half will look at some less expected spin-offs, including some surprising facts about the Magellanic Clouds, and new findings on progenitors of core-collapse supernovae.« Newer Older »
Upcoming talks
- Quantum Simulators for the Cosmos: From Confining Strings to the Early UniverseDr. Enrique Rico OrtegaThursday December 4, 2025 - 10:30 GMT (GTC)
- Colloquium by Junbo ZhangDr. Junbo ZhangThursday December 11, 2025 - 10:30 GMT (Aula)