Found 7 talks width keyword intergalactic medium

Abstract
We present the extended data release of the Calar Alto Legacy Integral Field Area (CALIFA) survey (eDR). It comprises science-grade quality data for 895 galaxies obtained with the PMAS/PPak instrument at the 3.5 m telescope at the Calar Alto Observatory along the last 12 years, using the V500 setup (3700-7500Å, 6Å/FWHM) and the CALIFA observing strategy. It includes galaxies of any morphological type, star-formation stage, a wide range of stellar masses ( ∼10^7-10^12 Msun), at an average redshift of ∼0.015 (90\% within 0.005 < z <0.05). Primarily selected based on the projected size and apparent magnitude, we demonstrate that it can be volume corrected resulting in a statistically limited but representative sample of the population of galaxies in the nearby Universe. All the data were homogeneously re-reduced, introducing a set of modifications to the previous reduction. The most relevant is the development and implementation of a new cube-reconstruction algorithm that provides an (almost) seeing-limited spatial resolution (FWHM PSF ∼1.0"). Furthermore we present the analysis performed using the pyPipe3D pipeline for these dataset. We include a description of (i) the analysis performed by the pipeline, (ii) the adopted datamodel for the derived spatially resolved properties and (iii) the catalog of integrated, characteristics and slope of the radial gradients for a set of observational and physical parameters derived for each galaxy. All these data has been distributed through the following webpage: http://ifs.astroscu.unam.mx/CALIFA_WEB/public_html/
Abstract
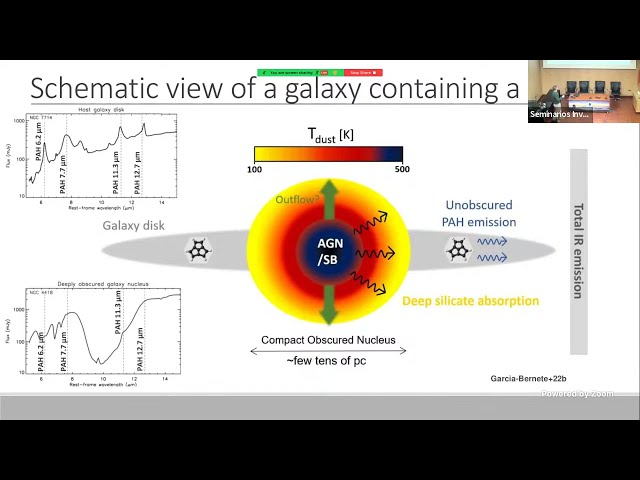
Finally, I will summarise our ongoing JWST work within the GATOS (Galactic Activity, Torus and Outflow Survey) collaboration. In particular, I will focus on our recent study about the survival of PAH molecules in AGN-driven outflows.

Abstract
Galaxies and the dark matter halos in which they reside are intrinsically connected. That relationship holds information about key processes in galaxy and structure formation. In this talk, I will consider how the galaxy-halo connection depends on position within the cosmic web - the familiar decomposition of large-scale structure in filaments, knots and voids. Simulations demonstrate the various ways in which the cosmic web modulates the growth and dynamics of halos. The extent to which the cosmic web impacts on galaxies is more difficult to establish. For example, galaxies might be sensitive only to the evolution of the host halo, in which case any effect of the cosmic web on galaxies is secondary, and can be inferred from the halo's history. There is evidence, however - from simulations and observations - that the cosmic web also impacts on the evolution of galaxies via the effect it has on the broader gas ecosystem in which they are embedded, as well as through "pre-processing" effects on group scale. So, how should we think of the cosmic web in its role as a transformative agent of galaxies? And what physical processes can we convincingly constrain from observations and simulations? In this talk I highlight recent work that addresses these questions.
Abstract
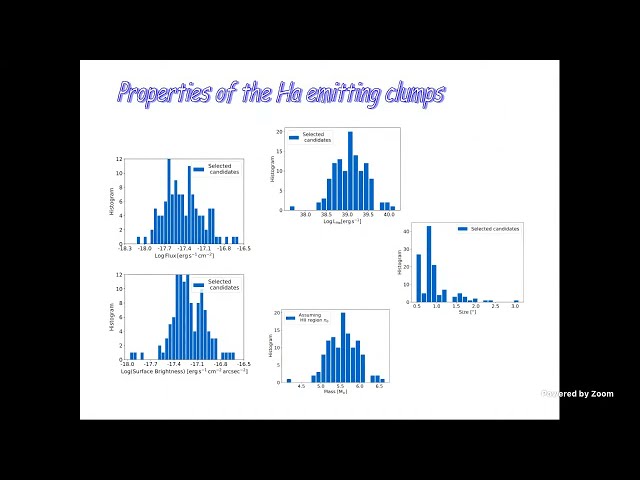
With the aim of detecting cosmological gas accretion onto galaxies of the local Universe, we examined the Ha emission in the halo of the 164 galaxies in the field of view of MUSE-Wide (Urrutia+19) with observable Ha (redshift < 0.42). An exhaustive screening of the Ha images led us to select 118 reliable Ha emitting gas clouds. To our surprise, around 38 % of the time the Ha line profile shows a double peak centered at the rest-frame of the corresponding galaxy. We have explored several physical scenarios to explain this Ha emission, among which accretion disks around rogue intermediate mass black holes (IMBHs) fit the observations best. I will describe the data analysis (to discard, e.g, instrumental artifacts and high redshift interlopers), the properties of the Ha emitting clumps (their fluxes, peak separation, and spatial distribution with respect to the central galaxy), and the arguments leading to the IMBH hypothesis rather than other alternatives (e.g., cosmological gas, expanding bubbles, or shocks in the circum galactic medium).
Abstract
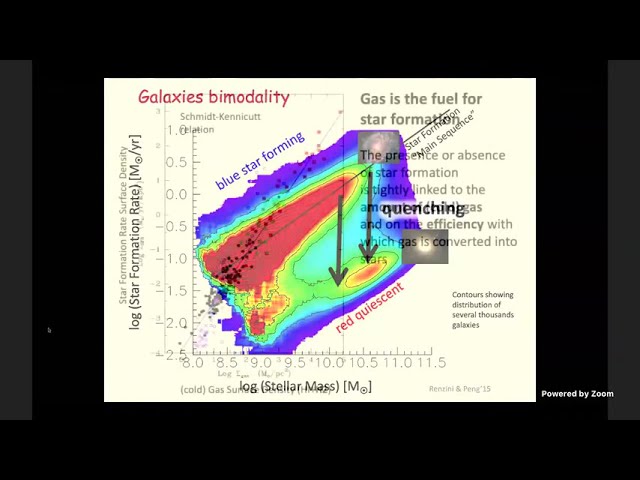
In the local universe most of the stellar mass is in passive galaxies, where star formation is
absent or at very low levels. Understanding what are the mechanisms that have been
responsible for quenching star formation in galaxies, and transforming them into passive,
quiescent systems, is one of the main observational and theoretical challenges of extragalactic
astrophysics. I will give a brief overview of the several possible quenching causes and physical
processes that have been proposed so far, ranging from feedback from black hole accretion and
starburst activity, to effects associated with the large scale environment in which galaxies live.
Although most of these mechanisms and causes play a role in different classes of galaxies and
at different epochs, multi-band observations are providing growing evidences that just a few of
them play the key, dominant role.
I will conclude by providing prospects for further investigating these aspects and tackling open
questions with the next generation of observing facilities.
Abstract
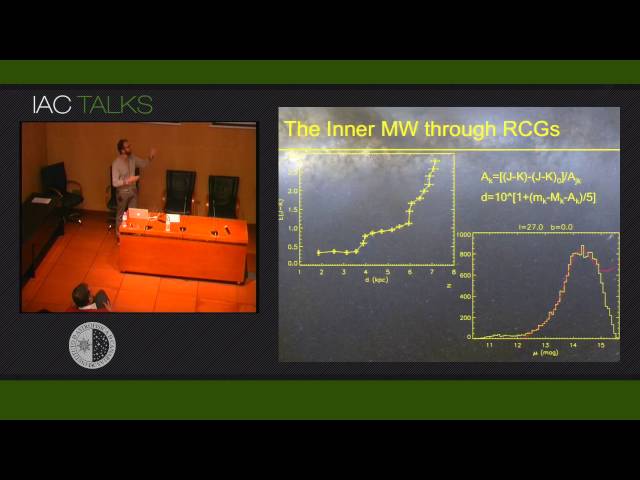
Abstract: The study of the structure of our Galaxy, particularly its inner disc, has always been hindered by two factors: interstellar extinction dims even the brightest stars at optical wavelengths and the high source density prevents us, as the proverbial trees, to see the big galactic picture.

Abstract
Large-scale outflows from galaxies are a crucially important yet poorly understood aspect of galaxy evolution. They redistribute gas and metals into the IGM, regulate star formation, affect the galaxy luminosity function and mass-metallicity relation, etc. Unfortunately, their detailed context in galaxy evolution is difficult to understand: locally, they are identified and studied in heterogeneous manners, while we have only recently begun to study them on cosmological scales and then only in known bright, starbursting galaxies. I will discuss increasing evidence that the so-called ultra-strong MgII intervening quasar absorbers select galactic superwinds over a large range of redshift in a manner independent of luminosity. As superwinds cover a small fraction of the sky at any epoch, only with recent huge quasar absorption lines surveys has it been possible to identify significant numbers of outflows in this manner. I will present new results from several of our studies -- including the measurement of the average SFR of their hosts using [O II] emission from SDSS composite spectra, WIYN, Gemini and WHT imaging of the superwind environments, Gemini/GMOS spectroscopy of superwind host galaxies, and VLT/UVES echellegrams of the absorption lines -- with the aim of understanding the nature of the outflows, their host galaxies, environments, and their evolution over cosmic time.« Newer Older »
Próximas charlas
- Colloquium by Junbo ZhangDr. Junbo ZhangThursday December 11, 2025 - 10:30 GMT (Aula)