Found 32 talks width keyword active galaxies

Thursday July 16, 2009
University of California Observatories, Lick Observatory, USA
Abstract
AEGIS (All-wavelength Extended Groth strip International Survey: aegis.ucolick.org) is on-going survey that opens up new views of the development of galaxies and AGN's at redshifts z about 1. AEGIS is panchromatic like GOODS, with coverage ranging from X-ray to radio, and nearly as deep but more panoramic by covering a 4x larger region. Its backbone is the most Northern (accessible to the GTC) of the four fields of the DEEP2 Keck spectroscopic survey, which provides not only precision redshifts that yield reliable pairs, groups, and environments, but also internal kinematics and chemical abundances. After an overview of the DEEP and AEGIS surveys, I will share some recent highlights, including using a new kinematic measure for distant galaxies to track Tully-Fisher-like evolution; discovering metal poor, massive, luminous galaxies; finding ubiquitous galactic gas outflows among distant star forming galaxies; and exploring the nature of distant x-ray AGNs.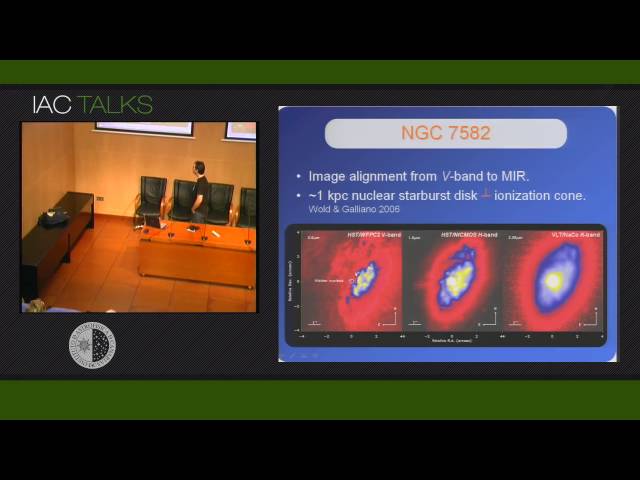
Thursday October 9, 2008
Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, Spain
Abstract
Starbursts and AGNs are frequently coupled in the central kiloparsecs of Seyfert galaxies, where molecular gas plays a critical role in fueling nuclear starburst activity and feeding the central black hole. Unveiling the dusty nuclear regions with high-spatial resolution techniques in the near-infrared (NIR) permits us to disentangle the AGN and the stellar clusters, characterizing both sources separately. In this context, a small sample of nearby galaxies have been observed with VLT/NaCo adaptive optics in the NIR. These observations were completed with similar high-spatial resolution data in the mid-infrared (VLT/VISIR), optical (HST) and radio wavelengths (VLA). A new alignment for the starburst galaxy NGC 253 was found based on NIR and radio data, due to the high-spatial resolution in both spectral regions, finding NIR counterparts for 8 known radio sources. It is remarkable the lack of any optical or IR counterpart for the radio core, proposed as a low luminosity AGN, which presents an IR-to-radio emission ratio similar (or even lower) than Sgr. A*. Using the high-spatial resolution aligned dataset from optical-IR to radio wavelengths we derived a representative spectral energy distribution (SED) based on 37 young dust embedded clusters resolved in the inner 0.4 kpc. The template is characterized by a maximum at 20 μ and a gentle bump in the 1-2 μ range. These features, absent in lower spatial resolution templates, can be well reproduced by considering an important contribution of very young stellar objects to the IR, and are thus associated with hot dust surrounding the protostars. The average SED was then compared with the nuclear star forming regions found in the Seyfert 2/starburst galaxy NGC 7582.<< First « Newer 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 Older »
Upcoming talks
- TODAY: Lighting up the sky: What gamma rays reveal about supernova remnant shocks (and shocks in general)Dr. Marianne LemoineThursday November 13, 2025 - 10:30 GMT (Aula)
- Sensores difractivos de frente de onda Dr. Manuel Pérez CagigalFriday November 14, 2025 - 10:30 GMT (Aula)









