Found 9 talks width keyword winds
Abstract
Zoom: https://rediris.zoom.us/j/86826646040?pwd=UmpEZmdKYW90QUpVelFKZitzTzhKUT09
Meeting ID: 868 2664 6040
Passcode: 610738

Abstract
Massive stars (at least eight times as massive as the Sun) possess strong stellar winds driven by radiation. With the advent of the so called MiMeS collaboration, an increasing number of these massive stars have been confirmed to have global magnetic fields. Such magnetic fields can have significant influence on the dynamics of these stellar winds which are strongly ionized. Such interaction of the wind and magnetic field can generate copious amount of X-rays, they can spin the star down, they can also help form large scale disk-like structures. In this presentation I will discuss the nature of such radiatively-driven winds and how they interact with magnetic fields.
https://youtu.be/jKmifm17bno

Abstract
Following Cowling's anti-dynamo theorem of 1933, there was a long period during which the very existence of dynamos was unclear. Even with the emergence of three dimensional simulations in the late 1980s, people were careful to distinguish true dynamos from just some sort of amplification. Meanwhile, we know of many examples of true dynamos - not only from simulations, but also from several laboratory experiments. Nevertheless, there are still problems, fundamental ones and also very practical ones. After all, we are really not sure how the solar dynamo works. Today, global three-dimensional simulations seem to have an easier time to reproduce the behaviors of superactive stars, but not really the group of inactive stars, to which also the Sun belongs. The Sun itself may actually be special; it has so well defined cycles and it is at the brink of becoming very different. Theoretically, slightly slower rotators should have antisolar rotation, but it is possible that some of those stars never become that slow if stellar breaking ceases for some reason. Sun and starspots are very evident indicators of solar and stellar activity. Their formation is also not well understood. Polarimetry reveals their magnetic helicity, which can be detected even with the solar wind.

Abstract
The new generation of spectrometers designed for extreme precision radial velocities enable correspondingly precise stellar spectroscopy. It is now fruitful to theoretically explore what the information content would be if stellar spectra could be studied with spectral resolutions of a million or more, and to deduce what signatures remain at lower resolutions. Hydrodynamic models of stellar photospheres predict how line profiles shapes, asymmetries, and convective wavelength shifts vary from disk center to limb. Corresponding high-resolution spectroscopy across spatially resolved stellar disks is now practical using differential observations during exoplanet transits, thus enabling the testing of such models. A most demanding task is to understand and to model spectral microvariability toward the radial-velocity detection of also low-mass planets in Earth-like orbits around solar-type stars. Observations of the Sun-as-a-star with extreme precision spectrometers now permit searches for spectral-line modulations on the level of a part in a thousand or less, feasible to test against hydrodynamic models of various solar features.
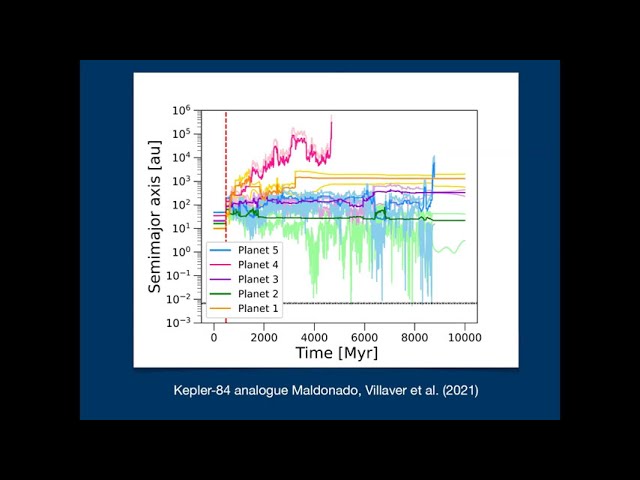
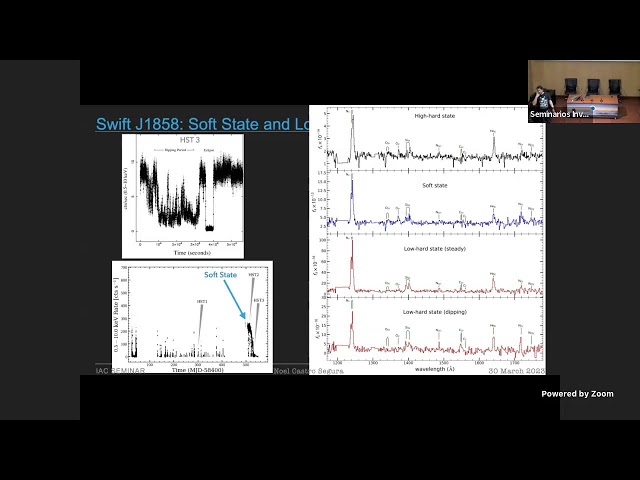
Abstract
Planetary systems have been found systematically orbiting main sequence stars and red giants. But the detection of planets per se during the white dwarf phase has been more elusive with only 3 systems. We have, however, ample indirect evidence of the existence of planetary debris around these systems in the form of material acreted onto the white dwarf, disks and even planetesimals. In this talk, I will review how we can put the pieces together: how we can reconcile what we see in white dwarfs with what we can infer regarding the evolution of planetary systems from the main sequence phase.
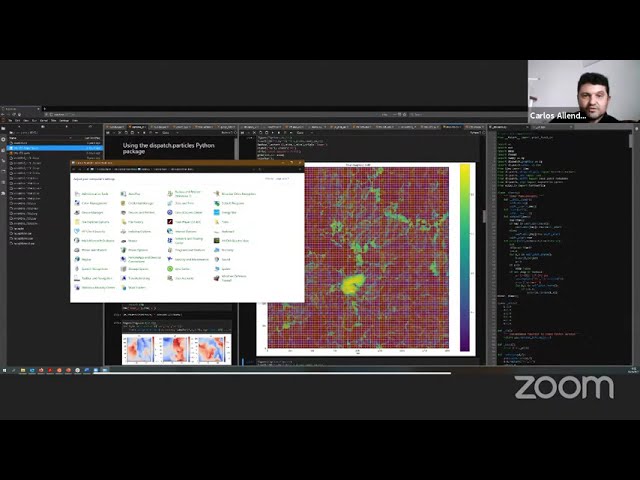
Abstract
(This seminar is organized by the IAU G5 commission on stellar and planetary atmospheres)
Task-based computing is a method where computational problems are split
into a large number of semi-independent tasks (cf.
2018MNRAS.477..624N). The method is a general one, with application not
limited to traditional grid-based simulations; it can be applied with
advantages also to particle-based and hybrid simulations, which involve
both particles and fields. The main advantages emerge when doing
simulations of very complex and / or multi-scale systems, where the
cost of updating is very unevenly distributed in space, with perhaps
large volumes with very low update cost and small but important regions
with large update costs.
Possible applications in the context of stellar atmospheres include
modelling that covers large scales, such as whole active regions on the
Sun or even the entire Sun, while at the same time allows resolving
small-scale details in the photosphere, chromosphere, and corona. In
the context of planetary atmospheres, models of pebble-accreting hot
primordial atmospheres that cover all scales, from the surfaces of
Mars- and Earth-size embryos to the scale heights of the surrounding
protoplanetary disks, have already been computed (2018MNRAS.479.5136P,
2019MNRAS.482L.107P), and one can envision a number of applications
where the task-based computing advantage is leveraged, for example to
selectively do the detailed chemistry necessary to treat atmospheres
saturated with evaporated solids, or to do complex cloud chemistry
combined with 3-D radiative transfer.
In the talk I will give a quick overview of the principles behind
task-based computing, and then use both already published and still
on-going work to illustrate how this may be used in practice. I will
finish by discussing how these methods could be applied with great
advantage to problems such as non-equilibrium ionization, non-LTE
radiative transfer, and partial redistribution diagnostics of spectral
lines.
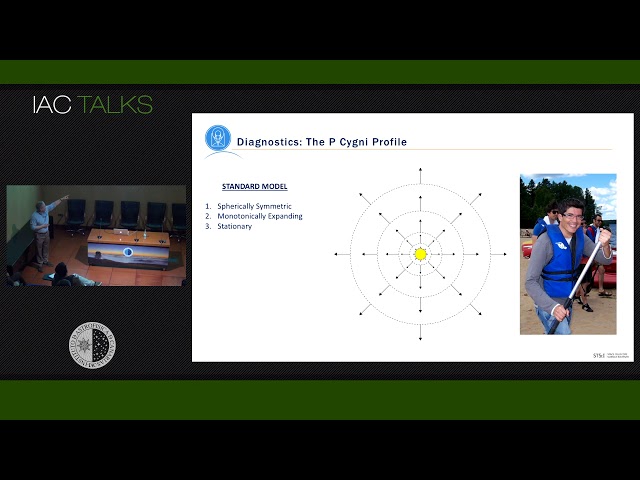
Abstract
The growth of astrophysical understanding typically results fromthe constructive interplay between theoretical ideas andobservational insights, with each mode of exploration drivingprogress at different times. The result is invariably a morecomplicated but richer picture of the phenomenon than initiallyenvisaged, as well as deeper appreciation of the behavior ofcomplex systems.In this talk, I will use the development of our understanding ofthe structure of outflows from massive O- and B-type stars toillustrate this collaborative “dance”. Starting from the smooth,spherically symmetric models for radiatively driven windsdeveloped in the late 1960s, our view of these outflows hasevolved to include the growth of inhomogeneities on a variety ofspatial scales. Explanations for the origin of this structure havein turn prompted the realization that non-radiative processesmust also shape the emergence of the wind from the stellarphotosphere. Consequently, O- and B-type stars are morecomplicated – and interesting! – objects than often thought.While many fruitful avenues of research remain to be explored,the current paradigm provides a (mostly) self-consistent pictureof massive stars and their outflows.

Abstract

Abstract
Massive stars lose mass through powerful, radiatively driven stellar winds. Building on the original "CAK" model for steady, spherical winds driven by line-scattering, this talk will review recent research on the multi-faceted nature of such wind mass loss under varied conditions, for example due to rapid rotation, magnetic channeling, binary interaction, or a luminosity near the Eddington limit. An overall theme is that wind mass loss can in this way lead to a wide variety of astrophysical phenomena, including bipolar nebulae, massive star magnetospheres, colliding winds or compact companion accretion, and luminous blue variable eruption. The discussion here will summarize these with an emphasis on their varied observational signatures.
« Newer Older »
Upcoming talks
- Quantum Simulators for the Cosmos: From Confining Strings to the Early UniverseDr. Enrique Rico OrtegaThursday December 4, 2025 - 10:30 GMT (GTC)
- Colloquium by Junbo ZhangDr. Junbo ZhangThursday December 11, 2025 - 10:30 GMT (Aula)