Recent Talks
List of all the talks in the archive, sorted by date.
Abstract
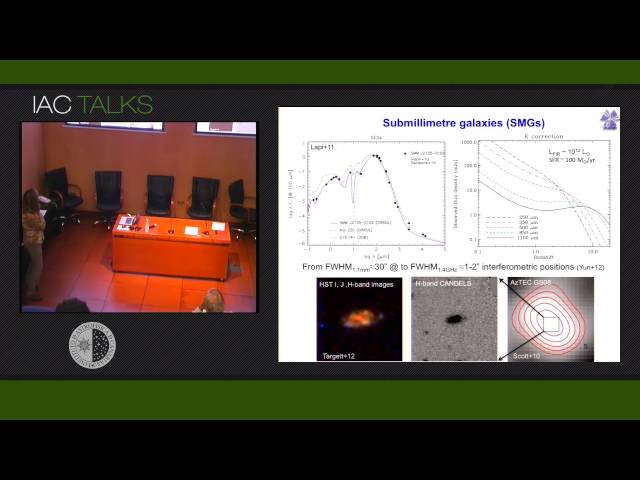
AzTEC is a sensitive bolometer camera that, coupled with 10-15m-class sub-mm telescopes, has mapped more than 3 sq. deg of the extragalactic sky to depths between 0.7 and 1.1 mJy at 1.1mm, prior to its current installation and operation on the 32m Large Millimeter Telescope (LMT). These extragalactic surveys targeted towards blank-fields and biased high-z environments alike have allowed us to identify regions of the sky where submillimeter galaxies (SMGs), powerful obscured starbursts at high-redshifts (z>1), cluster, and possibly mark the potential wells of accelerated galaxy-formation that will eventually form massive clusters. In this talk I will describe the evidence we have found for these overdense regions of massive galaxies, their structure and possible interpretation, as well as the follow-up observations we are carrying out with the LMT nowadays.
Abstract
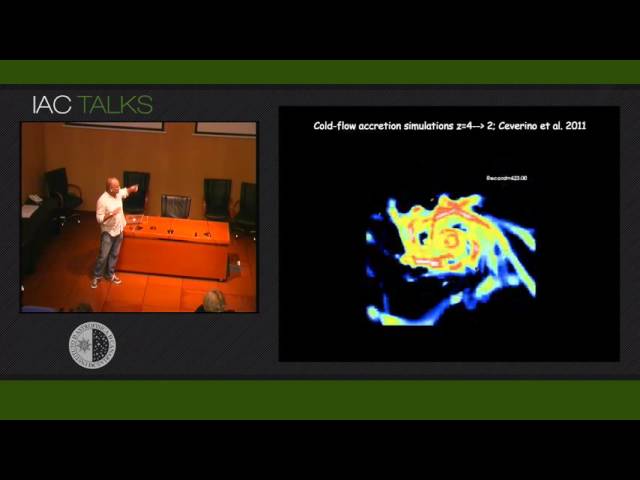
The direct accretion of pristine gas streams is predicted to be the main mode of galaxy disk growth in the early universe (cold-flows). We (think we) have discovered this physical process at work in the local Universe. The finding is one of the outcomes of our in-depth study of local extremely metal poor (XMP) galaxies. I will explain the main observational properties of XMPs, in particular, their tendency to have cometary or tadpole morphology, with a bright peripheral clump (the head) on a faint tail. Tadpole galaxies are rare in the nearby universe but turn out to be very common at high redshift, where they are usually interpreted as disk galaxies in early stages of assembling. We have found the heads to be giant HII regions displaced with respect to the rotation center, with the galaxy metallicity being smallest at the head and larger elsewhere. The resulting chemical abundance gradient is opposite to the one observed in local spirals, and suggests a recent gas accretion episode onto the head. Thus, local XMP galaxies seem to be primitive disks, with their star formation sustained by accretion of external metal poor gas. I will argue how the same mechanism may be driving the star formation in many other local galaxies. Ongoing observational projects to confirm these findings and conjectures will be briefly mentioned.

Abstract
El pasado 6 de Junio de 2012 tuvo lugar el ultimo transito de Venus frente al Sol del siglo XXI, visible desde la Tierra. Los transitos de Venus han sido observados historicamente proporcionando informacion sobre del tamaño del Sol o la distancia Tierra-Sol. Hoy en dia, con la explosion del campo de exoplanetas, y la cada vez mas cercana deteccion de planeta potencialmente habitables, el transito de Venus ofrecia una oportunidad unica de medir el espectro de transmision de un planeta rocoso. Con esta intencion, en el IAC se diseño intrumentacion especifica y se realizo una expedicion a Australia, al tiempo que se observaba tambien desde telescopios en Chile. Este es un resumen de las peripecias personales, intrumentales y cientificas que suponen este tipo de retos, y que llevaron a la *posible* deteccion del dioxido de carbono en la atmosfera de Venus.
Abstract
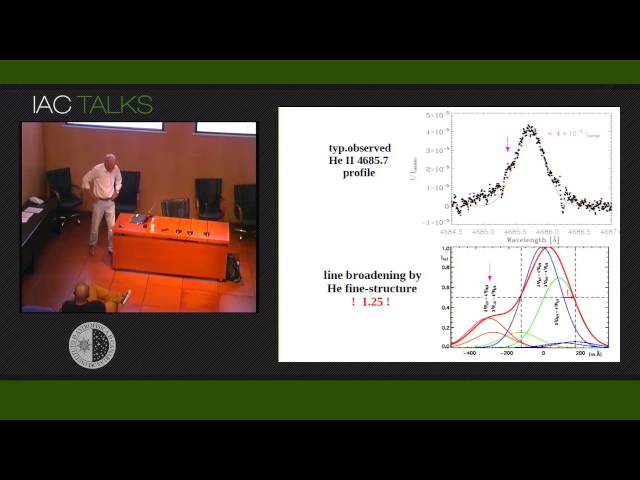
The strongest He II emission in the visible spectral range, at 4686 A, is for the first time observed at a spectral resolution sufficiently high for a line profile analysis in quiescent solar prominences. It is found that the He II line width exceeds by far that of emissions from neutral helium which, in turn, show significant differences between the triplet and singlet emissions. The width hierarchy from singlet over triplet to He II suggests an origin in increasingly hot plasma of the transition to hot coronal surroundings. The ratio of integrated line emission is found to be independent on the prominence size suggesting that each fine-structure has its own transition to hot coronal gas in between the treads.

Abstract
Over the past decade there has been a growing body of evidence for a closely regulated balance of heating and cooling of the intracluster medium in the cores of clusters. I will review this evidence with a particular emphasis on the role of cold gas and dust as the fuel for AGN feedback that dominates these systems.
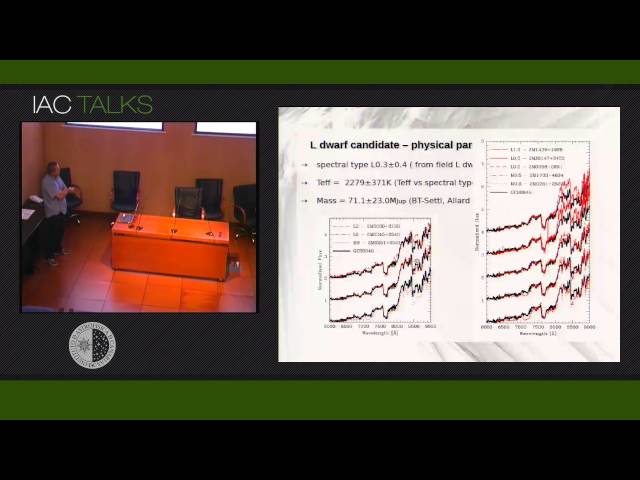
Abstract
Fundamental properties of brown dwarfs, such as luminosity and effective temperature, evolve with age. Large samples of spectroscopically-confirmed substellar objects with well-determined ages and distances are needed to constrain those parameters. We are embarked in a spectroscopic follow-up with GTC/OSIRIS of low-mass member candidates selected in several open clusters to constrain their membership. Here I will present the first L dwarf member in Praesepe confirmed by photometry, astrometry, and spectroscopy. We derived an optical spectral type of L0.3+/-0.4 and a mass placing it at the hydrogen-burning boundary. Considering the measured equivalent width of the gravity-sensitive sodium doublet, and the derived membership probability of ~80% or higher, we conclude that this object is likely to be a true member of Praesepe, with evidence of being a binary system.
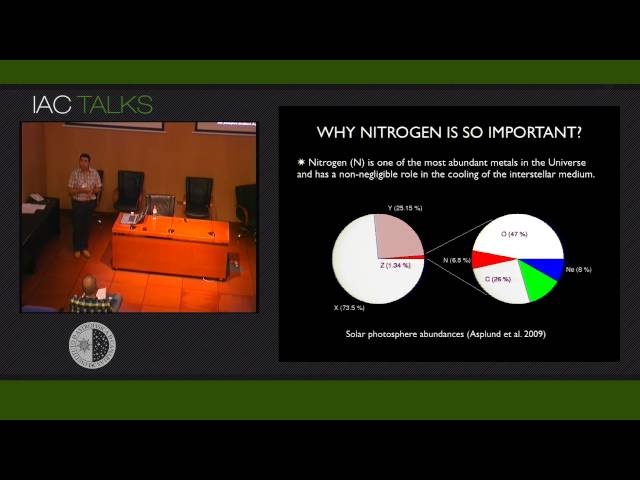
IAA
Abstract
Chemical abundances derived using emission-line spectra in ionized gaseous nebulae are between the most useful properties that can be derived to understand the evolution of galaxies from the local Universe up to very high redshifts. Since nitrogen is one of the most abundant metals in the gas-phase of galaxies and its emission-lines can be measured many times instead of those emitted by oxygen, it is important to be aware of the implications of the variations in the nitrogen-to-oxygen ratio for the derivation of total metallicity and what are the advantages of using this abundance ratio to derive other evolutionary properties in different emission-line objects. We will also see the utility of some observational techniques, such integral field spectroscopy, to disentangle between different processes implied in the excess of observed nitrogen as derived from integrated observations.
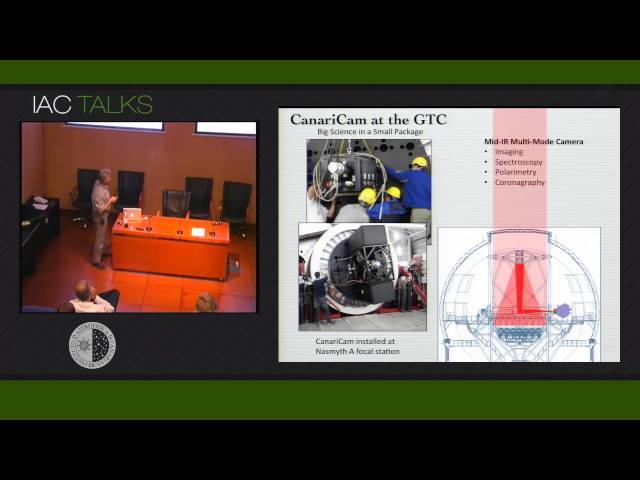
Abstract
CanariCam is the GTC multi-mode mid-IR camera developed by the University of Florida. CanariCam commissioning began in earnest in
mid-2012, and is still in progress. However, during that time it was also possible to begin science observations. After commenting on
the current status of CanariCam, I will present some highlights of these early science observations, with an emphasis on those of protoplanetary disks. These data are still being analyzed and interpreted, so my comments will be preliminary. However, they demonstrate that CanariCam is an outstanding instrument that can provide valuable insight into a variety of astrophysical processes. CanariCam's polarimetric mode is particularly unique, and I will show intriguing science results that may indicate the magnetic-field distribution
in a YSO outflow and in massive disks and their environments. I am presenting these results on behalf of the CanariCam Science Team, many of whom have contributed significantly to the early progress with CanariCam.
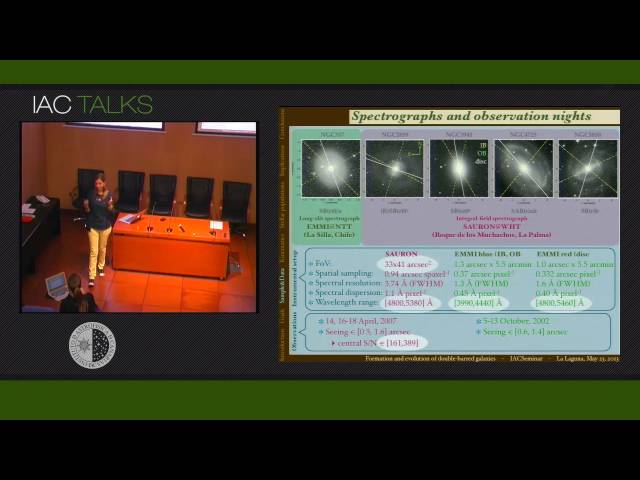
Abstract
The general picture of galaxy formation and evolution includes bars as the main drivers of the internal secular processes affecting the lifetime of disc galaxies. Bars are present in a very high fraction of all the spiral galaxies found at different redshifts, and the processes inducing their formation or the effects they may have on their host galaxies are still under discussion. Particularly interesting is the case of double-barred galaxies: at least 20% of all spirals have turned out to host not only one but two bars embedded in them. These two bars appear randomly oriented and independently rotating. The formation of such a double-barred system has been the goal of several numerical simulations and the results obtained so far can be roughly divided in two big groups: gas-rich and gas-free formation scenarios. In the same way a single bar does, double-bar systems might also promote gas inflow and contribute to the internal secular evolution. Moreover, they have also been proposed as a very efficient mechanism for the feeding of the active galactic nuclei.
All the previous theoretical hypothesis on the formation and evolution of double-barred galaxies have not been tested due to the lack of observational works focused on these systems. With this motivation, during my PhD I observed a sample of double-barred galaxies in order to fully analyse their kinematics and stellar populations. Among the most interesting results, it is important to highlight the discovery of the sigma-hollows, which are the only known kinematical signature of the presence of inner bars, or the fact that inner bars are younger and more metal-rich than their surrounding regions. In this talk I will present the whole work and discuss the results in the framework of the different formation scenarios and the role that these inner bars may be playing in the evolution of their host galaxies.
Abstract
En esta charla se abordarán herramientas de interés para el desarrollo de actividades en línea con equipos de trabajo ubicados es espacios geográficos diferentes. Se darán a conocer herramientas de utilidad para el trabajo en la nube, especialmente en aquellos casos en los que tenemos que contactar con personas ubicadas en espacios geográficos distintos.
Upcoming talks
No talks scheduled for the next days.