Found 111 talks archived in Telescopes and instrumentation
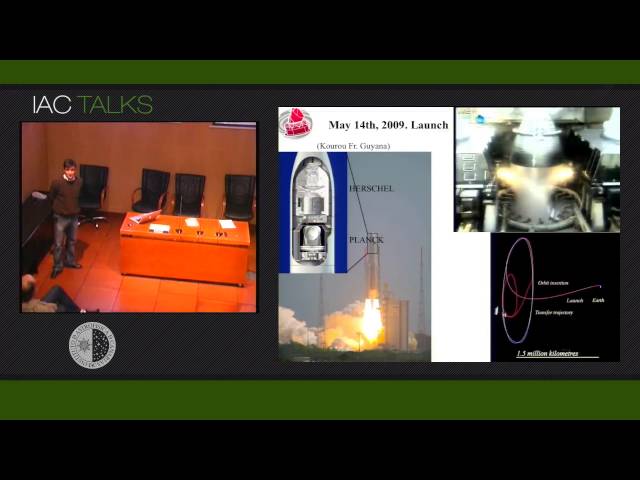
Abstract
The European Space Agency's Planck satellite was launched on 14 May 2009, and has been surveying the sky stably and continuously since 13 August 2009. Its performance is well in line with expectations, and it will continue to gather scientific data until the end of its cryogenic lifetime. I will present the first scientific results of the mission, which appeared as a series of 26 papers at the beginning of this year 2011, covering a variety of astrophysical topics. In particular, I will focus on the results on galactic diffuse emissions, as well as the first results on galaxy clusters detected by means of the Sunyaev-Zeldovich effect.

Abstract
Long Gamma-Ray Bursts (GRBs) are the most dramatic examples of massive stellar deaths, usually associated with supernovae (Woosley et al. 2006). They release ultra-relativistic jets producing non-thermal emission through synchrotron radiation as they interact with the surrounding medium (Zhang et al. 2004). Here we report observations of the peculiar GRB 101225A (the "Christmas burst"). Its gamma-ray emission was exceptionally long and followed by a bright X-ray transient with a hot thermal component and an unusual optical counterpart. During the first 10 days, the optical emission evolved as an expanding, cooling blackbody after which an additional component, consistent with a faint supernova, emerged. We determine its distance to 1.6 Gpc by fitting the spectral-energy distribution and light curve of the optical emission with a GRB-supernova template. Deep optical observations may have revealed a faint, unresolved host galaxy. Our proposed progenitor is a helium star-neutron star merger that underwent a common envelope phase expelling its hydrogen envelope. The resulting explosion created a GRB-like jet which gets thermalized by interacting with the dense, previously ejected material and thus creating the observed black-body, until finally the emission from the supernova dominated. An alternative explanation is a minor body falling onto a neutron star in the Galaxy (Campana et al. 2011).

Abstract
Las Cumbres Observatory Global Telescope is in the process of deploying a world-wide network of 1m and 40cm telescopes to facilitate studies in time-domain astronomy. I will describe the intended network, including the capabilities of the telescopes and instruments, the means for scheduling observations and controlling the telescopes, and the anticipated organization of the science collaborations that must develop in order to make best use of LCOGT's facilities.

Abstract
The success of the next generation of instruments for 8 to 40-m class telescopes will depend on the ability of Adaptive Optics (AO) systems to provide excellent image quality and stability. This will be achieved by increasing the sampling, wavelength range and correction quality of the wave front error in both spatial and time domains. The modern generation of AO wavefront sensor detectors started in the late nineties with the development of the CCD50 detector by e2v under ESO contract for the ESO NAOS AO system. With a 128x128 pixels format, this 8 outputs CCD runs at a 500 Hz frame rate with a readout noise of 7e-. A major breakthrough has been achieved with the recent development of the CCD220, also by e2v technologies. This 240x240 pixels 8 outputs EMCCD (CCD with internal multiplication) has been jointly funded by ESO and Europe under the FP6 programme. The CCD220 detector and the OCAM2 camera are now the most sensitive system in the world for advanced adaptive optics systems, offering an astonishing <0.2 e readout noise at a frame rate of 1500 Hz with negligible dark current. Extremely easy to operate, OCAM2 only needs a 24 V power supply and a modest water cooling circuit. This system will be extensively described in this talk. An upgrade of OCAM2 is foreseen to boost its frame rate to 2500 Hz, opening the window of XAO wavefront sensing for the ELT. Since this major success, new developments started in Europe. One is fully dedicated to Laser Guide Star AO for the ELT with an ESO involvment. The spot elongation from a LGS SH wavefront sensor induces an increase of the pixel format. Two detectors are currently developed by e2v. The NGSD will be a 672x672 pixels CMOS detector with a readout noise of 4e (goal 1e) at 700 Hz frame rate. The LGSD is a scaling of the NGSD with 1680x1680 pixels and 3 e readout noise (goal 1e) at 700 Hz frame rate. New technologies will be developed for that purpose: new CMOS pixel architecture, CMOS back thinned and back illuminated device, full digital outputs. In addition, the CMOS technology is extremely robust in a telescope environment. Both detectors will be used on the ELT, depending on the AO system considered. Additional developments also started for wavefront sensing in the infrared based on new breakthrough using ultra low noise Avalanche Photodiode (APD) arrays within the RAPID project. The latter should offer a 320x240 8 outputs 30 microns IR array, sensitive from 0.4 to 3.2 microns, with 2 e readout noise at 1500 Hz frame rate. First results of this project will be showed.
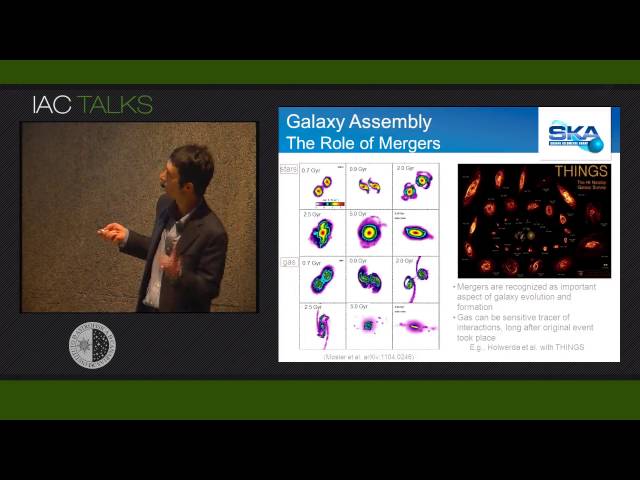
Abstract
The Square Kilometre Array is intended to be the centimeter- and meter-wavelength telescope for the 21st Century. Originally proposed as the "hydrogen telescope," the science case is now recognized to be much broader, and the SKA will address fundamental questions in astrophysics, physics, and astrobiology. The international science community has developed a set of Key Science Programs: (1) Emerging from the Dark Ages and the Epoch of Reionization; (2) Galaxy Evolution, Cosmology, and Dark Energy; (3) The Origin and Evolution of Cosmic Magnetism; (4) Strong Field Tests of Gravity Using Pulsars and Black Holes; and (5) The Cradle of Life & Astrobiology. I highlight how the SKA's Key Science Programs will be an integral component of the multi-wavelength, multi-messenger frontiers for astronomy and how the science pathfinding for the SKA is beginning now.
Abstract
The vision for the use of the WHT in the coming decade is taking shape. A key element is the construction and deployment of WEAVE, a wide-field massive-multiplex spectrograph. With 1000 fibres and spectral resolutions of 5000 and 20000, the opportunities for discovery are tremendous. Three key fields will be: Milky-Way and Local Group archaeology linked to the Gaia mission; cosmology redshift surveys; and galaxy evolution studies linked to photometric surveys such as VISTA, UKIDSS, LOFAR, EUCLID, and others. IAC has the opportunity to get involved in this important instrument for ORM from the beginning.

Abstract
The 2nd generation VLT instrument Multi Unit Spectroscopic Explorer(MUSE) is going to be an integral field spectrograph with wide field of view and high spatial sampling. It is currently being built by a European consortium to see first light end of 2012. I will describe instrumental properties, show some details of the optomechanical design, present the data processing, and give some examples for possible scientific use.

Abstract
At the end of 2008, on ideas of teams from the Observatoire de la Côte d’Azur (OCA) and IAC, the CoRoT satellite observed the star HD 46375, known to host a non-transiting Saturn-mass exoplanet with a 3.023 day period. HD 46375 is the brightest star with a known close-in planet in the CoRoT accessible field of view. As such, it was targeted by the CoRoT additional program and observed in a CCD normally dedicated to the asteroseismology program, to obtain an ultra-precise photometric lightcurve and detect or place upper limits on the brightness of the planet. In addition, a ground-based support was simultaneously performed with the high-resolution NARVAL spectro-polarimeter to constrain the stellar atmospheric and magnetic properties. In this seminar, I will present the main results, in particular the stellar constrain we obtained thanks to the detection of the oscillation mode signature and the plausible detection of the planetary signal, which, if confirmed with future observations, would be the first detection of phase changes in the visible for a non-transiting planet.

Abstract
ExPo is an imaging polarimeter that has been built in Utrecht University. ExPo works in the visible, and it combines the dual-beam technique, together with very short exposure times and a high polarization sensitivity. After four successful campaigns at the William Herschel Telescope, we have obtained polarization images of circumstellar environments around T Tau's and Herbig Ae's stars, evolved (post-AGB) stars and planets like Venus and Saturn. Our results prove the utility of imaging polarimetry to characterize faint structures around very different objects. In this talk I will go through the instrument details, and I will show some of our science results.

Abstract
VIMOS is visible multi-object spectrometer operating on the VLT. The high multiplex of the VLT visible imager and multi object/integral-field spectrometer, VIMOS, makes it a powerful instrument for large-scale spectroscopic surveys of faint sources. Following community input and recommendations by ESO's Science and Technology Committee, it was decided to upgrade the instrument in phases. The first phase of the upgrade is described and included changing the shutters, installing an active flexure compensation system, replacing the detectors with CCDs with a far better red sensitivity and less fringing, and improving the data reduction pipeline.
Upcoming talks
- The effect of magnetic fields on galaxy evolution Dr. Enrique López-RodríguezThursday April 18, 2024 - 10:30 GMT+1 (Aula)
- EMO-1: Construyendo un observatorio caseroEnol Matilla BlancoFriday April 19, 2024 - 10:30 GMT+1 (Aula)








