Found 12 talks width keyword quasars
Abstract
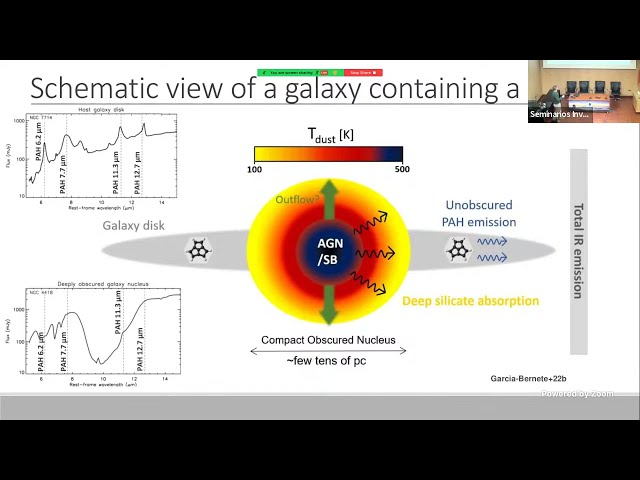
Finally, I will summarise our ongoing JWST work within the GATOS (Galactic Activity, Torus and Outflow Survey) collaboration. In particular, I will focus on our recent study about the survival of PAH molecules in AGN-driven outflows.
Abstract
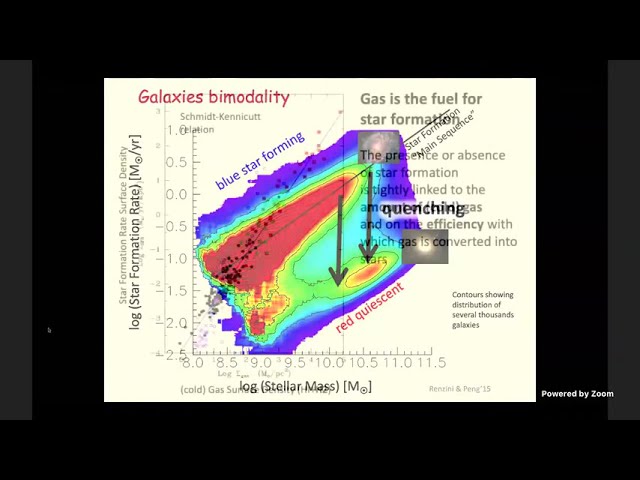
In the local universe most of the stellar mass is in passive galaxies, where star formation is
absent or at very low levels. Understanding what are the mechanisms that have been
responsible for quenching star formation in galaxies, and transforming them into passive,
quiescent systems, is one of the main observational and theoretical challenges of extragalactic
astrophysics. I will give a brief overview of the several possible quenching causes and physical
processes that have been proposed so far, ranging from feedback from black hole accretion and
starburst activity, to effects associated with the large scale environment in which galaxies live.
Although most of these mechanisms and causes play a role in different classes of galaxies and
at different epochs, multi-band observations are providing growing evidences that just a few of
them play the key, dominant role.
I will conclude by providing prospects for further investigating these aspects and tackling open
questions with the next generation of observing facilities.
Abstract
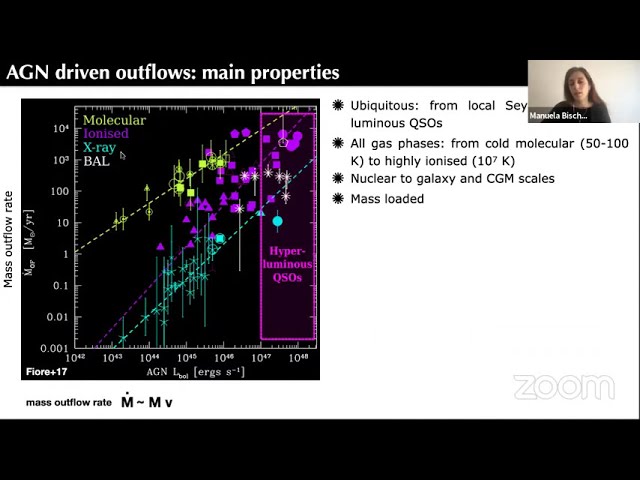
This talk will be dedicated to luminous (LBol~1E47 erg/s),
high-redshift quasars, which are ideal targets to investigate (i) feedback
from SMBHs, and (ii) the early growth phases of giant galaxies. I will
present evidence of SMBH-driven outflows at all Cosmic epochs, back to
the early Universe. These outflows involve all gas phases (molecular,
neutral, ionised) and extend on nuclear to galactic and circum-galactic
scales. I will report on the first systematic study of the molecular gas
properties in the host-galaxies of the most luminous quasars, fundamental
to probe the impact of SMBH feedback on the host-galaxy evolution. I will
show that luminous quasars pinpoint high-density sites where giant galaxies
assemble, and I will discuss the major contribution of mergers to the final
galaxy mass. To this aim, I will present a wealth of multi-wavelength (UV
to sub-millimeter) observations from the WISE/SDSS hyper-luminous quasars
survey at z~2-5 (WISSH), and recent results from the ESO large program
XQR-30, the Ultimate X-SHOOTER Legacy Survey of Quasars at the Reionization
epoch.

Abstract
Our Universe is filled with a mind-blowing diversity and different types and appearances of galaxies. Finding out about how they formed and evolved is one of the most challenging tasks in astronomy. When looking about 10 billion years back, to an epoch about 3 billion years after the big bang, we can see galaxies at earlier stages of their lives. In this talk, studies of different kinds of galaxies in the early universe will be presented. Two examples of the very intriguing population of massive quiescent z~2 galaxies were analyzed in terms of their stellar populations and morphologies. As the spectroscopic sample is still small, especially for galaxies at the faint end of the luminosity function, we make use of the biggest available "telescopes" in the universe: We search for red z~2 galaxies whose apparent brightnesses have been boosted by the Gravitational Lensing effect of intermediate redshift galaxy clusters with available mass models. Our findings indicate older ages for these galaxies than expected. Also, their remarkable compactness was corroborated. Furthermore, I'm going to present a study of a special case of so-called Damped Lyman-alpha Absorbers (DLAs), with two intervening galaxies in the line of sight of a higher-redshift QSO, which is also one example of only about a dozen known galaxy counterparts of a DLA. It fits into the emerging paradigm that galaxies which are responsible for higher metallicity DLAs are more massive and luminous than typical DLA galaxies. Motivated by that particular discovery, during the past few years we have undertaken a survey targeting candidate dust-reddened quasars missing in the sample from Sloan Digital Sky Survey. Spectroscopic follow-up with the NOT and the NTT has demonstrated a very high success rate of our selection (>90%). The main motivation is to search for quasars reddened by foreground dusty galaxies and we have found several such examples. We have also serendipitously found quasars with abnormal, very UV-steep extinction curves as well as a large number of broad absorption line quasars (BALs). The latter allow us to study the dependence of the BAL QSO population on redshift, reddening and luminosity. The results show a strong evolution of the BAL QSO fraction with cosmic time, with a peak at z~2.5 where several quantities in the Universe are also found to peak or vary. In addition,the dependence of this fraction with reddening and luminosity provides new constraints on the models for broad absorption origin in quasars. We are currently carrying out a pilot study of a search for even redder quasars selected from a combination of SDSS, UKIDSS and WISE photometry with the aim of selecting very dust-obscurred quasars or high-redshift BALs at z>2. Preliminary results from the first run et the NOT in March 2015 of the brightest candidates show very promising results which will also be briefly shown in the talk.

Abstract
Microvariations probe the physics and internal structure of quasars. Unpredictability and small flux variations make this phenomenon elusive and difficult to detect. Variance based probes such as the C and F tests, or a combination of both, are popular methods to compare the light-curves of the quasar and a comparison star. Recently, detection claims in some studies depend on the agreement of the results of the C and F tests, or of two instances of the F-test, in rejecting the non-variation null hypothesis. However, the C-test is a non-reliable statistical procedure, the F-test is not robust, and the combination of tests with concurrent results is anything but a straightforward methodology. A priori Power Analysis calculations and post hoc analysis of Monte-Carlo simulations show excellent agreement for the Analysis of Variance test to detect microvariations, as well as the limitations of the F-test. Additionally, combined tests yield correlated probabilities that make the assessment of statistical significance unworkable. However, it is possible to include data from several field stars to enhance the power in a single F - test or ANOVA nested designs, increasing the reliability of the statistical analysis. These would be the preferred methodology when several comparison stars are available. These results show the importance of using adequate methodologies, and avoid inappropriate procedures that can jeopardize microvariability detections. Power analysis and Monte-Carlo simulations are useful tools for research planning, as they can reveal the robustness and reliability of different research approaches.

Abstract
There is increasing speculation that quasars are intimately linked to the evolution of their host galaxies. Not only are they triggered as galaxies build up mass through gas accretion, but they also have the potential to drive massive outflows that can directly affect galaxy evolution by heating the gas and expelling it from galaxy bulges. However, there remain considerable uncertainties about how, when and where quasars are triggered as galaxies evolve, and the true energetic significance for the quasar-induced outflows and their acceleration mechanism have yet to be established. In this talk I will present new Gemini, VLT, Spitzer and Herschel results on samples of luminous AGN in the local Universe which provide key information on the triggering mechanisms for quasars and physics of their outflows.
Abstract
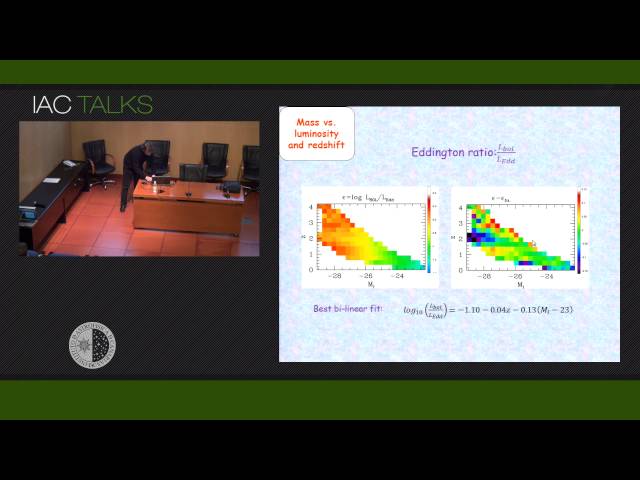
1) López-Corredoira & Gutiérrez (2012, RAA, 12, 249): Extremely luminous QSOs exist at high redshift but they are absent at low redshift. Our analyses show that it is not due to any significant evolution of black hole masses or Eddington ratios for equal luminosity QSOs, so the problem can be translated into a "Why are not there QSOs with very high black hole masses at low redshift?". 2) López-Corredoira & Perucho (2012, A&A, 544, 56): The MOJAVE survey contains 101 quasars with a total of 354 observed radio components that are different from the radio cores, among which 95% move with apparent projected superluminal velocities with respect to the core, and 45% have projected velocities larger than 10c (with a maximum velocity 60c). Relativistic Doppler boosting explains these apparent anomalies, but it requires a huge average kinetic power to produce such powerful ejections: ~7×10^{47} erg/s, a significant portion of the Eddington luminosity and on the order of the bolometric luminosity. This amount is much higher than previous estimates of kinetic power on kpc-scales. 3) There are many other pending problems in QSOs in the literature (review at López-Corredoira 2011, IJAA, 1, 73): the different structure of the clouds along the QSO's line of sight and their tangential directions; the spatial correlation between QSOs and galaxies; inconsistencies in the AGN unification model; etc.

Abstract
In the 50 years since their discovery, it has become increasingly recognised that quasars are not merely signposts to the distant Universe, but also play a key role in the overall galaxy evolution process. However, if we are to incorporate quasars into models of galaxy evolution, it's important to understand how, when and where they are triggered. In this talk I will review the latest observational results on the triggering of quasars, based on the morphologies of their host galaxies and star formation properties; I will also discuss the future prospects for understanding quasar triggering using Herschel and ALMA data.

Abstract
The massive black holes found at the centers of most nearby galaxies including our own, are believed to be the ashes of the fuel that powered quasars early in the history of the universe. I will briefly review the astronomical evidence for these objects and then describe some of the exotic dynamical phenomena that originate in their vicinity, including hypervelocity stars, resonant relaxation, and warped and lopsided stellar disks.
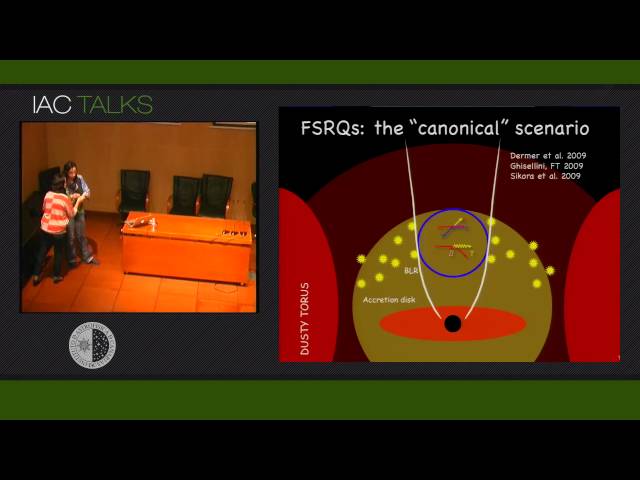
Abstract
The MAGIC telescopes discovered very high energy (VHE, E>100 GeV) gamma-ray emission coming from the distant Flat Spectrum Radio Quasar (FSRQ) PKS 1222+21 (4C +21.35, z=0.432). It is the second most distant VHE gamma-ray source, with well measured redshift, detected until now. The detection coincides with high energy MeV/GeV gamma-ray activity measured by the Large Area Telescope (LAT) on board the Fermi satellite. The VHE and MeV/GeV spectra, corrected for the absorption by the extragalactic background light, can be described by a single power law with photon index 2.72 ± 0.34 between 3 GeV and 400 GeV, consistent with gamma-ray emission belonging to a single component in the jet. The absence of a spectral cutoff constrains the gamma-ray emission region to lie outside the Broad Line Region, which would otherwise absorb the VHE gamma-rays. On the other hand, the MAGIC measurement of a doubling time of about 9 minutes indicates an extremely compact emission region, in conflict with the "far dissipation" scenario. This result challenges jet emission models in FSRQs and indicates the importance of jet sub-structures.
« Newer 1 | 2 Older » Last >>
Upcoming talks
- Classical Be stars - Constraining binary interaction physics in massive starsDr. Julia BodensteinerThursday April 25, 2024 - 10:30 GMT+1 (Aula)
- Runaway O and Be stars found using Gaia DR3, new stellar bow shocks and search for binariesMar Carretero CastrilloTuesday April 30, 2024 - 12:30 GMT+1 (Aula)









