Found 5 talks width keyword late-type galaxies
Abstract
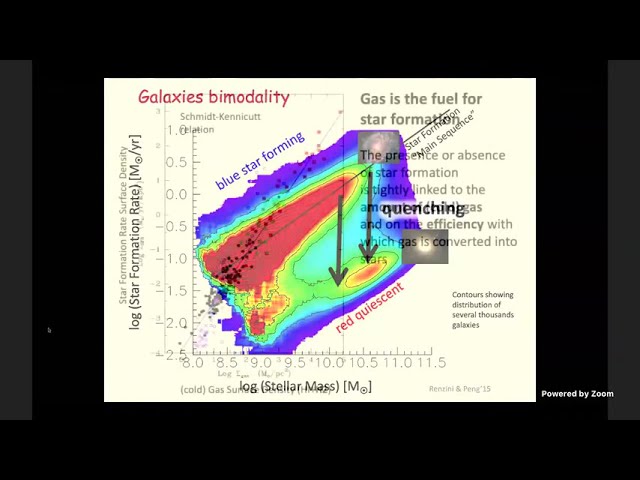
In the local universe most of the stellar mass is in passive galaxies, where star formation is
absent or at very low levels. Understanding what are the mechanisms that have been
responsible for quenching star formation in galaxies, and transforming them into passive,
quiescent systems, is one of the main observational and theoretical challenges of extragalactic
astrophysics. I will give a brief overview of the several possible quenching causes and physical
processes that have been proposed so far, ranging from feedback from black hole accretion and
starburst activity, to effects associated with the large scale environment in which galaxies live.
Although most of these mechanisms and causes play a role in different classes of galaxies and
at different epochs, multi-band observations are providing growing evidences that just a few of
them play the key, dominant role.
I will conclude by providing prospects for further investigating these aspects and tackling open
questions with the next generation of observing facilities.

Abstract
The ΛCDM model predicts that galaxies originate in dark matter haloes, undergoing in their early age a process of continuous merges with other galaxies that determines the first part of their evolution. The frequency of these events decreases with time and their gradual change turns to be internally driven, becoming much slower. Bars, elongated stellar structures in the central regions of galaxies, are known to play an active role in this phase of their evolution, so-called secular.
Bars are fundamentally responsible for the redistribution of matter and the angular momentum of the baryonic and dark matter components of disc galaxies. Different simulations predict that bars get stronger and longer in time, slowing down their rotation speed.
Based on the Spitzer Survey of Stellar Structure in Galaxies (S4G) 3.6 μm imaging, we aim to study the secular evolution of disc galaxies by focusing on their stellar bar parameters. We take a large well-defined sample of about 650 nearby barred galaxies and we infer the gravitational potential from 3.6 μm images. We calculate gravitational torques, the ratio of the maximal tangential force to the mean axisymmetric radial force, in order to obtain a quantitative measure of the bar-induced perturbation strengths. In addition, we estimate the bar strength from the m=2 normalized Fourier density amplitudes and determine bar lengths both visually and by using an ellipse fitting method. Bar morphology and the interplay with spiral arms are studied via image-stacking methods as well.
In this talk I will present the statistical results derived from our measurements, providing observational evidence for the evolution of bars in accordance with the current theoretical predictions. We study bar parameters as a function of the Hubble type, addressing how the different measurements of the bar strength correlate with each other and with the galactic mass. The quality of our data allows us to probe the properties of bars in the Local Universe and connect them to the evolution of other galactic structures.

Abstract
We revisit the question of the ionization of the diffuse medium in late type galaxies, by studying NGC 891, the prototype of edge-on spiral galaxies. The most important challenge for the models considered so far was the observed increase of [O III]/Hβ, [O II]/Hβ and [N II]/Hα with increasing distance to the galactic plane. We propose a scenario based on the expected population of massive OB stars and hot low-mass evolved stars (HOLMES) in this galaxy to explain this observational fact. In the framework of this scenario we construct a finely meshed grid of photoionization models. For each value of the galactic latitude z we look for the models which simultaneously fit the observed values of the [O III]/Hβ, [O II]/Hβ and [N II]/Hα ratios. For each value of z we find a range of solutions which depends on the value of the oxygen abundance. The models which fit the observations indicate a systematic decrease of the electron density with increasing z. They become dominated by the HOLMES with increasing z only when restricting to solar oxygen abundance models, which argues that the metallicity above the galactic plane should be close to solar. They also indicate that N/O increases with increasing z.
Abstract
CALIFA is the largest IFS survey ever performed up to date. Recently started, it will observe ~600 galaxies in the Local Universe with PPAK at the 3.5m of the Calar Alto Observatory, sampling most of the size of these galaxies and covering the optical wavelength range between 3700-7100 Å, using to spectroscopic setups. The main goal of this survey is to characterize the spatially resolved spectroscopic properties (both the stellar and ionized gas components) of all the population of galaxies at the current cosmological time, in order to understand in detail the how is the final product of the evolution of galaxies. To do so, the sample will cover all the possible galaxies within the color-magnitude diagram, down to MB ~ -18 mag, from big dry early-types to active fainter late-type galaxies. The main science drivers of the survey is to understand how galaxies evolve within the CM-diagram, understanding the details the process of star formation, metal enrichment, migrations and morphological evolution of galaxies.

Abstract
(1) We present SAURON integral-field stellar velocity and velocity dispersion maps for four double-barred early-type galaxies: NGC2859, NGC3941,NGC4725 and NGC5850. The presence of the nuclear bar is not evident from the radial velocity, but it appears to have an important effect in the stellar velocity dispersion maps: we find two sigma-hollows of amplitudes between 10 and 40 km/s at either sides of the center, at the ends of the nuclear bars. We have performed numerical simulations to explain these features. Ruling out other possibilities, we finally conclude that, although the sigma-hollows may be originated by a younger stellar population component with low velocity dispersion, more likely they are an effect of the contrast between two kinematically different components: the high velocity dispersion of the bulge and the ordered motion (low velocity dispersion) of the nuclear bar.(2) We have explored radial color and stellar surface mass density profiles for a sample of 85 late-type galaxies with available deep (down to ~27.0 mag/arcsec2 SDSS g'- and r'-band surface brightness profiles. About 90% of the light profiles have been classified as broken exponentials, exhibiting either truncations (Type II galaxies) or antitruncations (Type III galaxies). Their associated color profiles show significantly different behavior. For the truncated galaxies a radial inside-out bluing reaches a minimum of (g' - r') = 0.47 +/- 0.02 mag at the position of the break radius, this is followed by a reddening outwards. The anti-truncated galaxies reveal a more complex behavior: at the break position (calculated from the light profiles) the color profile reaches a plateau region - preceded with a reddening - with a mean color of about (g' - r') = 0.57 +/- 0.02 mag. Using the color to calculate the stellar surface mass density profiles reveals a surprising result. The breaks, well established in the light profiles of the Type II galaxies, are almost gone, and the mass profiles resemble now those of the pure exponential Type I galaxies. This result suggests that the origin of the break in Type II galaxies are most likely to be a radial change in stellar population, rather than being caused by an actual drop in the distribution of mass. The anti-truncated galaxies on the other hand preserve their shape to some extent in the stellar surface mass density profiles. We find that the stellar surface mass density at the break for truncated (Type II) galaxies is 13.6 +/- 1.6 Msun/pc2 and 9.9 +/- 1.3 Msun/pc2 for the anti-truncated (Type III) ones. We estimate that ~15% of the total stellar mass in case of Type II galaxies and ~9% in case of Type III galaxies are to be found beyond the measured break radii.
« Newer Older »
Upcoming talks
- Classical Be stars - Constraining binary interaction physics in massive starsDr. Julia BodensteinerThursday April 25, 2024 - 10:30 GMT+1 (Aula)
- Runaway O and Be stars found using Gaia DR3, new stellar bow shocks and search for binariesMar Carretero CastrilloTuesday April 30, 2024 - 12:30 GMT+1 (Aula)








